Good afternoon, dear reader.
This article will discuss the differences between the concepts of stopping and parking , as well as the traffic rules related to stopping and parking. In addition, possible fines for improper parking of vehicles will be considered.
- Parallel to the edge of the roadway.
Differences between stopping and parking
First of all, let's look at the difference between the concepts of stopping and parking. This will allow us to consider the rules for each of the maneuvers separately in the future.
To put it as simply as possible, these concepts differ in their duration. Stopping is a short maneuver, and parking is a long maneuver. However, these are not all their differences, so let’s turn to paragraph 1.2 of the traffic rules:
“ Stop ” is a deliberate stop in the movement of a vehicle for up to 5 minutes, as well as for longer if this is necessary for boarding or disembarking passengers or loading or unloading the vehicle.
“ Parking ” is the intentional interruption of the movement of a vehicle for a period of more than 5 minutes for reasons not related to the embarkation or disembarkation of passengers or the loading or unloading of the vehicle.
First of all, both stopping and parking are a deliberate cessation of movement, that is, they are carried out at the request of the driver. They should not be confused with stopping traffic in accordance with traffic regulations (for example, to let pedestrians pass at a crossing) and with a forced stop:
What is a forced stop?
Intentionally stopping the movement of a vehicle is a stop in two cases:
- If the car has not moved for less than 5 minutes. It does not matter what the driver and passengers were doing at that time.
- If the vehicle has stopped to pick up or unload passengers or to load or unload cargo. In this case, the duration of the maneuver does not matter.
All other intentional traffic stops (lasting 5 minutes or more and not related to boarding passengers or unloading cargo) are considered parking .
| Duration less than 5 minutes | Duration more than 5 minutes | |
| Passengers are boarding/disembarking or cargo is loading/unloading | stop | stop |
| There is no boarding/disembarking of passengers or loading/unloading of cargo | stop | parking |
Once again about the duration of the maneuver. 4 minutes 59 seconds - stop. 5 minutes 0 seconds - parking.
Once again about loading/unloading cargo. If the driver goes out to smoke for 10 minutes, then there is a parking lot. If the driver went out to smoke for 10 minutes and took a stool (load) from the trunk for convenience, then a stop occurs.
Equipment of parking spaces during the construction of an apartment building. Question answer
Question: Hello! Help us understand the situation: several more high-rise buildings were built in the courtyard of a multi-story building, and it turned out that there are no parking spaces in these new buildings. There are wide sidewalks, space for a children's playground, lawns, but no parking. In this regard, until the house is completed, please tell me where to go and what specifically to write in the application (possibly a collective one). There must be some rules that oblige the developer to provide a certain number of parking spaces for an apartment building. Already now everything in the yard is full of cars, but what will happen when the house is handed over and sales of apartments begin. Where to make noise in this case?
Based on the requirements of the current legislation, when designing apartment buildings, the developer, in order to obtain a construction permit, is required to include parking spaces in the project, the number and order of placement of which is established by law.
Thus, in accordance with SanPiN 2.1.2.2645-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for living conditions in residential buildings and premises”:
- The land plot allocated for the construction of a residential building must provide for the possibility of organizing a local area with clear functional zoning and placement of recreation areas, playgrounds, sports areas, utility areas, guest parking for vehicles, green spaces (clause 2.3);
- There should be no transit traffic on the internal driveways of the local area. It is necessary to provide access to the waste disposal sites for special vehicles (clause 2.5);
- On land plots, entrances and passages to each building must be provided. Places for parking or garages for cars must comply with the hygienic requirements for sanitary protection zones and the sanitary classification of enterprises, structures and other objects (clause 2.8).
Based on the level of motorization, the number of cars for the planned number of residents is calculated.
According to SP 42.133330.2011 “Urban planning. Planning and development of urban and rural settlements. The updated version of SNiP 2.07.01-89" transport provision is 350 cars per 1000 people (in practice this figure is higher). In fact, the provided spaces for cars will be 25 percent of the number of cars established for a given number of residents.
Local authorities may establish the number of parking spaces per apartment based on its area. For example, for an apartment with an area of up to 30 sq.m. one place is allowed, over 100 - two, and from 30 to 100 - 1.5. At least 10 percent of the designated number of seats must be reserved for motorists with disabilities.
When arranging parking spaces, the requirements for the distance from car storage areas to houses must be taken into account. The minimum distance cannot be less than 10 meters. Further, this gap is determined based on the number of spaces for cars and the presence of windows in buildings:
- parking with spaces from 10 to 50 should be located at a distance of 10 meters from buildings without windows and 15 meters from buildings with windows;
- parking for 50-100 cars at a distance of 15 meters from buildings without windows and 25 meters from buildings with windows;
- parking for 100-300 cars at a distance of 25 meters from buildings without windows and 35 meters from buildings with windows;
- parking lots with space for up to 10 cars should be located at a distance of at least 25 meters from children's and educational institutions, playgrounds, sports and recreation;
- parking lots with a large number of cars - at a distance of at least 50 meters.
The indicated distances are designed to ensure comfort for people living in the house, as well as basic fire safety requirements. Open parking for more than 50 cars is not allowed in the area near houses. For a larger number of cars, you need to organize covered parking or garage spaces. When arranging any parking lots, other elements of landscaping near the house should not be affected.
Thus, if the equipment of parking spaces during the development of the apartment buildings you specified does not meet the above requirements, you have the right to submit an application to the prosecutor’s office of your locality.
Where can I park the vehicle?
On the right side of the road
Let's consider clause 12.1 of the traffic rules:
12.1. Stopping and parking of vehicles is permitted on the right side of the road on the side of the road, and in its absence - on the roadway at its edge and in the cases established by paragraph 12.2 of the Rules - on the sidewalk.
1. If there is a shoulder to the right of the roadway, then cars are allowed to be parked only on the side of the road . If the side of the road is occupied by other cars or something else, then parking cars on the roadway is not allowed.
2. Parking cars on the roadway is only possible if there is no shoulder. In this case, the car must be parked at the edge of the roadway, that is, at the curb.
A huge number of cars are parked in populated areas, and in order to park next to the curb you will have to park in reverse. A driver who does not know how to parallel park and leaves the car a meter from the edge of the roadway is a violator.
3. In exceptional cases, you can park cars on the sidewalk . Below this situation will be discussed in more detail.
On the left side of the road
Let's consider the second part of paragraph 12.1:
On the left side of the road, stopping and parking are permitted in populated areas on roads with one lane for each direction without tram tracks in the middle and on one-way roads (trucks with a permissible maximum weight of more than 3.5 tons are allowed on the left side of one-way roads only stopping for loading or unloading).
You can stop on the left side of the road only in populated areas and only in the following cases:
1. On two-lane roads (one lane in each direction) without tram tracks in the middle. If tram tracks are located on the left or right, then they do not prohibit stopping on the left side of the road.
Note. In practice, a continuous marking line may be placed on the road, which will not allow stopping or parking on the left side of the road.
2. On one-way roads, parking on the left side is also allowed. In this case, the presence or absence of tram tracks does not matter at all.
Trucks heavier than 3.5 tonnes (category C) may stop on the left side of one-way roads only to load or unload. Those. On a one-way road, a truck cannot be on the left side of the road:
- perform parking;
- stop for less than 5 minutes (without loading);
- stop to pick up or drop off passengers.
However, a truck driver can park on the right side of a one-way road.
How to park the vehicle?
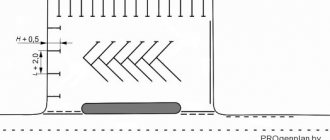
Parallel to the edge of the roadway
The answer to the question of how to park a vehicle is given in paragraph 12.2 of the traffic rules:
12.2. It is allowed to park the vehicle in one row parallel to the edge of the roadway. Two-wheeled vehicles without a side trailer may be parked in two rows.
Thus, vehicles should be parked parallel to the edge of the roadway and at the same time as close to this very edge as possible.
If the driver does not know how to parallel park and tries to park in front at a short distance, then with a high degree of probability he will park the car at an angle. Such parking is a violation of traffic rules, and there is a fine for it, which will be discussed below.
It is also worth considering the rules for parking two-wheeled vehicles (motorcycles, scooters, mopeds, bicycles). They are allowed to be placed in 2 rows, i.e. one of the motorcycles may not be standing at the edge of the roadway.
At an angle to the edge of the roadway
A separate paragraph of clause 12.2 regulates the placement of vehicles at an angle:
The combination of sign 6.4 with one of the plates 8.6.4 - 8.6.9, as well as road marking lines, allows the vehicle to be positioned at an angle to the edge of the roadway if the configuration (local widening) of the roadway allows such an arrangement.
Parking vehicles at an angle to the roadway is permitted only in those places where there is a local widening of the roadway, and only if this is indicated simultaneously by road signs and road markings.
On Pavement
The last paragraph of clause 12.2 is devoted to stopping and parking vehicles on sidewalks:
Parking on the edge of the sidewalk bordering the roadway is permitted only for cars, motorcycles, mopeds and bicycles in places marked with sign 6.4 with one of the signs 8.4.7, 8.6.2, 8.6.3, 8.6.6 - 8.6.9.
We are talking about the following signs and plates:
6.4 "Parking area."
8.4.1 — 8.4.8 "Type of vehicle." Indicate the type of vehicle to which the sign applies.
8.6.1 — 8.6.9 “Method of parking a vehicle.” 8.6.1 indicates that all vehicles must be parked on the roadway along the sidewalk; 8.6.2 - 8.6.9 indicate the method of parking cars and motorcycles in a sidewalk parking lot.
Please note that cars, motorcycles, mopeds and bicycles are allowed And only if there are appropriate signs.
In addition, vehicles must be parked exactly as shown on the sign:
Please note that only 6 out of 9 signs show a car parked on the sidewalk. 3 signs indicate stopping near the sidewalk. However, only the first plate applies to all vehicles.
It is prohibited to park any trucks on the sidewalk , not only category C, but also category B. Moreover, all trucks must stop only parallel to the edge of the roadway, and if there is one of the signs 8.6.2 - 8.6.9 on the road, they cannot stop at all.
It is also a violation of the rules to stop a car or motorcycle on the sidewalk in the absence of an appropriate sign.
Let's move on to fines for violating stopping and parking rules.
Spark in the gas tank
Such conflicts between motorists and parking lot guards have long been common. Everyone knows that parking lot owners never forget to take money from a citizen, but at the same time they try not to answer for the car and everything that happens to it. In a dispute between the owner of the damaged car and the parking lot security guards, the Supreme Court sided with the car owner.
The dispute, which was reviewed by the Supreme Court, began in the city of Kaliningrad. There, in a guarded parking lot that belonged to a certain company, a car burned down at night. The car was not new, but it was still a pity. The police arrived at the scene of the fire. A criminal case was opened, as the investigator established for sure that the car did not catch fire on its own, it was arson. The owner of the car was recognized as a victim in a criminal case. But whoever did it was never found.
The injured citizen outlined her claims in a lawsuit. The defendant is the company that owns the parking lot. The owner of the car felt that the parking lot did not provide proper storage of the car. And if so, then let him pay for it. The company did not appear in court, and the district court’s decision was in absentia.
The court agreed with the owner of the burnt car. The company already filed a complaint with the regional court, and the district decision there was canceled, considering that the guards were not at fault.
The plaintiff reached the Supreme Court, which analyzed the case and decided that the injured car owner was right.
This is how the Supreme Court reasoned. Considering the case, the district judge considered it proven that actions were taken between the citizen and the company to hand over and accept the car for storage. That is, a storage agreement has been concluded. The local court also said that the defendant company, which actually accepted the car for safekeeping, did not ensure its normal maintenance and did not control the quality of security of the facility. In overturning this decision, the regional court referred to the fact that there was no evidence of the conclusion of an agreement for the storage of the car between the parties. And in general, the regional court said, the place where the car was parked was not a parking lot at all, but a parking lot.
The Supreme Court did not agree with such arguments and stated the following.
According to Article 886 of the Civil Code, under a storage agreement, one party (the custodian) undertakes to preserve the thing transferred to it by the other party, who in legal language is called the bailor, and to return it in the form in which it was taken. According to the next, Article 887 of the Civil Code, such an agreement must be in writing. The simple written form of such an agreement is considered to be complied with if the taking of the thing for storage is certified by a receipt, a receipt, a token, a number - everything that certifies the acceptance of the thing for storage. The Supreme Court also emphasized that failure to comply with the simple written form of the storage agreement does not deprive the parties of the right to refer to witnesses.
Article 162 of the Civil Code states that even without a written form of the transaction, in this case, other evidence can be cited in the dispute.
In other words, failure to comply with a simple written form does not invalidate the storage agreement, but only limits the parties’ means of proof.
And now about the terms that are of primary importance in this kind of conflict. So, in this case, is the place where the car is stored - a parking lot or a parking lot? According to the Town Planning Code, parking is considered a specially designated place, which can be both part of the road and adjacent to it. Or it may be part of the sidewalk or curb. Parking is intended for organizing parking of vehicles for money or for nothing. The latter is decided by the owner of the building or land. The same definition of parking is in the Traffic Rules.
The conclusion from all that has been said is this: parking is an element of improvement of roads, buildings, sidewalks and other things. It plays a supporting role in organizing parking for vehicles.
Well, the operation of parking lots is regulated by the Rules for the provision of parking services. They were approved by the government on November 17, 2001 (N 795). It says that a parking lot is a building, part of it, or a special area for storing vehicles. According to the rules for the provision of parking lot services (clause 32), in the event of loss, theft, damage or “compromise of completeness” of a car while being stored in a parking lot, the owner of the parking lot is obliged to compensate for the damage. If, due to damage, the quality of the car has changed so much that it cannot be used, the driver can demand that the custodians reimburse the full cost of the car.
The Supreme Court especially emphasized that if the courts find out whether the place where the car was damaged was a parking lot or a parking lot, then they must proceed from specific circumstances that indicate the purpose of the site. In particular: is this facility independent, is there equipment, fences, how is the entry and exit of cars arranged?
According to the Rules for the provision of parking services, if the service provides for the car to arrive and leave regularly, then a permanent pass is issued upon conclusion of the contract. It records the make of the car, its license plate number, parking space, and the expiration date of the pass. If the car was delivered, as they say, one-time (for a period of more than a day), then the conclusion of the contract will be an issued receipt or receipt with the car number. The responsibility for preparing documents and accounting for money received from clients lies with the service provider.
In our case, the fact that the burnt car was parked on the company’s premises and that the owner put it there is a proven fact that neither party disputed.
From the case materials it is clear that the parking area where the car burned down is isolated. There is a fence, security, a checkpoint, and an entrance. It is clear from the company’s agreement with the city that it rented the land specifically for the parking lot. And the operation of a parking lot is one of the main activities of the company. The car owner, judging by the documents, paid the company 1,800 rubles monthly. But the receipts, which were also a parking pass, burned along with the car. Fighting off the claims in court, the company argued that they accepted the car from the citizen not under storage conditions, but simply provided a parking space. According to the Supreme Court, the company did not confirm its words in any way. The businessmen did not have information on how much the woman paid them; there was no evidence that the businessmen accepted the car only under the conditions of parking and without conditions of storage.
The Supreme Court emphasized that the execution of the contract and cash and accounting accounting for payment for the service are the responsibility of the service provider. That is, at the company. And the loss of a civil receipt is not a basis for depriving a consumer of the rights provided for by law.
The Supreme Court also drew attention to the rules for the provision of parking services, which the company brought to court. These rules were signed by its director. And it says that the parking lot does not bear any responsibility for the loss or damage of cars. The Judicial Collegium for Civil Cases responded to this - the appeal ignored that there are Rules for the provision of parking services, which were approved by the government of the country. And it says that the contractor is responsible for the storage of vehicles.
According to the law, a professional custodian, such as a parking lot, is exempt from compensation for damage only if he proves that the damage was caused by “force majeure circumstances” or if the damage occurred due to “properties of the thing that he could not and should not know about.” . Arson does not apply to such cases.
So the Supreme Court overturned the decision that the company was not guilty.