You can leave your vehicles in strictly designated places. These places must be marked with a special sign or have special road markings.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem , contact a consultant:
+7 (499) 938-81-90 (Moscow)
+7 (812) 467-32-77 (Saint Petersburg)
8 (800) 301-79-36 (Regions)
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FREE !
What is this
A parking lot is a place to park a vehicle.
It is specially equipped for the safe location of the vehicle. In addition, parking can be done in specially designated areas.
You can park:
- in specially designated places marked with the appropriate sign;
- at the edge of the road, that is, parallel to the roadway or with access to the sidewalk, if there is a special road
- on the side of the road.
The difference between a parking lot and a parking space is that it is part of the road. You cannot park on the lawn or in the green zone, or in spaces for the disabled, if the vehicle does not have a special badge.
A parking space is a part of a building or structure, the boundaries of which are clearly defined and fixed. This place is intended for parking vehicles.
What is regulated
The rules for marking parking spaces are regulated by the National Standard of the Russian Federation GOST R 52289-2004 “Technical means of organizing traffic. Rules for the use of road signs, markings, traffic lights, road barriers and guide devices ,” which was approved on December 15, 2004 , and which is numbered No. 120-ST .
The main law that regulates the movement of all vehicles is the Federal Law of December 10, 1995 No. 196-FZ “On Road Safety” .
Why you need to follow marking rules
Every driver, regardless of vehicle category, is required to follow the markings in the parking area. It is allowed to park only in places where there are special road markings and where appropriate signs are present.
You must park the car exactly as shown on the information signs and stands.
Failure to comply with these rules may result in the driver being subject to administrative liability in the form of a fine.
Basics
The rules for marking a parking zone should be taken into account by both those who equip themselves with a personal parking space and the owners of large parking lots.
There are 2 basic rules:
- it is necessary to take into account the dimensions of the vehicle for which the parking is equipped;
- When the doors are open, a person must pass between vehicles.
According to GOST
On road surfaces you can use:
- arrows;
- inscriptions;
- lines;
- other signs.
Parking must also be marked with special signs.
The following types of markings are distinguished:
- horizontal;
- vertical.
Minor nuances
But you should rely not only on GOST standards when applying markings in the parking zone. It is worth focusing on the secondary rules.
This:
- some car owners have great difficulty parking;
- the lines should be moderately thick and clearly visible even in the dark;
It is advisable to use paint that has reflective particles.
- it is necessary to minimize the presence of various elements in the parking area that reduce space;
- Don’t forget about decorative elements and compliance with green space standards.
Width
The minimum width of a parking space should not be less than 2.3 m. If the space is intended for a disabled person, the width increases to 3.5 m per parking space. These dimensions are necessary to calculate the optimal area of the parking space.
Do you know if you can stop your car in front of a pedestrian crossing? See the article: parking in front of a pedestrian crossing. What paid parking is is written here.
General technical requirements
4.1 Marking can be made using various materials (paint, thermoplastic, cold plastic, polymer tapes, piece forms, reflectors, etc.) that meet the technical requirements below.
4.2 When drawing marking lines, their deviation from the design position should not exceed 5 cm.
The deviation of the dimensions of marking lines from those established by this standard should not exceed:
1 cm - along the width of the line;
5 cm - along the length of strokes and breaks.
4.3 The markings should not protrude above the roadway by more than 6 mm.
Retroreflectors (reflectors) used for optical orientation of the driver in combination with horizontal marking lines or independently should not rise more than 15 mm above the roadway.
4.4 The curing time of markings made from plastic marking materials after their application to the coating should not exceed 20 minutes, and drying of paints and varnishes to degree 3 according to GOST 19007 - 30 minutes, at a temperature of (20 ± 5) °C and relative humidity (65 ± 10) %.
4.5 The adhesion coefficient of horizontal markings during any period of operation should not differ by more than 25% from the adhesion coefficient of the coating on which this marking is applied.
4.6 Markings made with thermoplastic, cold plastic or other similar materials must have a functional durability of at least one year, and with paint and varnish materials - at least 6 months.
The functional durability of the marking is determined by the period during which the marking meets the requirements of this standard, and on any control section with a length of 50 m, the destruction of markings made of thermoplastic or other durable materials, except paints, does not exceed 25%, and the wear of markings made of paint does not exceed 50% of it area.
4.7 When applying markings according to the changed scheme, there should be no visible traces of the old markings.
4.8 Plastic marking materials must be resistant to the static effects of water at a temperature of (20 ± 2) °C and a saturated sodium chloride solution at a temperature of (0 ± 2) °C for at least 72 hours, paint materials - for at least 48 hours.
4.9 Color coordinates x and y of road markings applied to the pavement of roads, determined in the 1931 CIE colorimetric system with light source D and measurement geometry 45°/0° (see Figure B.1), must correspond to those specified in Appendix B (Table B.1).
4.10 Marking of highways, except for roads of the 4th category, must be carried out using reflective materials.
On sections of roads that do not have artificial lighting, white marking stripes 2.1 - 2.3 must be made of retroreflective material (except for bollards with internal lighting), and fencing and guide devices marked with markings 2.4 - 2.6 must have reflective elements.
Types of retroreflective elements, their sizes and installation rules must comply with the requirements of GOST R 50970 and GOST R 50971.
4.11 Retroreflective elements used in conjunction with markings 2.4 - 2.6 or without markings on galvanized surfaces of road fences, located to the right of the roadway in the direction of travel, must be red, and on the left - white or yellow.
4.12 The brightness coefficient of road markings must correspond to the values specified in Appendix B (Table B.2), taking into account the characteristics of the road.
4.13 The retroreflectivity coefficient of road markings must correspond to the values specified in Appendix B (Tables B.3, B.4), taking into account the characteristics of the road.
4.14 The requirements for the brightness coefficient and retroreflectivity coefficient of road markings specified in paragraphs 4.12 and 4.13 must be maintained:
- for markings made of paints and varnishes - within the first 3 months. operation;
- for markings made of thermoplastic, cold plastic and other durable materials - within the first 6 months. operation.
During further use of road markings, it is allowed to reduce the values of the brightness and retroreflectivity coefficients given in Appendix B by no more than 25%.
Application in the parking lot
The parking area must be marked not only with special road signs, but also have special markings on the road surface.
The application of special markings is carried out by organizations that have the appropriate permission to carry out such activities. The markings are applied in accordance with what kind of parking will be equipped and for what vehicles.
How to apply markings so that it is correct? Application must be carried out in accordance with the regulations.
This:
1. it is necessary to make more correct calculations depending on where and what kind of transport will be parked; 2. the width of the passage space cannot be less than 6 m ; 3. for markings for disabled people, you need to use stencils and yellow paint; 4. The material for marking must be carefully selected, and it must be applied according to the following rules:
- deviation from the planned lines cannot be more than 5 cm ;
- if there was already a marking in this place before, then when applying a new one, the old marking line should not be visible;
- It is advisable to carry out all application work in warm and dry weather. Recommended air temperature + 20°;
- each line must be at least 10 cm wide;
- You can use material that contains reflective particles only in rooms where there is little daylight;
- if the coating was done with paint and varnish, then it needs to be renewed every six months ;
- if reflective materials should be used near important objects in the parking lot (fire hydrants and crowns, fire extinguishers, etc.).
The owner of the parking area must adhere to all these rules.
Marking of parking spaces sizes according to GOST
This set of rules was developed in accordance with federal laws dated December 30, 2009 N 384-FZ “Technical Regulations on the Safety of Buildings and Structures” [1], dated November 23, 2009 N 261-FZ “On Energy Saving and Improving Energy Efficiency and on amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation" [2], dated July 22, 2008 N 123-FZ "Technical regulations on fire safety requirements" [3].
The work was carried out by the team of authors of JSC "TsNIIPromzdanii" (Doctor of Technical Sciences V.V. Granev, Candidate of Architectural Sciences D.K. Leikina, Candidate of Technical Sciences T.E. Storozhenko).
Change No. 1 was prepared by the team of authors: JSC "TsNIIPromzdanii" (Doctor of Technical Sciences V.V. Granev
, Ph.D.
architecture D.K. Leikin
, Ph.D.
tech. Sciences T.E. Storozhenko
,
A.E. Ivanov
).
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
1.1 This set of rules applies to the design of buildings, structures, sites and premises intended for parking (storage) of cars, minibuses and other motor vehicles.
1.2 This set of rules does not apply to garages intended for routine repair (TR) and maintenance (MOT) of vehicles, as well as parking for vehicles used for the transportation of explosive, toxic and radioactive substances, parking for fire, medical, and emergency services vehicles.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
This set of rules uses regulatory references to the following documents:
GOST 12.1.005-88 System of occupational safety standards. General sanitary and hygienic requirements for the air in the working area
GOST 14254-2015 (IEC 60529:2013) Degrees of protection provided by enclosures (IP Code)
GOST 29322-2014 (IEC 60038:2009) Standard voltages
GOST R 50571.3-2009 (IEC 60364-4-41:2005) Low-voltage electrical installations. Part 4-41. Security requirements. Protection against electric shock
GOST R 51631-2008 (EN 81-70:2003) Passenger elevators. Technical accessibility requirements, including accessibility for people with disabilities and other low-mobility groups
GOST R 52290-2004 Technical means of organizing road traffic. Road signs. General technical requirements
GOST R 52382-2010 (EN 81-72:2003) Passenger elevators. Elevators for firefighters
GOST R 53296-2009 Installation of elevators for firefighters in buildings and structures. Fire safety requirements
GOST R 53771-2010 (ISO 4190-2:2001) Freight elevators. Main parameters and dimensions
GOST R ISO 6469-1-2016 Electric road transport. Safety requirements. Part 1. Onboard battery energy storage systems
GOST R IEC 61851-1-2013 Conductive charging system for electric vehicles. Part 1. General requirements
GOST R IEC 62196-1-2013 Plugs, sockets, connectors and bushings for vehicles. Conductive charging for electric vehicles. Part 1. General requirements
GOST R IEC 62196-2-2013 Plugs, sockets, connectors and bushings for vehicles. Conductive charging for electric vehicles. Part 2: Dimensional compatibility and interchangeability requirements for AC power pin connectors and accessories
SP 1.13130.2009 Fire protection systems. Evacuation routes and exits (with change N 1)
In this set of rules the following terms with corresponding definitions are used:
3.1 outer radius:
The smallest radius of curvature (curve) along the edge of the roadway (on the right side of the driver), ensuring unhindered passage of the turn.
3.2 Entry and exit lanes:
Dimensions of passage within the carriageway of a vehicle's lane.
3.3 garage:
Building and structure, premises for parking (storage) repair and maintenance of cars, motorcycles and other vehicles; It can be either part of a residential building (built-in and attached garages) or a separate building.
3.3a chargers (stations, speakers) for vehicles with electric motors:
Mains power supply equipment that performs the necessary functions to charge the battery of an electric vehicle.
3.3b wheel breakers:
Fencing devices fixed to the surface of the roadway or floor, designed to limit the movement of vehicle wheels.
3.3a, 3.3b. (Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 1).
3.4 mechanized parking:
A parking lot in which vehicles are transported to storage areas (cells) using mechanized devices (without the participation of drivers).
3.4a multi-row car parking:
Parking in which cars are parked one after another and the second car can leave only after the one in front has left.
3.4b charging power for electric vehicles:
Type 1 - 240 V 16 A;
Type 2 - 240 V 32 A;
Type 3 - up to 690 V, three-phase alternating current, 63 A, (22, 43 kW), - fast charging with alternating current;
Type 4 - up to 600 V and up to 400 A, (240 kW) - fast charging with direct current.
3.4a, 3.4b. (Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 1).
3.5 closed surface parking lot:
Car parking with external enclosing structures.
3.6 open ground car parking:
A parking lot in which at least 50% of the external surface area of the external fences on each tier (floor) consists of openings, the rest is parapets.
3.7 bunded parking lot:
Above-ground or in-depth car parking with more than 50% of the outer enclosing structures lined with soil and protruding above ground level.
Placement of places for transport
It is beneficial for the owner of the parking area to accommodate as many vehicles as possible, especially if parking is paid.
Therefore, when drawing up a parking plan, you need to choose the most convenient and spacious arrangement of spaces.
There are several nuances to consider:
- if the vehicles stand perpendicular to the road, this will not save space, but will allow any vehicle to drive on the roadway. This type of parking is optimal if there are small pockets or in the yard;
- if vehicles are parked parallel to the roadway, this will also not save space;
Such parking is optimal only in those places where it is possible to go deeper from the roadway by more than 2 meters . So you can park your car along the road, but not near a public transport stop.
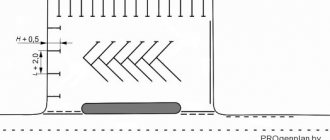
- Herringbone parking allows you to park cars at an angle of 45° - 60° to each other and place the largest number of vehicles in the parking lot.
When choosing a car placement option, do not forget that there are strictly established dimensions of a parking space for a passenger car.
Marking parking spaces: rules and GOST
The parking area differs from the classic parking area in that the latter zone is part of the road. Therefore, based on the operational characteristics of passenger cars, the principle of their placement in specially designated areas comes down to 3 methods:
- parallel to the direction of movement;
- perpendicular to the main axis of the road;
- “herringbone” (at a specific angle to the traffic).
Each version has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it is always worth remembering that the size of the space is limited to 2.5 m: this format allows you to freely open the car door without touching the vehicle standing nearby.
This method of installing vehicles involves placing them close to the sidewalk along the roadway. The main disadvantage of this configuration is the problems when placing a significant number of cars in a certain area. But this type of arrangement is relevant for narrow streets: with a parallel layout and a gap of 1 m, two cars will occupy exactly 10.8 m. Otherwise, a passenger car parked parallel to the sidewalk runs the risk of easily blocking neighboring cars and beginners will not be able to leave.
Here the vehicle should be positioned at an angle of 90° to the road. This type allows you to squeeze the largest number of cars into a limited space. But not all motorists can easily and correctly position the body this way, because with a perpendicular layout, two cars have 9.8 m. Statistics show that it is when leaving such parking lots that a huge number of minor accidents occur (in heavy traffic), if you do not timely appropriate maneuver.
Naturally, any road markings are regulated by separate rules and recommendations. For example, SNiP 21-02-99 regulates the optimal width of the passage (6 m). The parking space should preferably have a width of at least 230 cm, and spaces for the disabled - 350 cm. When organizing the markings, the material is also of great importance. The classic option is special paint, but our company offers marking in other ways. The lines must be clearly visible, so their recommended width is at least 10 cm. The choice of material for marking largely depends on the operating conditions of the parking lot. Paint is one of the most abrasion-prone materials. When using it, you will need to regularly update horizontal lines and parking space numbers . Plastic coatings, such as thermoplastic, are more durable. Application of axial markings in internal areas helps to reduce the number of accidents, organized traffic, and compliance with traffic rules. Axial traffic markings delimit oncoming flows, as well as flows in the same direction.
The growth of automobile traffic requires clear separation of vehicle lanes from their parking areas. Determining the area and designing parking lots based on assessments of local needs is carried out using various methods: 1. Based on the number of residents. The number of parking spaces in the business part of the city is assumed to be 0.5-1% of the total population of the city. 2. By the number of cars in the city. In the business part of the city, one parking lot is provided for every 5-8 passenger cars registered in the city, 3. According to traffic flows. One parking lot for 7-9% of cars annually entering the business part of the city. The parking area for one car is 20-25 m2.
Parking lots on the street 1. Parking lots and car stops with the long side along the sidewalk (Fig. 1 - 3 and 5). 2. Parking strips along the sidewalk for transverse or oblique parking of cars, depending on the width of the street (Fig. 4, 6 and 7). Cars in such parking lots should not interfere with the view of the streets at intersections, therefore the distance between the car parking strip at the intersection and the building line (if there are front gardens - to the building line of the transverse street) should be ≥ 6 m, preferably up to 10 m (Fig. 1 - 4).
Peculiarities
Depending on the type of vehicle, the category of the driver and the type of parking, there are some rules for marking parking spaces that need to be taken into account.
For invalids
Disabled persons have the right to an improved parking space. Larger parking spaces are provided for this category of drivers. In addition, such places should be located as close as possible to the entrance to the institution.
The length of the parking space depends on the type of vehicle it is driving.
But, as a rule, it is standard - 6 m. And the width will be slightly larger than for healthy drivers - at least 3.5 m. This is due to the fact that a disabled person must fully open the doors of the car in order to perform any maneuvers.
10% of the total number of parking spaces at a given site must be allocated for people with disabilities
They must be marked with a special sign. A sample parking lot marking for the disabled according to GOST is indicated by a special sign in the form of a wheelchair.
On a semicircular
What does this parking method mean? With this method, one parking space must be at least 18 square meters. m area, while the length is 5 m . Such dimensions are relevant if cars will be parked at 45 degrees 1 seat .
If you make markings for parking cars at an angle of 60° , then slightly less space will be required.
One car will occupy about 16 square meters. m , while the length of one parking space must be at least 5.4 m.
Paid
Regardless of whether parking is paid or free, the minimum size of one parking space must be observed. In paid parking, spaces for vehicles must be located in accordance with GOST.
Do you want to understand how to park correctly for a person with disabilities? Read about this in the article: parking for disabled people. Don't know how to pay a parking fine? Read here.
All parking rules are collected here.
Dimensions of parking spaces in open parking lots
The size of a parking space for 1 car in a parking lot is easy to calculate if you know that the following parameters are the minimum:
- The length of the parking space is 5.3 meters.
- The width of the parking lot is 2.5 meters
Moreover, the width of the marking, which is 10 cm on each side, is not taken into account. That is, a parking space must have a minimum area of 13.25 square meters.
It is important that the standard length of a car is considered to be 4.4 meters, width - 1.8 meters.
At the discretion of the owners of the parking area, the size of the parking space may be increased. For example, parallel parking will be most comfortable if the length of one parking space is 8.8 meters, that is, equal to the length of 2 standard cars. In this case, the comfortable size of a parking space is considered to be the width of a standard car plus 1 meter, that is, 2.8 meters. This width of the parking space allows you to ensure the safety of the driver or his passenger getting out of the car.
If we talk about herringbone parking, then more space is needed. According to the standard, one such parking space must have an area of 18 square meters.
Parking spaces intended for parking cars for disabled people reach their maximum dimensions. Their width reaches 3.6 meters, and their length is 6.2 meters.
The law allows deviations from the specified dimensions, but such a deviation must be within 5 cm. Such dimensions are primarily due to fire safety measures. In addition, they help reduce the likelihood of accidents in parking areas.
What are the standards for parking lot markings?
Violation
Each driver must adhere to the markings provided in the parking space. Traffic regulations prohibit drivers from crossing parking lines.
If this happens and the fact is noted by a traffic police officer, the following sanctions may be applied to the driver:
- warning if such an offense is committed for the first time ;
- a fine of 500 rubles if the driver has already been noticed for such an offense.
If the driver neglects the markings that indicate parking spaces for disabled people, the fine will be much higher - 5,000 rubles .
Even if there are no free parking spaces for healthy people in the parking lot, you cannot leave a vehicle in a space intended for a disabled person. It is also prohibited to organize parking without markings.