Home/Electricity supply/Electricity MOP in the housing and communal services receipt
As part of the reform of public utilities, all apartment buildings are equipped with common building electricity meters. This is necessary to determine the number of kilowatts consumed for general purposes. Residents of high-rise buildings continue to argue about the correctness of the calculations and the lack of accounting for the share of electricity consumed.
Normative base
Responsibility for the maintenance of property in joint use is regulated by Art. 30 clause 4 of the Housing Legislation, as well as Art. 209-210 of the Civil Code. The legality, validity and legality of including MOP electricity in the general housing and communal services bill for the general needs of the house is determined by Government Resolution No. 354, adopted on May 6, 2011, which describes the procedure for the provision of utility services.
Attention! If you have any questions, you can chat for free with a lawyer at the bottom of the screen or call Moscow; Saint Petersburg; Free call for all of Russia.
The requirement to make a payment for MOP electricity spent on the general needs of an apartment building is also stipulated:
- in Federal Law No. 261, dated November 23, 2009 and defining ways to save energy and increase the efficiency of the existing energy system;
- in Government Decree No. 491 of August 13, 2006, approving the rules for maintaining common space and changing fees in connection with emergency situations.
PP No. 354 states that the amount of payment in the housing and communal services receipt for MOP electricity depends on the difference between the data of the collective meter and the readings of individual devices. The resulting value is distributed among all residents of the high-rise building.
Electricity MOP: consumption standards and tariffs
MOP electricity involves spending the resource for the common purposes of the residents of an apartment building (AMD). The calculation is made using a special formula.
Legislative basis
Provisions of Art. 30 of the Housing Code reflect the rules providing for rules on the maintenance of property that is in common ownership of apartment building residents.
In addition, Art. 209 and 210 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Government Decree No. 354 of 2011 “On the rules for the provision...” from a legal point of view justifies the correct inclusion of MOP in the ODN. There are also acts that stipulate payment for electricity in the common areas of apartment buildings.
These include:
- Federal Law No. 261 of 2009 “On Energy Saving...”;
- Government Decree No. 491 of 2006 “On the rules for development and approval...”.
According to Government Resolution 354 of 2011, MOP electricity depends on the difference between the readings of the general and individual meter. The resulting values are divided among all residents.
MOS Electricity Concept
In the receipts for which payments for housing and communal services are made every month, a separate item is included - MOP electricity.
This point of accrual should be understood as the use of this resource in general purpose areas . This term applies only to MKD.
Previously, the service in question was hidden in the line “maintenance and repairs in the house.” The changes occurred after the entry into force of Government Resolution No. 354 of 2011.
Composition of MOS electricity
In the provisions of Art. 36 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation reflects the premises that are common in an apartment building.
These include:
- attics;
- corridors;
- elevators;
- other non-residential premises where lighting is used.
Payment for electricity is the responsibility of the owner of the residential premises. This is stated in the provisions of Art. 158 Housing Code of the Russian Federation.
Regions set their own standards for payment of the receipt line in question. However, most often, this figure is 7 kW.
This value is set for houses that are not equipped with elevators. For MKDs equipped with these devices, the standard increases to 14 kW.
Important! Replacing light bulbs cannot be included in this expense line. Such work is carried out by a specialist, whose presence must be ensured by the head of the management company (MC) or homeowners' association (HOA).
Calculation of electricity charges
The calculation of MOP electricity depends on whether the house is equipped with general metering devices or not. When the meter is not installed, the formula below is used.
PE = N * PN*PC/OP , where:
- О – consumed energy;
- N – standard expenditure per citizen, determined by Government Decree No. 354 of 2011;
- PN - the size of the common premises in the apartment building;
- PC – apartment area;
- OP – the size of the entire house excluding non-residential premises.
To calculate the cost of services provided, you need to multiply the value obtained as a result of the calculation by the current tariff . To understand how payment is calculated, a specific example should be given.
The region has established a consumption standard of 2 kW per square meter. The size of non-residential premises is 200 square meters, of which 40 square meters are the property of citizen I. The total area of residential premises is 1600 square meters. The tariff is 3.25 rubles/kW.
The calculation will be as follows: 2*200*40/1600 = 10 *3.25 = 32.5 rubles.
Calculating payment in a house where there is a meter
When an apartment building is equipped with a common meter, a different formula should be used.
OP = (PO-KN-KZHS-KZHSS-EO)*RK/OP , where:
- OP – volume of energy consumed;
- PO – indicator of a common house metering device;
- KN – kW value in non-residential premises;
- KZhS – electricity consumption by apartments not equipped with meters;
- KZhSS – the amount of resource used in premises equipped with metering devices;
- EO – energy spent on heating water and heating;
- RK – the size of a specific apartment;
- OP – total area of the building.
To calculate the total amount of payment per month, you need to multiply the resulting figure by the tariff.
For example, by the end of the month the general meter indicated a value of 16,000 kW. This amount includes 10,000 kW, which is consumed by premises equipped with meters. Apartments not equipped with meters accounted for 5,000 kW. The total size of residential premises is 5000 square meters.
A separate apartment is 40 square meters, the tariff is set as before - 3.25 rubles/kW.
Payment: (16000-10000-5000)*40/5000 = 8 kW * 3.25 = 26 rubles.
What will affect the payment for electricity MOP
Electricity for SOI in a house that is not equipped with a common meter is paid in accordance with current regulations. To achieve this, payment for all energy consumed is divided among residents . The amount of payment depends on the size of the apartment owned by the citizen.
Loading …
At the same time, the amount of electricity consumed for individual purposes does not affect the amount. When a meter is installed in the house, certain factors will influence the calculation.
Including:
- the condition of the electrical system in the house;
- timely submission of readings from all meters;
- the number of premises equipped with such devices.
If the house has offices, shops or beauty salons, the receipt may contain a large amount for the payment of MOP electricity. This applies to situations where tenants have not entered into electricity supply agreements.
Important! The absence of such an act indicates the need to divide the consumed resource between apartment owners.
Electricity fee MOP
The amount of payment is subject to calculation based on the provisions of Government Decree No. 354 of 2011.
In order for the residents of the house to be sure that the payment consists only of meter readings that take into account the electricity spent for the SOI, it is necessary to invite a specialist.
This person takes inventory of the equipment. The specialist checks whether commercial organizations located in the house are connected to the general network. If such connections are revealed during the inspection, it is necessary to influence the merchants, for example, by filing a complaint with the Criminal Code.
Possible problems and solutions
In practice, paying for electricity to MOP causes certain difficulties. In particular, it happens that no one controls the equipment operating in the house. Then residents should take the matter into their own hands and turn on/off the light bulbs in the entrance only when it is really necessary.
In addition, you can equip common areas with devices with motion sensors or energy-saving lamps.
When the wiring system in common areas is worn out, you will need to generate an application on behalf of all residents and submit it to the Criminal Code . If the network repair is not carried out, you can appeal this in court or the prosecutor's office.
A complaint against neighbors conducting commercial activities can be sent to the police department, criminal investigation department, or resource supply company. Sometimes residents whose apartments have had their electricity turned off connect to the public network. Then you need to contact an authorized organization and ask to turn it off again or put a lock on the cabinet.
In addition, citizens living in apartment buildings can request that individual residential premises be equipped with metering devices . This applies to situations where the amount of kW used by an individual citizen exceeds the established consumption standard. In this case, the difference must be divided among all residents.
Thus, MOP electricity is subject to payment by all residents of the apartment building. This amount is indicated as a separate item on the receipt. If a citizen refuses to pay, penalties in the form of a fine are applied to him. The resource supply company has the right to go to court to collect the debt.
Source: https://zkhrf.ru/kommunalnye-uslugi/elektroenergiya/mop
What is included in MOS electricity?
Article 36 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation includes in common areas (MOP): elevator, corridors, platforms, attics, basements, etc. non-residential premises in which electricity is used. In accordance with Art. 158 of the housing legislation, each owner of an apartment in a multi-storey building must regularly pay housing and communal services receipts related to utilities and the maintenance of his own home, as well as take a share in the care of the common space.
For your information
Electricity consumed by light bulbs on sites and in basements was always paid for, but at the expense of the “housing maintenance” line. Houses equipped with common metering devices do not experience difficulties in calculating payments for MOP, since we are talking about actual expenses. And residents of old buildings, which in most cases do not have meters, are outraged by too high payments.
In almost all regions, the standard is 7 kW per month for MOP in a building that is not equipped with an elevator and approximately 14 kW if the number of floors of the building requires a lifting mechanism.
Mop decoding in construction: what is a mop in an apartment building
When receiving receipts for housing and communal services, many come across the unfamiliar abbreviation “MOP” without decoding. This line, provided in payment documents, characterizes a certain amount of payments that is indicated in it. In this regard, questions arise related to calculating the amount of money to pay for electricity in an apartment building.
What it is
This abbreviation stands for public areas. Absolutely everyone can use them, but at the same time they are the property of the residents of the house.
In construction, the MOP determines what kind of repairs are made in these places: the complexity of the construction work, the design project and the materials used.
Definition
This name is typical for apartment buildings. Article 36 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation specifies the premises of an apartment building (apartment building), which are included in the MOP.
In fact, this includes the entire area of the house, excluding apartments that are the personal property of their owners. Accordingly, all these places must be properly maintained.
They are not part of the apartments, but require constant care and inspection by specialists.
Standards
The standards for maintaining MOP per 1 m² of apartment area vary depending on the management company and region.
This includes:
- frequency of implementation of the prescribed work (for example, once a week);
- the cost of the services provided (for example, current repair of a power plant - 3.58 rubles).
What's included
The MOP includes the areas of various premises that are in the public domain. They depend on the layout of the house and the places provided by the designer to meet the various needs of the owners.
The general list of MOP areas includes:
- stairs and elevators;
- dressing rooms for storing things;
- attic and boiler room;
- roof;
- porch;
- places intended for smoking, etc.
All the above-mentioned places are designed to create maximum comfort for the residents of the house.
MOP include the provision of the necessary types of work to maintain their normal condition. The normative act establishing the procedure for the use and maintenance of places for public use is the Housing Code of the Russian Federation and Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 491 of August 13, 2006.
Types of jobs:
- Identification of malfunctions of any types of equipment and their parts located on the territory of the MOP.
- Checking the functionality of lighting devices near and inside entrances.
- Inspection of fire-fighting equipment and alarm systems.
- Garbage removal.
- Landscaping in summer.
Cleaning
Common areas must be cleaned. Its regularity, cost and types of work are specified in the contract with the management company.
Cleaning typically includes:
- rodent and insect control;
- snow removal from the local area;
- grass cutting;
- roof cleaning;
- maintaining the entrance in proper condition.
If there is a garbage chute, then, accordingly, clean this place as necessary.
Repair
The timing of general capital repairs is established based on the characteristics of the technical operation of various residential buildings. However, employees of the management company, when identifying the need for repair work on equipment, elevators, staircases, etc., are required to immediately take corrective action.
Electricity cost calculation
Most owners have a question: MOP electricity - what is it? Previously, all costs for power supply to common areas were included in the expense column for “and repairs of residential premises,” but with the introduction of appropriate changes they were deducted from there.
The calculation of the payment amount is determined by the area of the apartment. Common property is divided in proportion to the area of each apartment, and not to the number of residents. After the meter readings are taken, they are sent to the management company. She makes a calculation that determines the monthly cost of “Power supply to the MOP”.
When calculating electricity spent on public needs, they rely on the following indicators:
- total electricity consumption in the house;
- total electricity consumption in all residential premises;
- electricity costs of legal entities that are connected to the public network.
Possible problems
When installing additional lighting in common areas or illegally connecting to the power grid, all residents of the house pay the amount of money associated with the leakage of electricity.
Repayment of the bill for the electricity supply of public premises is calculated by square meters: whichever owner has the larger area pays more.
Energy loss accounting
Electricity leakage is usually associated with many unfavorable factors.
For example:
- outdated electrical wiring;
- lack of energy-saving light bulbs;
- meter breakdown;
- illegal connection to the network, etc.
To account for energy losses and reduce the amount of payment for electricity supply to the MOP, residents must assemble an initiative group. It will monitor the reading of individual meters by all residents of the house and identify illegal connections to the power grid.
Who pays and how much
All costs associated with the provision of utility services, which include the maintenance of the MOP, are borne by the owners of the premises. This is established by Article 39 clause 1 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation.
Resolution No. 354 determines that owners are required to pay for electricity supply to the MOP every month, even if they do not live in the given location.
The total number of people registered in a residential premises is not relevant to the lighting of public areas of the house.
Liability for non-payment
Agreements concluded with utility companies provide for liability for failure to fulfill obligations to pay for the resources provided.
If the owner systematically does not pay the required amount of money, then the energy supplier has every right to sue and collect the debt from such person.
As practice shows, in most cases, if the Management Company and the Homeowners Association file claims to collect a debt from the owner, the court satisfies them.
Poor awareness of what the new item that appears on the receipt means means the population is unwilling to pay for it. Every owner must know that lighting of public areas is a paid service that has always existed, but became a separate property relatively recently. Therefore, it is important and necessary to pay for it.
Tricks of management companies
The tricks that management companies resort to include adding additional services to the list of paid services. Therefore, in many apartment buildings a “house council” has been created. He checks the management company's action report.
The following are subject to verification:
- services for which funds collected from residents were spent;
- proper execution of the management agreement;
- list of services provided by the management company.
Other abbreviations
It is worth noting that the abbreviation “MOP” has many more meanings. It can stand for “rag for cleaning and washing the floor.” A special attachment for a mop or brush, which is suitable in size and type of attachment. Designed for cleaning and maintaining floors.
The abbreviation can also mean “junior service personnel.” It includes such employees who do not participate in the processes of production and management of these processes. They perform maintenance functions.
The video provides information on what MOP is in an apartment building.
The following video contains a breakdown of MOP in construction.
Source: https://uristi.guru/kvartira/rasshifrovka-mop.html
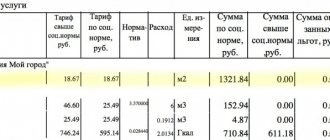
Cost calculation
The payment for MOP electricity in the housing and communal services receipt is determined in different ways:
- If the house does not have a common meter, then according to the formula:
VMOS = NMOS * Pl. Non-residential* Sq./Sq. total sq.
Where,
NMOP is the monthly standard value of electricity consumption for each family member, determined by RF PP No. 306 in 2006,
Pl. unlived - size of common premises,
Sq.m - area of occupied living space,
Total area - the area of the entire multi-apartment building excluding non-residential premises.
The fee is calculated as follows:
Pmes. = VMOS * T
Where,
VMOS is the total size of MOS electricity;
T is the tariff applicable to the utility resource.
Example
The location of the apartment building is a region that has determined the standard for electricity consumption to be 2 kW per 1 m2. The area of public non-residential space is 200 m2, private housing is 40 m2, and all residential premises occupy 1600 m2. We will take the tariff equal to 3.72 rubles/kWh.
It turns out: 2 * 200 * 40/1600 = 10 * 3.72 = 37.20 rubles.
- If the multi-apartment building is equipped with a common building meter:
VMOP = (Vtotal - ∑ Vnon-residential - ∑ Vresidential required - ∑ Vresidential volume - Vcr.) * Sq./Sq. total
where Vtot. — the amount of electricity accounted for by a common household appliance;
∑ Vnon-residential — the number of kilowatts used in non-residential space;
∑Vliv. required — general residential consumption without a meter;
∑Vliv. about. - the total number of kilowatts used in residential apartments equipped with metering devices;
Vcr. - the amount of electricity consumed by the contractor for heating and water heating (if the house is not connected to a centralized system).
Sq.m. - the number of square meters of a separate apartment;
Pl. total - the total area of the entire building.
The monthly amount is:
Pmes. = VMOS * T
Example
The common house meter showed 16,000 kW. At the same time, all residential apartments in which metering devices are installed consumed 10,000 kW. The total amount of kilowatts in a non-metered residential space is 5000 kW. The sum of residential square meters in the entire house is 5000 m2. The dimensions of a single apartment are 40 sq.m. The tariff is the same - 3.72 rubles/kWh.
(16000-10000-5000)*40/5000 = 8 kW * 3.72 = 29.76 rubles.
We resolve legal and financial issues
Moreover, the city prosecutor’s office filed a lawsuit against the management company (Zhilservice). Its employees were forced to do this because they received complaints almost every day from citizens living in houses managed by the above-mentioned business entity.
Where did this expense item come from?
The energy supplier has the right to sue for non-payment with a demand to collect the debt, and the court, in most cases, satisfies these claims. In turn, the management company and the homeowners association file claims to collect the debt from the owner, since it is his responsibility to pay for the utility resource provided to him. Reforming the housing and communal services brings a number of innovations that residents of the country cannot always immediately understand.
In accordance with Part 1 of Article 157 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, the amount of payment for utility services is calculated based on the volume of their consumption, determined by the readings of metering devices, and in their absence, based on consumption standards. The rules for the provision of utility services to citizens (hereinafter referred to as the Rules) were approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 307 of May 23, 2006. They regulate the relationship between providers and consumers of utility services, establishing their rights and obligations, responsibilities, as well as the procedure for determining the amount of payment for utility services using metering devices and in their absence.
More to read —> Sanctions for late submission of a payment order to the Pension Fund
For example, for a family of two people occupying two rooms in a communal apartment in an apartment building or dormitory), the utility consumption standard for electricity supply will be 52 kW hour per person per month.
But electricity stolen by unscrupulous residents is also included in the bill for electricity in common areas. Why should other residents pay for them?
– In non-residential premises located in multi-apartment residential buildings, there are electricity meters. Basically, these devices are included in the general power supply system, and when making calculations, meter readings in non-residential premises must be subtracted from the readings of the general house meter. Owners or tenants of non-residential premises conclude energy supply contracts with the energy supply organization independently, but control over electricity consumption in this case is exercised by the energy sales company and management organization, since it is she, as a representative of the owners of residential premises, who allows the entrepreneur to connect to the intra-house network.
Based on these data, actual consumption is calculated by subtracting the total consumption for all apartments. The consumption of electricity by legal entities connected to the public network is also taken into account. As a result, the remaining volume is considered the electricity of the MOS.
The energy supplier has the right to sue for non-payment with a demand to collect the debt, and the court, in most cases, satisfies these claims. In turn, the management company and the homeowners association file claims to collect the debt from the owner, since it is his responsibility to pay for the utility resource provided to him. Reforming the housing and communal services brings a number of innovations that residents of the country cannot always immediately understand.
How is MOP electricity calculated now?
Currently, comprehensive reform of the housing and communal services sector is ongoing in Russia. As a result, many enterprises that provide relevant services to the population systematize their own relationships with consumers, which mainly include people living in high-rise buildings.
May 14, 2021 uristgd 29
Share this post
Related Posts
What affects the payment amount?
Residents of an apartment building that is not equipped with a collective meter pay for electricity for MOP in accordance with current standards by distributing it between apartments on a shared basis. The payment amount in the housing and communal services receipt directly depends on the number of personal square meters, and not on the consumption of electricity for individual needs.
If the house is equipped with a metering device, then the amount of charges is influenced by various factors:
- technical condition of the general house electrical system;
- synchronization of readings received from public and personal electricity meters;
- percentage of apartments equipped with personal meters, etc.
Attention
The amount of payment in the housing and communal services receipt for MOP electricity may be too large if the house is equipped with a common meter, but the main part of the non-residential space is distributed between offices, shops, medical centers, hairdressers, who rent space, but have not entered into an energy supply agreement. The absence of a document indicates that electricity consumed for commercial needs is distributed among apartment owners.
Rules for using MOP
- inspection of the mine and removal of waste from waste receptacles;
- cleaning bins from loading valves;
- periodic cleaning and disinfection of the waste chute;
- timely elimination of malfunctions and minor blockages.
Norms
Many residents of an apartment building have encountered obscene inscriptions on the walls of their entrances or damage to property in the surrounding area. To prevent such phenomena, you can resort to installing CCTV cameras or hiring a concierge.
More to read —> How a Bailiff Seizes Accounts If Not the Whole Amount Is There
Considering the fact that the problem of payment of utility bills by the owners of premises appeared not so long ago, local judges rarely have to deal with cases of debt collection from owners of residential premises in apartment buildings.
Homeowners' associations and management organizations are usually responsible for unscrupulous owners. Usually, management organizations and homeowners' associations become the "extreme" in this situation. The reluctance of owners to pay for the electricity needed to illuminate the MOP forces homeowners' associations and management companies to avoid establishing contractual relations for the supply of electricity to the MOP.
Problems in calculating MOS lighting
An important factor in the indignation of residents related to the incorrect calculation of the amount for electricity spent on lighting common areas is the so-called “payment for a neighbor.” Unscrupulous residents transmit false data, connect bypassing the meter, etc., which leads to losses that the HOA and management company distribute among the owners. If the owners have not done this themselves, then by July 1, 2021, the meter will be installed by the resource supply company.
Now, in accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 23.05. 2006 No. 307, the cost of electrical energy spent on general house needs is highlighted in the receipt as a separate line. Thus, with the introduction of a new form of payment, expenses for general house needs are distributed and accrued individually to each owner or tenant of the residential premises of an apartment building.
Is it possible to refuse payment?
In accordance with the rules for the provision of utility services to owners and users in multi-apartment buildings and residential buildings, approved by Government Decree No. 354 of May 6, 2011, payment for electricity consumption on the MOP in the housing and communal services receipt in the presence of a common building meter is distributed among the owners, in proportion to the occupied square meters . If a multi-storey building is not equipped with a collective meter, then the MOP electricity is calculated based on the standard established in the region.
Attention
The rules require that payment for kilowatts used in common areas be made even if personal square meters are empty for a long time, because the formula is based on the area of the apartment.
Concept of MOS lighting
Why is the problem of lighting in public spaces so acute, since residents had previously paid for this service as part of another item. Until 2021, the amount for the item “repair and maintenance of housing stock” was calculated according to the tariff, i.e. was fixed.
Problems in calculating MOS lighting
Actual electricity consumption in common areas is calculated as the difference between the indicators. It is multiplied by the tariff established in the region and divided among all owners, in proportion to their share in the right of common ownership of the property. It turns out that the area of the property affects the amount of payment. The exact calculation formula is presented in Appendix No. 2 to Government Resolution No. 354.
The supplier is obliged to recalculate the negative difference in one-time tax for a utility service, dividing it between residential apartments. In this case, a value is taken that is proportional to the people living in a particular apartment or the size of the total area. This procedure is stipulated in Art. 354 Government Decree.
Consequences of non-payment
Management companies and homeowners associations are responsible for timely payments based on agreements with utility companies. Ignoring the requirements allows the MOP energy supplier to solve the problem in court. Servants of Themis usually satisfy these types of claims. Service organizations similarly resolve the issue with homeowners.
The housing and communal services sector is constantly being updated, and apartment owners are not always aware of these innovations. Likewise, the line “MOP electricity” in the housing and communal services receipt became an unpleasant surprise for many. Failure to pay utility bills on time, including in public areas, can result in fines, penalties and litigation.
Judicial precedents
At the same time, several years ago, citizens living in the city of Livny, located in the Oryol region, managed to prove in court that they were illegally overcharged for electricity supply to the MOP.
Moreover, the city prosecutor’s office filed a lawsuit against the management company (Zhilservice). Its employees were forced to do this because they received complaints almost every day from citizens living in houses managed by the above-mentioned business entity.
People were sent payments with huge sums, the size of which significantly exceeded the fee for energy consumption in apartments.
It took both judicial and prosecutorial officials a lot of time to study all the documents presented, as well as the current ones:
- standards;
- techniques;
- instructions.
As a result, it was possible to establish that the problem arose due to incorrect application of the calculation formula. The prosecutor's office noted that representatives of the energy supply company took into account the electricity costs declared by consumers themselves, while they should have relied only on the data received from the meters.
This is not the first year we have been writing about this, but city residents continue to ask the chronic question: what is a MOS board, why is it so big, what is included in it. Many residents complain that it is impossible to find out this from their management companies and HOAs - despite the fact that the residents themselves accept the MOP tariff in each house - usually by absentee voting. But, alas, there is no calculation in the ballot papers (decisions of the owners), only the amount is worth - more than last year. Since management companies and HOAs are mainly guided by the “Duma tariffs” adopted by the City Duma for municipal apartments, we present the most common option from the decision - an apartment building with all amenities and a passenger elevator. I. Maintenance of common areas - 1.01 rubles: 1.1 Sweeping floors in the POP - 6 times a week; 1.2 Wet cleaning of POP - once a month; 1.3 Wiping dust from hoods, window sills, cleaning the attic and basement - once a year; 1.4 Washing and wiping doors and windows in the POP - 2 times a year. II. Cleaning the land plots of an apartment building - 2.69 rubles: 2.1 Sweeping the land plot (concrete) in the summer - 3 times a week; 2.2 Removing garbage from the lawn, emptying trash cans - 3 times a week; 2.3 Shifting and sweeping snow in the absence of snowfall - 3 times a week; 2.4 Shifting and sweeping snow during snowfall - if necessary; 2.5 Lawn mowing - 2 times a year; 2.6 Routine repair of children's and sports grounds, landscaping elements - once a year; 2.7 Elimination of ice - if necessary; 2.8 Removing snow from roofs, knocking down icicles - if necessary; 2.9 Collection, removal and disposal of solid household waste - daily (RUB 0.79) III. Maintenance of elevators, including dispatch communications - 24 hours a day - 3.16 rubles. IV. Preparing an apartment building for seasonal use - 1.30 rubles: 4.1 Preservation of the central heating system - once a year; 4.2 Replacement of broken glass windows and doors in POP - if necessary; 4.3 Repair, adjustment and flushing of central heating and cleaning of ventilation ducts - once a year; V. Inspection and minor repairs - 1.82 rubles: 5.1 Inspection of ventilation, smoke removal, electrical devices - 2 times a year; 5.2 Emergency maintenance - permanent; 5.3 Deratization - once a year; 5.4 Disinsection - once a year; 5.5 Inspection and elimination of minor faults in water supply, sewerage, heat supply, and electrical systems; 5.6 Maintenance of VDGO (at least once every three years) - 0.22 rubles. VI. Repair of common property - 2.87 rubles: 6.1 Restoration (repair) of doors in the POP - if necessary; 6.2 Repair of entrances - if necessary; 6.3 Elimination of leaks and other roof repairs - if necessary; 6.4 Sealing, thermal insulation of interpanel seams - if necessary; 6.5 Restoration (repair) of the blind area, repair of external improvement objects (approaches, sidewalks) - if necessary; 6.6 Repair, replacement of in-house networks of cold and hot water supply, sewerage and repair of in-house electrical equipment for general use - if necessary; 6.7 Repair of equipment, instruments and fittings of the public water supply network - if necessary; 6.8 Repair of balcony slabs; 6.9 Repair of supporting structures of canopies - if necessary. VII. Management of an apartment building - 1.21 rubles. Total - 14.06 rubles. Roman numerals indicate general services of a targeted nature, Arabic numerals indicate a specific list of works included in each service. Money for each service is distributed among specific works that are not financially fixed - with the exception of clause 2.9 - collection, removal and disposal of solid waste (79 kopecks) and clause 5.6 - maintenance of VDGO (22 kopecks). These works were calculated due to the involvement of third-party organizations (to the company servicing the house): the garbage is removed by Eco-Service, and the gas equipment is serviced by Kurskgaz. In some management companies and homeowners associations, these services are displayed as separate lines in the housing and communal services receipt. The fact that the rest of the work is not costed, and their frequency is indicated as “if necessary,” suggests some kind of backlash in their production. For example, clause VI “Repair of common property” - 2 rubles. 87 kopecks. per square meter assumes for this money either routine roof repairs (item 6.3) or repairs of entrances (item 6.2) - in a word, those works that are urgently needed and for which the collected money is enough.
We cannot help but note some cunning in the list, when the same work is repeated in different services (compare paragraphs 2.6 and 6.5, 5.5 and 6.6, 6.7).
When receiving receipts for housing and communal services, many come across the unfamiliar abbreviation “MOP” without decoding. This line, provided in payment documents, characterizes a certain amount of payments that is indicated in it. In this regard, questions arise related to calculating the amount of money to pay for electricity in an apartment building.
Nuances
The owner of an apartment in a multi-storey building is obliged to participate in payments for general house electricity costs in accordance with the share of his living space. That is, the amount of payment directly depends on the area of the apartment. This procedure can be followed if the building is equipped with a collective meter. In a house that is not equipped with a metering device, payments for MOP electricity are made based on the standards established in the region.
Additional Information
Until September 2012, different rules were in effect: the share of expenses for MOP was proportional to personal expenses. But this caused serious disputes between neighbors living on similar square meters, but spending different amounts of kilowatts for their own purposes.
Property owners, outraged by large general household expenses, must initiate a meeting and decide on the best ways to combat it: install personal meters, provide readings in a timely manner, eliminate illegal connections and theft on the part of apartment and business owners. You can combat the high energy consumption of MOS by installing energy-saving equipment, motion sensors and other devices that allow you to automatically turn on and off the light bulbs.
Comments Showing 0 of 0
What is MOP in an apartment building?
This abbreviation stands for public areas. Absolutely everyone can use them, but at the same time they are the property of the residents of the house.
In construction, the MOP determines what kind of repairs are made in these places: the complexity of the construction work, the design project and the materials used.
Subtleties of premises privatization
Privatization applies only to premises rented under a social tenancy agreement. The tenant can transfer one or more premises into his own ownership, but not the communal apartment as a whole.
If minor children live in the room, then the consent of the guardianship and trusteeship authorities will be additionally required. Their decision depends on arguments in favor of the interests of the child. The following requirements must be met:
- the child will be provided with housing equivalent to the previous one;
- sanitary and hygienic requirements will be met at the new location.
During privatization, the consent of neighbors is not required.
MOP include the provision of the necessary types of work to maintain their normal condition. The normative act establishing the procedure for the use and maintenance of places for public use is the Housing Code of the Russian Federation and Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 491 of August 13, 2006.
- Identification of malfunctions of any types of equipment and their parts located on the territory of the MOP.
- Checking the functionality of lighting devices near and inside entrances.
- Inspection of fire-fighting equipment and alarm systems.
- Garbage removal.
- Landscaping in summer.
Let's sum it up
cleaning equipment market provides mops from foreign and domestic manufacturers in a wide price range.
The quality of the mop determines its durability and cleaning efficiency.
If you take into account the type of room covering, its functionality, the areas of the room to be cleaned, the size of the objects to be cleaned and choose the right mop, it will last a long time, performing its functions efficiently.
- Pros of using mops:
- Significant reduction in the time required for cleaning
- Improving the quality of cleaning
- Detergent costs are reduced
- Great durability (from 2-3 months), abrasion resistance
- Used for cleaning walls, ceilings, corners, baseboards, steps
- Possibility of spray cleaning
- Pressed out using a wringer
- Disadvantages of using mops:
- Initial investment in purchasing equipment
- A short training course for staff is required before use.
Rules for living in a communal apartment and the rights of owners
In a communal apartment, where you regularly have to take into account the opinions of strangers, the key to a quiet life will be compliance with living standards and respectful attitude towards your neighbors.
In fact, these problems can be easily avoided if you know the rules of living in such an apartment.
Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, please contact the online consultant form on the right or call the numbers below. It's fast and free!
According to the Housing Code, a communal apartment is understood as a residential property consisting of several residential premises separated from each other.
The apartment has common areas that residents can use together, such as a kitchen, corridor, drying room, and bathroom.
Homeowners and tenants can live in this type of apartment.
All residents can use and own the apartment to the same extent; the owners have the right to dispose of the property that belongs to them.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with land surveying through the court
The owner can register citizens on the territory of his premises, both on a temporary basis (up to six months) and on a permanent basis; he has the right to sell his own share in the communal apartment, donate it to another person, or exchange it.
The tenant of a residential premises (if the housing is municipal) has the right to rent it out, observing a number of the following requirements:
- There must be at least 12 sq.m. per person;
- The lessor must give his consent to this in writing.
Both tenants of housing and its owners have the right to accommodate residents free of charge without the consent of the other parties.
Owners and tenants of housing are obliged to use residential premises for their intended purpose, for living.
The owner’s responsibilities include maintaining the residential premises in proper condition while respecting the interests of neighbors, as well as timely payment of bills for water, heating and other utilities.
Maintaining silence
The silence regime must be observed from 11 o'clock in the evening until 7 o'clock in the morning, the noise during this period should be 45 dB.
Source: https://KPPKDirection.ru/drugoe/elektrichestvo-mop.html