Legal encyclopedia of MIP online - » Housing law » Renting residential premises » Provision of housing under contracts for the rental of residential premises for social use
Get an expert’s opinion on rental agreements for residential premises for social use in two clicks
The Housing Code of the Russian Federation sets out the categories of entities that can apply for improved housing conditions.
Today, the Russian state is taking a number of measures that are aimed at ensuring the social well-being of citizens. In particular, special attention is paid to needy and low-income families who cannot independently ensure a trouble-free existence.
In such situations, political and social programs aimed at providing certain categories of citizens with free housing with the possibility of further privatization play a significant role. In other words, we are talking about such a concept as social hiring. What is this program? What are the conditions for its implementation?
Conditions for the provision of living space under rental agreements
If we talk about a social tenancy agreement, then the procedure and conditions for providing residential premises to the needy layers of citizens are regulated by Ch. 7 Housing Code of the Russian Federation. Additional legal norms affecting this area are prescribed in civil legislation, the Code of Administrative Offenses and other legal acts of the Russian Federation.
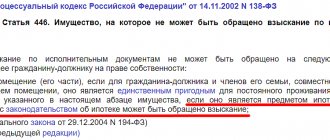
In this situation, we are talking about the fact that, under rental agreements, housing is allocated from a specialized fund, which is owned either by the state or the municipality, which are recognized as landlords. The other party to the legal agreement is the tenants - citizens who need to improve their living conditions.
According to Art. 60 of this Code, the landlord must provide for free use (in some cases for a small fee) comfortable living quarters that meet all legal requirements. At the same time, the term of the social tenancy agreement is not specified in the agreement, and the allocation of residential premises itself occurs in strict order as individuals are registered.
The Housing Code of the Russian Federation sets out the categories of entities that can apply for improved housing conditions. There are 2 of them in total:
- low-income citizens who are recognized as such by social protection authorities;
- persons in need of improved housing conditions.
In order to become the owner of residential premises under a rental agreement, you must contact the authorized state or municipal authority, provide a complete package of documents confirming the status of those in need, write an application for the allocation of an apartment and register for housing registration.
Social housing
Initially, social facilities belong to local authorities. They are transferred to citizens who meet certain conditions.
Find out if housing is available for single mothers. How to use maternity capital to buy a home? See here.
For the poor
The level of profit received influences the determination of low-income status. But there is not only the need to improve living conditions and increase living space. It is important to determine if there are conditions that do not meet any minimum.
You will have to rely only on your own strength when solving the housing problem with an income exceeding the established minimum. The income of close relatives is taken into account, even if the citizen lives separately for some time.
The reason for the formation of queues is the lack of housing from municipal authorities that would meet all established requirements. It is necessary to take into account possible changes in the status of the family.
Extraordinary provision of residential premises under a rental agreement
Despite the fact that the Housing Code of the Russian Federation is aimed at equalizing the rights of all those in need of improved housing conditions, the normative act also provides for cases when an extraordinary provision of an apartment from the social fund occurs. Similar nuances are spelled out in Art. 57 Housing Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, emergency provision of residential premises is possible only for several categories of citizens:
- individuals who live on the territory of residential premises recognized as unfit for habitation or in emergency condition;
- individuals who suffer from severe forms of disease in the chronic stage, which makes it impossible for them to live in the same territory as healthy citizens.
More recently, a third category of persons was identified, who also had the right, under tenancy agreements, to the emergency provision of housing. This included orphans and children without parental care. However, according to Federal Law No. 15-FZ, this paragraph of Art. 57 of the RF Housing Code has lost its legal force.
Particular attention should also be paid to the issue of who else may be recognized as in need of improved housing conditions under tenancy agreements. In particular, if we delve into the legal nuances, we can conclude that those citizens who were granted this status before March 1, 2005 can exercise their right and enter into employment with the state out of turn. However, in this case the person had to be registered with the housing stock.
Before this date, many categories of citizens were recognized as in need of improved housing conditions, but as practice shows, few people knew about this and even fewer were able to exercise their legal right. Therefore, if the subject of legal relations had the opportunity to enter into rental agreements with the state, but for some reason was not included in the list of priorities, then he has the right to demand the provision of housing through a judicial authority.
Citizens who have lost their property as a result of a fire have the right to priority provision of housing.
A similar norm is enshrined in the position of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation. In particular, the Resolution states that Art. 57 does not exclude the possibility of allocating residential premises under rental agreements to fire victims, even if they were not registered as those in need of improved housing conditions.
Thus, the extraordinary provision of residential premises under social tenancy agreements has a number of nuances, which only a practicing lawyer or advocate can help you understand. This is due to the enormous flexibility of Russian legislation, including in the housing sector.
Who can draw up a social tenancy agreement?
Preferential categories of citizens who receive priority rights to settlement include:
- disabled people of groups I and II;
- persons who became disabled as a result of eliminating the consequences of the Chernobyl accident;
- veterans of the Second World War and other military operations;
- persons who lost their housing as a result of natural disasters;
- citizens who need special living conditions for health reasons (the list of diseases is given in Article 51 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation);
- military personnel injured during their service.
This list is approved at the federal level. In addition, the following are entitled to receive social housing:
- low-income and large families who do not have their own housing;
- persons living in dilapidated housing that cannot be repaired;
- orphans and minor citizens left without parental care.
Residential premises that are not suitable for their intended use may be transferred to non-residential use based on the results of the commission. Then citizens are also entitled to the allocation of municipal housing.
Accommodation is available on a first-come, first-served basis. However, the administration also has a separate preferential queue for people who agree to receive housing of a smaller area. The required meters are compensated by other advantages. For example, a newer house or a prestigious area.
Requirements for the size of the provided living space
As stated above, renting residential premises must meet all legal requirements prescribed in the legal norms of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation. In particular, special attention is paid to the square footage of the provided living space. If we turn to federal legislation, then regulatory legal acts establish the standard of living space under contracts when rent is concluded between the state and the employer. Thus, the Government Resolution No. 541 establishes the standard square footage for 1 person, which is equal to 18 square meters. meters.
However, it is worth remembering that although such a parameter exists, it can vary depending on the region where the citizen recognized as needing improved housing conditions lives. This is due to the fact that:
- All subjects of the Russian Federation have different incomes of citizens, which, in general, affects the well-being of the entire region. In other words, one cannot compare Moscow, as one of the most prosperous agglomerations in Russia, and Saratov, Penza and other provincial cities.
- Each region has a different housing stock, which is replenished with the construction of new comfortable houses at the expense of budget funds. But it is practically impossible to provide all citizens with housing according to the standard standard (18 meters), since this will cause an irreparable blow to the regional budget, which will lead the subject of the Russian Federation to financial bankruptcy.
In addition, when improving housing conditions under contracts that imply social rent, two parameters are taken into account:
- provision rate;
- accounting norm.
Regarding the issue of the norm of provision, the definition of this definition is given in Art. 50 Housing Code of the Russian Federation. In accordance with the legal acts, the provision norm is the minimum size of the usable area of a residential premises, which forms the basis for calculating the total area of housing if a rental agreement is concluded between the subjects of legal relations.
The provision rate is fixed by decrees of local authorities, depending on the conditions that we indicated above. However, there is a clearer gradation of the norm for the provision of living space, which is established by federal and regional legislation:
- Residential premises with a total area of 33 meters are rented if a citizen of the Russian Federation living alone is recognized as needing improved living conditions.
- If a family of 2 people needs to improve their living conditions, then in this case housing should be provided with an area of 42 square meters. meters (total area).
- If the lease is concluded by a family with 3 or more members, then each subject must have at least 18 sq. meters.
In some cases, citizens of the Russian Federation may be provided with additional living space, the size of which will not exceed 10 square meters. meters. In this case, the procedure and conditions are additionally specified in federal or regional legislation. Situations are possible when needy persons who have entered into a lease are allocated an apartment whose size is 10% less than the required area. This only happens in situations where the housing stock of a particular constituent entity of the Russian Federation does not have housing that meets the requirements.
The definition of the accounting norm is also spelled out in Art. 50 Housing Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, the accounting norm refers to the minimum size of living space per citizen, which forms the basis for establishing the fact that the parties to the agreement have enough living space.
The accounting norm has a direct connection with the provision norm, since the calculation of the provision of housing to needy categories of citizens, as well as the procedure for registering individuals with housing, depends on their proportion.
The competence to establish accounting standards belongs to local self-government bodies. But when fixing it, the condition is taken into account that the accounting norm should not exceed the provision norm. Otherwise, it turns out to be a vicious circle, from which it will be simply impossible to get out. The accounting standard may constantly change depending on current conditions. The fact that the region is provided with housing for social purposes, the pace of construction of new residential buildings to replenish the specialized fund, as well as the technical condition of the houses within which the living space is allocated are taken into account.
Advantages and disadvantages
Let's look at the positive aspects that social housing has for citizens:
- Possibility to install water meters.
- Carrying out major repairs at the expense of the state.
Almost no shortcomings were noticed. You just need to remember that the use of such housing is associated not only with rights and benefits, but also with certain responsibilities. This applies to the payment of utilities and relevant taxes.
Some costs may be associated with repair procedures and replacement of broken equipment.
Refusal to provide housing under a social tenancy agreement
It is possible for government bodies to refuse to register citizens as needy. This possibility is regulated by Art. 54 Housing Code of the Russian Federation. This legal norm specifies an exhaustive list of grounds for the exercise of such powers, in particular:
- If the employer does not provide documents to the authorized body, which are a prerequisite for registration.
- If the subject of legal relations has provided documents, but they do not confirm the status that would allow the person to be registered as a person in need.
- If the period specified in Art. 53 Housing Code of the Russian Federation. In particular, we are talking about a 5-year period, which begins from the moment the employer commits an offense, which is the determinant of the imposition of certain sanctions on the subject of the relationship.
The decision to refuse registration to a citizen is made only by a competent person. The resolution must necessarily contain reasoned reasons that served as the reason for such a decision. The document is sent to the applicant within three working days after its acceptance in writing, certified by the signatures of an authorized representative of the government of the Russian Federation. The employer, if he does not agree with the verdict, has the legislative opportunity to challenge such a decision in court.