Water supply tariffs in Russia
In the Russian Federation, the cost of cold water and a separate tariff for hot water supply have been established. Its size is regulated by the authorities of the subject of the federation and local self-government, so prices for utility services are not the same in the regions.
The tariff is set taking into account the costs that local water utilities and heating networks incur in connection with the supply of the resource, as well as the surcharges added to them within the limits of the indices established for the region.
Typically, the water tariff is calculated based on the costs of:
- electricity and reagents for water purification;
- employee salaries;
- transportation of the resource to the final consumer;
- maintenance of water utility property, utility networks, and so on.
As for hot water supply (DHW), its tariff consists of the price for the supply of cold water, the cost of heating it to the required temperature and the tariff growth index.
In 2021, as in previous years, tariff increases are planned for the second half of the year, in accordance with the order of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 30, 2020 No. 2827-r.
Features of water supply rationing in rural areas
The supply of water to private houses in rural areas is subject to rationing in the case of centralized water supply to consumers by utility companies. It is possible to assign a separate payment if there is a water stand on a public street.
We recommend: Box for gas meter
It must be taken into account that water is additionally consumed for watering the garden, therefore, in the appropriate season, if there is no water meter in a private house, a separate fixed amount is assigned for these needs.
If residents of the private sector do not provide water supply centrally, including installation and maintenance of systems, utility standards are not applicable in this situation.
DHW temperature standards
As mentioned above, the amount of payment for a hot water supply utility service is determined, among other things, based on the cost of heating it - this is the largest expense item.
Most consumers would like to understand what they are paying for. One of the main criteria for the quality of the service provided is the temperature of the supplied hot water. According to SanPiN 2.1.4.2496-09, approved. , the temperature of hot water in the tap should not be lower than 60 and not higher than 75˚C.
Sanitary standards mention the permissible limit of deviations from the norm. So, from 12 at night to 5 in the morning, fluctuations can be ± 5˚С, at any other time – ± 3˚С.
Consequently, the temperature of the water in the hot tap cannot fall below 55–57˚C. Violation of this norm gives residents the right to seek a tariff reduction of 0.1% for each hour during the entire period of deviation.
What is cold water supply for hot water supply and how is it calculated
They indicate the volume of water consumption in cubic meters. The red numbers are the amount of liquid in liters up to 1 m3. They are used to monitor the consumption of domestic hot water by persons living in the premises and are not reporting data. The period of time during which hot water supply consumption is measured is determined by regulatory documents.
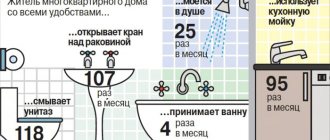
- Residential premises with existing water supply and sewerage - 120 liters per day per person.
- Similar residential premises with gas supply - 150 liters per day.
- Premises with existing water supply, sewerage, bathroom and solid fuel water heater - 180 liters per day.
- Similar houses or apartments with water heaters, the energy carrier of which is gas - 225 l.
- The same rooms with high-speed gas boilers - 250 l.
- Apartments with centralized hot water supply - 230 liters per person.
Using this formula, DHW is calculated for those apartments where individual flow meters are installed. If the housing does not have these, then the calculation is made on the basis of the standard established in the region. Its value must be divided by the number of registered occupants of the apartment. However, the final result is inaccurate. Housing organizations involved in settlements additionally include in receipts expenses for repairs and maintenance of metering devices in houses.
If an apartment dweller’s hot water meter shows 2 m3, the tariff for cold water is 14 rubles, and the cost of heat energy is 2000 rubles, then the calculation will be as follows: 0.06 gigacalories * 2000 = 240 rubles. + (14 * 3) = 282 rub. This is the price of 2 m3 of hot water. The number 0.06 indicates the approximate amount of energy used to heat 1 m3 of water. If your home does not have water meters, then you must first multiply the standard by 0.06, and then multiply the resulting product again by the heat tariff.
You may like => Gift Over 4000 Taxation 2021
Q one i - the volume (quantity) of thermal energy used to heat water in order to provide public services for hot water supply for the billing period for general house needs, is calculated as the product of Vi one and the approved standard for the consumption of thermal energy used to heat water for the purpose of providing public services for hot water supply provided for general house needs;
N one - consumption standard for hot water supply, provided for the billing period for general house needs in an apartment building, established in accordance with the Rules for establishing and determining standards for consumption of utility services, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of May 23, 2006 No. 306
Two-component tariff for hot water supply: what is it?
In 2021, payments for hot water consumed by the population must be made according to a two-component tariff. Previously it was assumed that this would happen before 2018. Let's figure out what it is.
The concept of “tariff for hot water” as a single product is not used anywhere in the world - most often it is heated directly at the heating supply facility. But even where the practice of centralized supply of hot water still exists, the product is primarily the coolant that heats this water.
Following international experience, the Russian authorities introduced the so-called two-component tariff for hot water supply in 2013. The calculation of the payment for hot water according to the two-component tariff in the housing and communal services receipt in closed water supply systems is carried out based on the following components:
- the actual volume of cold water used, paid at the standard tariff for cold water;
- the actual amount of heat used to heat cold water. It is paid at a separate rate.
Simply put, the cost of hot water at the tap is determined by the prices of cold water and thermal energy to heat it.
The volume of resource consumed is determined by the hot water meter, and if it is missing, by the generally accepted consumption standard. Payment for water heating in utility bills is calculated according to the standard heat consumption used for heating.
In open water supply systems the following components are used:
- coolant;
- thermal energy for water supply purposes.
Currently, regional executive authorities are authorized to independently decide which principle for calculating the cost of hot water supply to use to determine the tariff in a closed system: one-component or two-component. By 2021 they must finally switch to a two-part tariff, and until then a special regulatory framework needs to be developed.
Myths of housing and communal services: What is “DHW heating”
Additionally, it is worth noting that if DHW is produced inside the house using a heat exchanger (or boiler), then the amount of heat energy spent on “heating up DHW” is calculated based not on the standard heat energy consumption, but on the actual heat consumed (or other utility resource spent on heating ).
If there is a significant difference in the elevations of the territory, cold water supply systems are divided into zones, the design of which makes it possible to reduce excessively high water pressures for consumers located in low areas of the territory and reduce the energy consumption spent on raising water. Zoning can be carried out using parallel or sequential schemes. In the first case, a single pumping station is provided with pumps providing different pressures to service the department. zones in the second - pumping stations for each zone. With parallel zoning, the length of water pipelines and the weight of pipes is greater than with sequential zoning.
May 05, 2021 polrostov 106
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Cost of Legalization of Redevelopment
- Advocacy Functions Briefly
- Article Invasion of Privacy in the Republic of Belarus
- Entrepreneurial Activities of a Lawyer
Normative base
The possibility of applying a two-component tariff for hot water supply is established by the following laws:
- clause 9 art. 32 – in closed systems;
- clause 5 art. 9 – in open water supply systems.
But these laws only determine the possibility and components of such a tariff, and specific provisions are contained in the by-laws.
In particular, the obligation to establish water and heat consumption standards, as well as switch to a two-component tariff from 2021, rests with the regional authorities in clause 2. He also makes changes to the Rules for determining standards for the consumption of utility services, approved. , and Rules for the provision of public services, approved. .
According to the listed documents, the authorized body is obliged to establish a heat standard for heating water, taking into account:
- water supply systems;
- design features of apartment buildings;
- availability of water folding devices;
- sanitary equipment and so on.
What is “thermal energy”
For DHW purposes, it is necessary to simultaneously take into account two components for which the subscriber pays: cold water (or coolant, if we are talking about open systems) and thermal energy.
With water, everything is clear - it is calculated in m3 depending on the meter readings or consumption standards. But not everyone is familiar with the concept of “thermal energy” and what function it performs.
This component is the main component of heating cold water to established standards. To determine the amount of thermal energy expended, you need to multiply the amount of water used by the heat standard required to heat 1 m3. This standard is adopted by local authorities.
If the standard is not established, housing offices and other management organizations calculate it independently using the formula approved. Government Decree No. 306.
Consequently, a one-component tariff for hot water is when the subscriber pays only for the cubic meters of water used, a two-component tariff is when the cost of heating it is also included in the tariff.
New line in receipts: cold water heating for domestic hot water
Direct-flow water supply is a system consisting of a pumping station and pipe outlets. Recycling water supply is a more economical option because it uses fewer resources. The concept of heating cold water for domestic hot water means heating cold water to obtain hot water supply. An additional line has appeared in receipts for payment for this service. It is necessary to understand in detail how legal the charges are.
The management company should not ignore the request, but there are cases when a response is not received within the established time frame. Also, in case of refusal, they file an appeal to the court or prosecutor's office. The basis will be Article 395 of the Civil Code. An application to the administration is also an effective way to solve the problem. The supplier must fully reimburse the costs caused by the calculation error.
Will there be an increase in the cost of hot water in 2021?
The issue of tariff growth is perhaps the most socially significant for the country's population. Therefore, it is worth immediately reassuring readers: a significant increase in utility tariffs is not expected in 2021. However, the cost of hot water supply services will still increase.
Both the hot water tariff per cubic meter and the two-part tariff, if adopted in the region, according to the order in accordance with the order of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 30, 2020 No. 2827-r, will be increased from July 1, 2021.
Different increases are allowed for each region. The average indices are determined by the specified order. The cost of utilities cannot rise above the established limits.
But the index specified in the order is a maximum, and not a mandatory, percentage increase. Thus, regional authorities decide what the tariff for heating hot water is from July 1, 2021.
More information in the material “Increase in housing and communal services tariffs in 2021.”
The procedure for calculating the cost of hot water supply according to a two-component tariff
The legislative framework regarding accounting and payment for domestic hot water services at a two-rate tariff is quite complex. To understand how to calculate a hot water tariff from two components, you need to be a professional. Taking this into account, many regions of the Russian Federation have published special practical explanations and instructions designed to convey to citizens the procedure for applying tariffs for hot water. Having studied the published methodological recommendations, we tried to generalize regional practice.
How the cost of hot water is calculated according to a two-component tariff in apartments depends on the presence or absence of an individual water meter in the residential premises. For calculations, formula No. 23 is used, approved. Appendix 2 to the Rules, approved. Government Decree No. 354.
This formula assumes taking into account the readings of water meters and standards for heat consumption required for heating. So, if there is a hot water meter in the apartment, the calculation of hot water supply in an apartment building in 2021 is carried out as follows:
Cost of 1 m3 cold. water x consumption volume + (consumption volume x heat consumption standard) x cost of 1 Gcal of heat = cost of DHW services
For example: the cost of 1 m3 of cold. water is 30.09 rubles, consumption volume is 5 m3, heat consumption standard is 0.06, and the cost of 1 Gcal of heat is 1775.45 rubles. Then the calculation looks like this:
30.09*5+(5*0.06)*1775.45 = 683.08 rub.
If there is no individual meter, instead of the actually consumed resource, the local standard is taken into account in the formula. Let it be 3.89 m3/person. Therefore, if 3 people live in an apartment, the calculation procedure is as follows:
(30.09 x 3.89+(3.89 x 0.06) x 1775.45) x 3 = 1360.22 rubles
We will also consider a simple calculation option for those who are interested in how to calculate the hot water tariff per 1 m3, converting it into a single-component one. So, the actual cost of 1 m3 of hot water in our case is calculated as follows:
30.09+1775.45 x 0.06=136.17 rubles/m3
Are there any differences in tariffs with and without a meter?
As can be seen from the above, the cost of hot water supply does not depend on whether the subscriber has an individual metering device: the tariff for hot water according to the meter is always the same. In the calculations, only consumption volumes change:
- if there is a counter, the actual volume is used;
- without a metering device - standard.
This is also reflected in the final cost of consumed resources. The more residents there are registered in the apartment, the higher the utility costs will be.
In addition, the state is trying in every possible way to encourage the population to install metering devices. One of the incentives is the introduction in 2017 of an increasing coefficient for subscribers who have the technical ability to install meters, but do not do so.
For apartments without metering devices, an increasing factor of x = 1.5 is applied (increase by 50%).
So, using the data from the above calculation, you can see that for residents who have not installed metering devices, 1 m3 of hot water will cost not 136.17 rubles, but already 151.662 rubles. (30.09 x 1.5 + 1775.45 x 0.06).
To learn how to avoid an increase, read the article “How to install a water meter in an apartment.”
What is ODN or general house needs?
According to the rules for the provision of communal services No. 354 “On the procedure for the provision of communal services to owners and users of premises of multi-apartment buildings and residential buildings houses" the general needs of the house must be paid for by the owners of the apartments located in it. The operation of this rule is not affected by the particulars of the building, residential and non-residential premises, the type of accounting equipment, or the form of management of a multi-apartment building.
Some management organizations solve their financial problems by unreasonably inflating certain items in receipts, including ODN. Such cases appear in the absence of proper control on the part of regional authorities and the residents of apartment buildings themselves. To combat such violations, the government is introducing an information system in which the readings of metering devices and bills for housing and communal services made on the system should be displayed ove these indications.
You might like => What's Included in the Kindergarten Fee
Controversial aspects of the application of a two-component tariff
Despite a fairly transparent calculation scheme, the use of a two-component tariff seems quite controversial, as evidenced by contradictory judicial practice. Below we look at some of the most high-profile cases.
Public meter readings
One of the most controversial issues is the use of a common house heat meter when calculating for domestic hot water. It would seem that its presence makes it possible to objectively measure the amount of heat expended by the resource supplier to heat water, and this practice is the only correct one. In reality, not everything is so simple.
According to the Rules for the Provision of Utility Services, when calculating the cost of hot water supply, only the established standards for heat used to heat water should be used.
Even if the heat meter is used under a contract, its indicators still cannot be taken into account when making payments to consumers and domestic hot water suppliers.
This position was supported by the Ministry of Construction of the Russian Federation and the Supreme Court, although it potentially leads to an unreasonable increase in the cost of the resource.
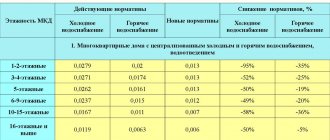
Imperfect calculations
As is known, in the regions, the receipt for heating and hot water may contain different standards for the heat spent on heating a cubic meter of water. The difference between some regions exceeds 15%. For example, in the Omsk region the standard is 0.0503 Gcal/1m3, in St. Petersburg - 0.06 Gcal/1m3, and in the Rostov region - from 0.054 to 0.066 Gcal/1m3, depending on the design features of the house.
Probably the reason for this difference is the uncertainty in the calculations regarding the temperature of the water that needs to be heated and the temperature of the already hot water. Temperature changes at different times of the year are not taken into account in the calculations, which leads to inflated tariffs for hot water supply.
Design features of houses
The use of a two-component tariff has created a problem for management organizations that service houses equipped with heated towel rails, heated floors, and so on.
The peculiarity of the hot water supply system of such houses is that the water circulating in the circuit should not cool down. This requires additional heat (about 30% of the total amount of heat used to heat the water).
Payments between management companies and residents are carried out based on apartment meters, which do not take into account these losses. As a result, the management company receives 25-35% less money from residents than it must pay to the hot water supply supplier.
Do they have the right to charge for water heating?
Note! Receipts also contain the column “DHW at one-way service station”. The last abbreviation means general house needs (pressure testing of pipes, preparation for seasonal heating, delivery of coolant to common areas). Domestic hot water supply on one heating system implies the consumption of energy to heat water, which will be used for the needs of all inhabitants of the house, and not just individual apartments in it.
The line “DHW” implies an accrual for the volume of water consumed during the month that passed through the hot water supply flow meter. If the water meter does not work or is not present in the home, then the volume of water calculated according to the average indicator or a unified standard taking into account the number of officially registered persons is taken as a basis. The volume of DHW supply is calculated according to the same scheme as the tariff for cold water supply.
According to current legislation, cold water, or more precisely, the volume of its consumption in a residential building, must be recorded using individual metering devices (cold water meters), if all the technical capabilities are available for their installation in the premises.
- readings from a common building meter are taken and compared with data from individual meters in apartments;
- if the difference is below the norm, then residents pay the costs of one-way heating for hot and cold water according to the actual volume of total consumption by all residents of the house;
- if the readings are higher than the established standards, residents also make payments according to the actual volume of consumption, and the difference is paid by the housing organization from its own funds.
You may like => The right to carry out legal activities is received by a lawyer from the moment
To calculate the amount of payment for heating up hot water, it is necessary to determine how much resource was spent; to do this, you need to take readings from the meter or make a calculation for hot moisture, if there is none. The amount of remuneration for heating hot water is calculated using the following formula:
Hot water supply to houses, heating in winter with hot water is one of the most expensive services among utility bills. Therefore, today experts have divided it into two parts in order to take into account all components of the process. Now tariffs for water heating are called two-component. One part is the supply of cold water to users. The second part is heating the water.