Real estate objects
Real estate includes objects that are characterized by such characteristics as durability, material value and stationarity. This means that such a structure cannot be moved to another location without destruction, the building provides benefit to the owner and has physical characteristics whose value can be determined in monetary terms, and also has a service life of at least 15 years.
Concept and classification of structures
First of all, real estate objects can be divided into man-made and non-man-made . The second type includes land plots, and the first type includes all kinds of buildings.
Structures, in turn, are divided into buildings and structures:
- According to the All-Russian Classification of Fixed Assets (OK 013–94), a building is an object built according to an architectural design that people use for living, working, relaxing, producing wealth, storing things and providing various services to the population. Buildings of this type have walls, a roof and all the necessary communications.
- Structures are real estate objects designed for technical purposes. These include bridges, overpasses, and oil wells.
Another classification divides real estate into commercial and residential. Within each of these types, there are divisions of objects according to different criteria. For example, among residential real estate there are city and country houses.
It is more appropriate to consider the classification of commercial and residential real estate in relation not to entire buildings, but to premises, which, being separate parts of buildings, can be used for various purposes.
Buildings intended for living
The definition of this property is given in Part 2 of Art. 15 Housing Code of the Russian Federation. According to the law, such premises must be isolated and suitable for long-term habitation . Russian law has a number of legislative acts that approve sanitary and technical standards that residential premises must comply with. These include:
- No. 184-FZ “On technical regulation” dated December 27, 2002.
- No. 52-FZ “On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population” dated March 30, 1999 (as amended on August 22, 2004).
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 24, 2000 No. 554 “Regulations on sanitary and epidemiological regulation” (as amended by resolutions dated February 6, 2004 No. 51, dated November 17, 2004 No. 648).
A room is considered residential if it has the following characteristics:
- suitable for long-term living;
- is isolated;
- in all respects it fits the definition of real estate;
- legally recognized as residential.
Classifications of residential premises:
- Based on the type of building in which they are located, residential premises are divided into dormitories, apartments and dachas, suitable for living throughout the year.
- According to the method of use, they are divided into permanent and intended for residence for a relatively short period, i.e. temporary.
- By type, residential premises can be either simple apartments, rooms, or separate houses, etc.
- Based on the grounds on which people use real estate, housing can be provided under a social tenancy agreement, under a commercial tenancy, in housing and housing-construction cooperatives, by right of ownership, as an official one, etc.
Non-residential objects
A premises that for some reason does not fit the definition of residential belongs to the category of non-residential premises. It is distinguished by the following features:
- isolated from other premises;
- registered as a real estate property in accordance with No. 122-FZ (as amended on 04/06/2015);
- is part of the building;
- has a specific address (read about how a non-residential premises number is assigned during cadastral registration, which determines the location of an object at a specific address);
- is part of a non-residential fund;
- has a purpose that excludes use as permanent housing.
Classifications of non-residential premises:
- Based on the nature of use, non-residential premises are divided into main and auxiliary. The latter serve to ensure the normal functioning of the main areas. In a business center building, the main premises include the offices themselves, and the auxiliary ones include the hall, corridors, toilets, etc.
- According to their purpose, non-residential premises are divided into industrial and non-industrial (schools, kindergartens, hospitals, shops, dry cleaners, cinemas, public utilities, etc.).
- By industry, non-residential premises are divided depending on their belonging to industrial facilities (metallurgical, fuel, chemical, engineering), electric power, etc. (about what industrial and production buildings are, what are the nuances of their operation, and how they differ from structures for other purposes, we discussed in this article).
Do you want to learn more about the rules for the use and ownership of non-residential real estate? Read our articles about how to do this in non-residential premises:
- settle and register;
- formalize the division procedure;
- carry out redevelopment, refurbishment and reconstruction.
How to change the status of an area
Transferring an apartment to another fund and vice versa simply won’t work.
The Housing Code specifies a number of requirements, compliance with which is mandatory . If the listed conditions are not met, you can not count on changes in status.
In order for an apartment to become non-residential, you need to consider:
- If the area is more than 100 sq. meters, provide a second exit to the street;
- If the premises in which you plan to carry out your activities are located on the second floor or even higher, prepare for the fact that you will have to change the status of all the apartments that are located below. According to the rules, these square meters must also become non-residential;
- Provide all engineering communications;
- Check out of your home before starting the transfer procedure, because... no person can be registered in non-residential premises either on permanent or temporary terms;
- Legalize all redevelopments.
Remember that premises located in a building classified as a cultural heritage site cannot become non-residential.
In addition, only the owner has the right to change the status.
You cannot make non-residential the area where you live under the terms of a social tenancy agreement.
Not everything is so simple with the transfer to housing stock. It must also meet certain requirements:
- The building in which non-residential premises are located must have durable structures. It also should not be classified as an emergency fund or subject to reconstruction or demolition;
- The premises must be absolutely safe and equipped in such a way that future residents cannot be injured or injured. The same requirement applies to the adjacent territory;
All utility networks must be in order and suitable for use.
We are talking about heating networks, sewerage, water supply and electricity. Utilities located in the house must also meet safety requirements.
When converting to a living space, the owner will have to think about the height of the ceilings, the concentration of harmful substances in the air, the number of floors of the building, and sound insulation. All this must also comply with the standards that were determined by the Housing Code.
In addition, during the transfer, no matter to which fund, the property should not be encumbered with anything : debts, loans, etc.
Non-residential premises in an apartment building - is this possible?
In addition to the definition of residential premises, Art. 17 of the RF Housing Code regulates the methods of its use. Such properties are intended for human habitation. They are not permitted to be converted for industrial production purposes.
Important. The laws of the Russian Federation contain a loophole that allows individual entrepreneurs to carry out professional activities in the premises of the housing stock that they own.
This becomes possible if a number of conditions can be met:
- the rights and interests of other people are fully respected;
- technical and sanitary requirements for residential premises are not violated.
Residential premises can be legally used as work offices, for example, by lawyers. This right is granted to them by Law No. 63-F3 “On advocacy and the legal profession in the Russian Federation” dated May 31, 2002.
If an entrepreneur rents housing in which he intends to conduct professional activities, he must obtain permission from the owner of the premises, as well as from all members of his family who have reached the age of 18. Theoretically, such a room could be a separate private house. Thus, the residential building will be used for purposes for which non-residential premises are usually used .
You can find out what non-residential premises in an apartment building are and how to purchase them here.
Non-residential premises (difference from residential)
All legal owners of non-residential premises have the right of shared ownership of property of this type by virtue of law. Disputes about the size of the share are resolved taking into account the area of the real estate of each interested party. Owners of premises in one building can transfer individual structural elements of the building for use, for example, for placing outdoor advertising.
- educational: areas of kindergartens, universities, schools;
- healthcare: isolated spaces of clinics, hospitals, ambulance stations, medical posts;
- trade, public catering: areas are part of shops, food and manufactured goods, property complexes that produce and sell food products, restaurants, canteens, cafes;
- administrative and managerial: offices; public utility services: studio space, repair shops, dry cleaners, control centers, funeral service enterprises;
- recreation and entertainment: cinema halls, night clubs; other real estate.
- Industrial non-residential premises are divided by industry into objects:
- industry (fuel, petrochemical, chemical);
- metallurgy, non-ferrous and ferrous;
- electric power industry, etc.
Can a non-residential building have residential premises?
Recently, the popularity of two-level studio apartments and spacious lofts has been growing. The layout of apartments in standard high-rise buildings, as a rule, is not suitable for arranging such interiors. Production areas of abandoned factories and factories are being bought up for fashionable lofts. Often, in one such building, both residential premises and offices, as well as infrastructure facilities, coexist.
Attention. Converting premises originally intended for industrial needs into housing is not an easy task. A major renovation will be required, including the necessary communications, to make it habitable.
For non-residential premises, the owners of which wish to transfer it to residential use, the legislation imposes the following requirements:
- is the property and is not subject to any rights of third parties (lease, collateral, etc.);
- meets all the conditions for recognizing the premises as residential in accordance with Part 4 of Art. 22 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation or can be arranged in accordance with these conditions.
A residential building is a residential building or non-residential building
As we can see, the formulation of lifting restrictions is accompanied by the court (stipulated) by certain conditions. Registration (registration) in a residential building is possible, provided: 1) if this building is “suitable for permanent residence” (read year-round), 2) if the garden plot of land is included within the boundaries of the populated area.
At the same time, the existing reality is such that, regardless of the legal regime of a garden plot of land, comfortable residential buildings are often erected on the lands of gardening partnerships, which can hardly be called “buildings”. According to technical standards and construction characteristics (in fact), these objects are residential buildings, according to the legal regime (virtually) - residential buildings. In this case, the purpose is fundamentally different from the actual use. Citizens concerned about the housing problem have long found a practical solution to it in the construction of dwellings on garden lands. The absence of the need to prepare and approve design documentation for the development of garden and dacha land plots allows their owners to create residential properties suitable for permanent residence. According to Article 1 of Law No. 66-FZ, residential buildings can be located on both garden and dacha land plots. At the same time, as noted in Resolution No. 7-P, the Housing Code of the Russian Federation does not directly provide for the possibility of converting residential buildings into residential buildings. Based on the fact that housing legislation and legislation on urban planning activities are the sphere of joint jurisdiction of the Russian Federation and the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, the constituent entities of the Russian Federation have the right to implement appropriate legal regulation by determining the procedure for recognizing residential buildings on garden and dacha land plots as suitable for permanent residence, and the authorities local government - to approve, as provided for in Article 32 of the Urban Planning Code of the Russian Federation, the rules of land use and development.
We recommend reading: Mortgage to buy out a share in a bank apartment
Purpose of objects
The intended purpose of residential real estate is for citizens to live in them (Part 1, Article 17 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation). The use of such buildings for other purposes entails administrative liability. Private individuals can register an individual entrepreneur in their home and carry out certain types of professional activities that will not violate the interests of other citizens.
The concept of housing stock is introduced in Art. 19 Housing Code of the Russian Federation. According to the law, it includes all residential premises recognized as suitable for habitation. Non-residential premises cannot be part of the housing stock.
Decoration of country houses and non-residential buildings
Next, we move on to describe the process of obtaining a construction permit, commissioning and registration of rights to residential buildings located on the lands of settlements provided for personal farming or individual housing construction. By the way, for residential buildings that have not yet been built (reconstructed).
Registration of rights to economic buildings and structures (garages, sheds, outbuildings, etc.) located on the lands of settlements provided for running personal subsidiary plots (LPH) or individual housing construction (IHC) also occurs on the basis of a technical plan .
What is the difference?
Residential and non-residential properties have a huge difference between them. The main difference between one type of building or structure from another is their different designation. Citizens may use residential properties only for direct residence in them, with the exception of certain cases provided for by law.
Housing must meet strict sanitary and technical requirements set out in the relevant legislation. Non-residential real estate has a commercial purpose. Such premises are used for warehouses, production workshops, shopping centers, and locations of public and municipal institutions.
Owning real estate is not only a privilege for the owner, but also a certain degree of responsibility. The owner is obliged to maintain his property in proper technical condition so as not to cause damage to other people. Real estate should be used within the framework strictly regulated by the laws of the Russian Federation. Misuse may result in administrative liability.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
The difference between a residential building and a non-residential building
The legal regime of horticultural and dacha land plots provides for their use for growing fruit and vegetable crops, in combination with recreation. Due to this, the exploitation of residential buildings erected on these sites is limited to the purposes of ensuring the process of growing horticultural crops and recreation. The very use of the term “structure” in the phrase “residential building” characterizes the temporary, seasonal, unfounded nature of the building and emphasizes the inconstancy of the use of these buildings by people. If for owners of dacha land plots the Federal Law of April 15, 1998 No. 66-FZ provided for a legal alternative - to erect a “residential building” or “a residential building with the right to register residence”, then for garden land plots the law did not provide such an alternative.
At the same time, the existing reality is such that, regardless of the legal regime of a garden plot of land, comfortable residential buildings are often erected on the lands of gardening partnerships, which can hardly be called “buildings”. According to technical standards and construction characteristics (in fact), these objects are residential buildings, according to the legal regime (virtually) - residential buildings. In this case, the purpose is fundamentally different from the actual use. Citizens concerned about the housing problem have long found a practical solution to it in the construction of dwellings on garden lands. The absence of the need to prepare and approve design documentation for the development of garden and dacha land plots allows their owners to create residential properties suitable for permanent residence. The only legal documents limiting owners in their construction impulse remain the rules of land use and development - in territories included within the boundaries of populated areas and planning projects for the territory of a non-profit partnership - on agricultural lands. In such conditions, developers of lands of gardening partnerships are limited only in terms of parameters - a height of no more than three ground floors, an area of no more than 1500 sq.m., a setback from the boundaries of the site - by the amount provided for by the development rules or the planning project. Who, in this case, would deny themselves the pleasure of building a residential building on a garden plot. Only those who are limited in funds or imagination.
08 Aug 2021 piterurist 2195
Share this post
- Related Posts
- When depriving parental rights, is the child’s opinion taken into account?
- If the lease agreement does not specify a period, the agreement is considered
- How long can it take not to pay a traffic fine?
- Complaint to housing and communal services about water
Non-residential premises; definition according to the housing code
As already mentioned, the Housing Code of the Russian Federation does not have a clear definition of non-residential real estate. However, on the other hand, there is a fairly detailed description of the living space. It can easily be assumed that if an object is not residential, then, quite logically, it is classified as non-residential. However, this is not entirely true.
- RF PP No. 354 states that non-residential premises are understood as those that are indicated as non-residential in the design/technical documentation and are not common property.
- Order No. 37 of the Ministry of Land Development clarifies that non-residential premises are not intended for permanent residence of people and can be used for sanitary, medical, trade, household and other similar purposes.
Type of room located in a building or structure
- The residential premises must be located in a building that is located in a residential area.
- The condition of load-bearing and enclosing structures in residential premises, as well as those located in the common elements of the property owners, must be operational and meet operating standards. They should not have damage or destruction that leads to the formation of deformations and cracks that reduce the overall load-bearing capacity of the structure.
- The arrangement of residential premises should prevent the risk of injury to residents when moving on or around it.
- It is necessary to have engineering systems in such a room: electric lighting, drinking and hot water supply, heating and ventilation, drainage, gas supply. In premises located in a settlement with no centralized utility networks, there may be no running water and sewerage latrines.
- Engineering systems (ventilation, heating, water supply, drainage, elevators, etc.), equipment and mechanisms that are located in a building with residential premises, or are present as part of the common property in apartment buildings, must meet all sanitary and epidemiological safety standards. Ventilation systems in residential premises should not allow air to move directly through apartments and between the kitchen and sanitary facilities.
- In addition, all engineering systems must be installed in accordance with the safety requirements established by the relevant regulations, as well as the manufacturers' factory instructions. Strict compliance with hygienic standards is required, including the permissible level of noise and vibration created by these systems.
- Structures located outside the residential premises and enclosing them, which are included in the joint property of the residents of an apartment building, must be thermally insulated. This is necessary to ensure that the relative temperature and humidity in the premises established by regulations is maintained during the cold periods of the year. This prevents the accumulation of excess moisture and condensation in the building structure.
- The living space must be protected from water from the external environment (melt, rain, groundwater).
- In a building with residential premises, the number of floors of which is more than five, it is necessary to have a lifting mechanism - an elevator.
- The floor in the living space must be above ground level. It is unacceptable to place residential premises in basements and ground floors.
- It is prohibited to place a restroom, bathroom and kitchen above living rooms. It is allowed to locate the kitchen above the restroom or bathrooms if there are two levels in a residential building (apartment).
- Every room in a living space must have natural light. It is not necessary in rooms used as auxiliary (corridor, vestibule, hall, sanitary unit, bathroom, storage rooms, etc.).
- In addition to the above-described requirements for premises used for human habitation, there are many acts establishing limit standards for electromagnetic radiation, alternating electric field, radiation dose rate, concentration of substances harmful to the health of residents, etc.
A structure is a volumetric, linear or planar building system that has underground or above-ground parts. It consists of load-bearing and enclosing building structures and is designed to perform various production processes, temporary stay of people, storage of finished products, movement of goods and people.
However, situations cannot be ruled out when a premises structurally and technically intended for permanent residence due to the influence of external factors becomes unsuitable for habitation over time. Taking this into account, the concept of suitability of residential premises for permanent residence also includes requirements regulating the permissible degree of environmental impact on residential premises. Such requirements apply to the level of noise, vibration, infrasound, electromagnetic radiation, concentration of harmful substances in the air of a residential premises, the intensity of electromagnetic radiation and electric field strength in a residential premises and are enshrined in clauses 26-32
At the same time, according to Part 2 of Art. 17 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, it is allowed to use residential premises for professional activities or individual entrepreneurial activities by citizens living there legally, if this does not violate the rights and legitimate interests of other citizens, as well as the requirements that the residential premises must meet (fire safety, sanitary and hygienic and etc.). Various categories of citizens can engage in professional activities at home: scientists, writers, etc. Such citizens also include lawyers who have chosen a lawyer’s office as their form of activity. According to paragraphs 6 and 7 of Art. 21 of the Federal Law of May 31, 2002 No. 63-F3 “On advocacy and the legal profession in the Russian Federation”1 a lawyer has the right to use residential premises belonging to him or members of his family by right of ownership, with their consent, as well as residential premises to locate a lawyer’s office occupied by a lawyer and members of his family under a rental agreement - with the consent of the landlord and all adults living with the lawyer.
What is a room - definition, types and features
Now let's focus our attention on the provisions of the LCD. It does not say what such a premises is, it only refers to a residential unit. The law defines the latter as an isolated premises that is suitable for permanent residence of people and is considered real estate. Suitability for human habitation means compliance with sanitary and technical standards.
The Civil Code has an entire chapter regulating the rental of premises from a citizen or organization not related to the state. It describes the essential conditions under which housing is provided. There are contracts of a short-term nature and those concluded for a long time. The terms of the agreement depend on the choice of the parties.
May 13, 2021 klasterlaw 31
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Retirement in the Chernobyl Zone Relocation Zone Under the New Law
- State Poshdina To the Court of the Moscow Region for the Cancellation of the Sentence
- How many days does it take for disability to be issued after a stroke?
- St. Petersburg cost of living for a disabled person of group 3
Residential and non-residential premises: what are they and for what purposes are they suitable? Let's deal with it wisely
- signs of their isolation;
- attitude towards real estate;
- purpose - not for human habitation, but to ensure social or production purposes;
- location - in residential and non-residential buildings, which distinguishes them from buildings;
- suitability for use in accordance with the requirements of regulatory documents.
We recommend reading: How many days does it take to transfer maternity capital when buying an apartment?
The classification of housing allows us to divide it into places of permanent and occasional (non-permanent) use as a habitat. The first type includes dwellings that are state (municipal) property, as well as those belonging to citizens or included in a housing cooperative or residential complex.
What is non-residential premises - definition according to the Housing Code of the Russian Federation
Example. To live in an apartment, you do not need to undergo inspections by the fire inspectorate or Rospotrebnadzor. Permission from these authorities is not required. But if a person wants to open a store in NP, depending on the type of activity, he will have to obtain opinions from inspectors.
- Status of real estate.
- Isolation from other premises, residential and non-residential, not owned by the owner.
- Suitability for permanent residence of people.
- Compliance with sanitary, technical, fire and other requirements.
- Registration in accordance with the established procedure in Rosreestr.
Residential premises: concept and types, purpose
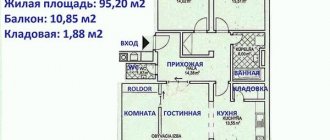
• apartment (part of it) – a structurally separate room in an apartment building, providing direct access to common areas in such a building and consisting of one or more rooms, as well as auxiliary premises;
We recommend reading: At what age can you re-register a car in your name 2021
Transactions with residential premises are also subject to state registration in cases and in the manner provided for by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and the Federal Law of July 21, 1997, as amended. dated July 19, 2011 “On state registration of rights to real estate and transactions with it” (SZ RF. 1997. N 30. Art. 3594; 2003. N 24. Art. 2244;
- As the owner of the premises (tenants are not allowed), you draw up an application to change the status of the property. If there are several owners, then written consent of all parties is required.
- Make sure there are no debts on utility bills.
- The property must not have any encumbrances, for example, be pledged.
- Everything complies with existing safety standards and has connections to all utilities.
- When transferring from one type to another, no actions are taken that bring danger to residents of nearby residential premises.
- Instead of a separate entrance, free access through a common entrance is required.
- execution of a transaction - Articles 550-551, 554 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- state registration of rights to such premises - Article 131 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- the procedure for foreclosure with a pledge is Article 349 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- the statute of limitations from the date of acquisition is Article 234 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- jurisdiction at the location of the property - Article 30 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.