March 22, 2019
Adviсe
The law provides penalties for an owner who fails to take care of a pet or deliberately fails to fulfill his or her duties. How to get compensation for damage to health or property caused by a dog, and in what case will the victim receive nothing?
A person must be responsible for his property and maintain it so that no harm is caused to others. Otherwise, he will have to pay damages. The same applies to animals (Article 137 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). If a dog causes harm, its owner will be held liable (Articles 15, 137, 209, 210, 393, 1064 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
However, this rule does not always work. Thus, the Arkhangelsk Regional Court indicated in November last year that, even if a dog bites a person, its owner is not obliged to compensate for the damage if the totality of the following facts is established1:
- the plaintiff, i.e. the one who went to court, does not live in the premises where he was bitten by the dog;
- he cannot visit this premises without the permission of the dog owner, since it does not belong to the plaintiff by right of ownership or other legal right (for example, it was not received under a social tenancy agreement);
- the plaintiff knew that there was a dog in the premises, nevertheless he entered there without warning, thereby provoking its attack; however, he did not prove that he was bitten elsewhere;
- The owner of the dog claimed that it was tied, and the plaintiff did not deny this fact or prove that the animal was improperly kept.
It turns out that the issue of the relationship between the rights and responsibilities of dog owners is debatable.
What rules should pet owners follow?
A legal artifact called “Rules for keeping dogs and cats in cities and other populated areas of the RSFSR”2 is still in force. Courts continue to refer to it when recovering damages caused by a dog to human health3. Dog owners in clauses 2 and 6 of these rules are obliged to:
- ensure the safety of others;
- prevent animals from polluting apartments, common areas in residential buildings, as well as courtyards, sidewalks, streets, etc.;
- ensure silence in residential areas;
- do not allow animals into playgrounds, shops, canteens and other similar public places;
- register and re-register dogs in a timely manner;
- do not allow animals to be kept in numbers greater than those established by the district and city executive committees. (This norm is actually “dead”. Where are these district executive committees now? However, it was “reanimated” in the new Law on the Responsible Treatment of Animals, which will be discussed below.);
- treat animals humanely: do not throw them away, do not leave food and water unattended, do not beat them, etc.;
- present animals at the request of veterinary specialists for examination, diagnostic studies, vaccinations and therapeutic and preventive treatments;
- immediately inform the veterinary institution and health authority that a dog or cat has bitten a person or other animal;
- immediately inform the veterinary institution about the sudden death of dogs or cats, about suspected rabies in animals and isolate them until specialists arrive;
- compensate for damage caused by animals.
Walking dangerous breeds
When walking dogs of a dangerous breed, the owner is obliged to ensure the safety of the people around him. Such dogs can only be in public places on a leash and muzzle. In fact, potentially dangerous animals are kept without restraints (muzzle, leash) only in the apartment.
Notice! Certain categories of people are prohibited from walking dangerous breed dogs. These include:
- Children under 18 years of age
- Persons who have not received a certificate of training in the rules of keeping dangerous breeds of dogs,
- Disabled people.
What responsibilities does the new law impose on dog owners?
Late last year, the Responsible Animal Welfare Act4 was adopted, most of which have already entered into force. Article 9 of this law establishes general requirements for keeping animals that each owner must fulfill:
- proper care;
- timely provision of veterinary care and implementation of mandatory preventive measures;
- preventing the appearance of unwanted offspring;
- provision of an animal at the request of officials of state supervisory authorities in the field of treatment of animals during inspections;
- management of biological waste in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation (the owner’s obligation to ensure that his dog does not pollute public places and urban areas was established in Soviet legislation, and responsibility is provided for by modern laws, for example the Code of Administrative Offenses of Moscow);
- If a person can no longer keep an animal, he is obliged to transfer it to a new owner or to a shelter.
For violation of these rules, dog owners are subject to liability, which will be discussed in detail below.
In addition to meeting the general requirements for keeping animals, the dog owner must:
- respect the rights of persons living in the same apartment building as him;
- while walking the dog, ensure the safety of citizens and animals, the safety of other people's property; exclude the possibility of uncontrolled movement of the animal when crossing the roadway, in elevators and common areas of apartment buildings, in courtyards, on children's and sports grounds; ensure the cleaning of animal waste products in public areas; do not walk the animal outside the places where it is permitted by the local government.
Animal registration rules
After purchasing a dog, the owner is required to register it. Based on the results of registration, the owner is issued a certificate and a token. Such documents are issued by licensed organizations or employees of a state veterinary clinic after vaccination against rabies. It is also possible to implant a chip containing information about the animal and its owner.
These requirements are not mandatory and there is no liability for failure to comply with them (unless there is an emergency). However, strict requirements are imposed on owners of dogs of dangerous breeds. Such dogs must be registered without fail. The owner of such a dog is required to attend a course on the maintenance of this breed before registering. Based on the results, the owner is given a certificate.
What prohibitions should a dog owner observe?
The Responsible Animal Welfare Act prohibits a dog owner from:
- use pets in business activities;
- keep a large number of animals, without taking into account their ability to provide them with conditions that comply with veterinary standards and sanitary and epidemiological rules (this norm has not yet been clarified, but it is possible that such clarifications will appear soon. In the Law on the Responsible Treatment of Animals (Article 19, will come into force on January 1, 2021) and the Law on Veterinary Medicine (Articles 8, 9, 19) for the bodies that will monitor the implementation of animal legislation, serious powers are laid down, but they have not yet been fully distributed);
- walking a potentially dangerous dog without a muzzle or leash. The exception is when the dog is in a fenced area belonging to its owner. The presence of a dog must be indicated by a warning sign at the entrance to the territory.
Where to walk
The bill clearly establishes the places where pets can be walked. For such a territory, special requirements are established:
- The area of the area intended for walking should not be less than 400 square meters. m,
- The dog walking area must be located at a sufficient distance from residential buildings (at least 45 m from public institutions and 20 m from residential and office buildings),
- Places intended for walking animals include parks, groves, and squares.
It is prohibited to walk animals in places where many people, especially children, gather: sports and children's playgrounds, near medical and educational institutions.
To organize dog walking areas in large cities, areas marked with special symbols are equipped. At such sites, special containers are installed to receive waste.
Watch the video. Pet Rules and Laws:
Which dogs can only be walked with a muzzle?
It will be possible to walk potentially dangerous dogs only with a muzzle and a leash.
These include dogs of certain breeds, their hybrids and other dogs that pose a danger to human life and health. They are listed in the List of Potentially Dangerous Dogs approved by the Government of the Russian Federation. Let us note that this list is included in the draft resolution, which was recently published by the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs. It is likely that the project will be accepted as presented or with minor changes. After this, the final list of dogs that will not be allowed to be walked without a muzzle will be known.
Owners of dangerous dogs, their neighbors, dog breeders, breeders, dog handlers, and owners of catering establishments with “restaurant” dogs and cats should study the draft resolution (there are already precedents with pug cafes and cat cafes). If a resolution is adopted, you must be prepared to comply with its requirements, which duplicate the dog walking rules discussed above, set out in the Responsible Treatment of Animals Act. Additionally, it will include a ban on setting animals on people. An exception will be cases of necessary defense, dog training by dog handlers and the use of service animals in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Traveling by transport
The Law on Keeping Animals also establishes the procedure for transporting them by public transport. Transport of dogs of aggressive breeds is only possible with a muzzle and a short leash. The owner is obliged to limit the pet’s movements in every possible way, even if there are practically no passengers in the transport. Small animals should be transported in special carrier bags. Large animals are transported near the rear seats.
The driver or conductor has the right to demand documents for the animal from the owner. So, for the trip, the dog owner has a veterinary certificate confirming the health of the pet and the presence of vaccinations against rabies. Travel for animals on public transport is subject to payment. The payment amount is equal to the cost of baggage transportation.
What to do if your dog is hit by a car?
For what can pet owners be held administratively liable?
Let's consider the situation using Moscow as an example. The most common violations are:
- keeping animals in common areas of communal apartments and apartment buildings;
- pollution by pets of common areas of the home and public places;
- violation of walking rules, for example, showing up with a dog without a leash and muzzle;
- an attack by one domestic animal on another, resulting in the latter being injured or killed;
- setting an animal on people or other animals;
- an animal attack on a person, causing harm to the latter’s health (in the absence of signs of a crime under Article 118 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation);
- causing damage to other people's property by animals.
According to Art. 5.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of Moscow, the maximum sanction for these violations is no more than 5 thousand rubles.
At the same time, punishing a dog owner for a violation is often a difficult task. For example, difficulties arise with the imposition of a fine for failure to ensure the removal of animal waste products. The ineffectiveness of the mechanism for collecting fines in such cases is explained by the fact that representatives of local government bodies do not have the right to demand documents from the owner of the animal. And this is necessary to bring him to justice. Only a police officer can demand documents. After this, an act is drawn up in his presence, submitted to the authorized local body, and this body issues a decision on a fine. However, more often than not there is no police officer nearby. Therefore, in practice, this whole procedure works with difficulty.
What is enshrined in law
Many residents of our country believe that the rules for keeping animals in the house are not precisely regulated by existing legislation. At the local level, regulations have been established that establish the rules for living pets.
Attention! The main laws in this area include:
- Civil and Criminal Codes of the Russian Federation,
- Government Decree “On approval of principles for the use of residential premises” No. 25 of January 21, 2006,
- Federal Law “On the Sanitary and Epidemiological Welfare of Society” No. 52 of March 30, 1999,
- Law of the Russian Federation “On Veterinary Medicine” dated May 14, 1993 No. 4979-1,
- Draft Federal Law “On Keeping Dogs in the Russian Federation”.
The most complete legislative act regulating the actions of dog breeders living in an apartment building is the draft Federal Law “On Keeping Dogs in the Russian Federation.” This bill sets out a procedure for a dog owner to avoid possible consequences from the pet’s activities on the health and well-being of people around him.
The normative act includes 5 chapters and 33 articles. Chapter 1 is devoted to the main provisions of the law. Here are the terms and concepts used in formulating the rights and responsibilities of pet owners, and the procedure for monitoring compliance with the law by government agencies.
Important! Chapter 2 sets out government oversight and regulation. This section is dedicated to:
- The procedure for purchasing animals,
- Features of purchasing dogs of potentially dangerous breeds,
- Rules for registration of individual dog breeds,
- Licensing of activities related to the sale, purchase and keeping of dogs,
- Obtaining a license and expiring its validity,
- State fees when registering a dog,
- Duty collection procedure.
Chapter 3 outlines the responsibilities of animal owners in relation to keeping animals. The procedure for keeping, the requirements for living conditions, the need for vaccination, the rules for being with animals in public places. Responsibility for violating the above rules is also described.
Chapter 4 formulates the procedure for combating stray dogs, the rules for catching and placing animals in nurseries. Chapter 5 indicates the final provisions of the legislative act and the date of entry into force. Dog owners need to carefully study the rules for keeping pets and adhere to them.
How to punish the owner of a dog that bit my child?
Are there also criminal penalties for dog owners?
Such liability is provided for in Part 1 of Art.
118 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation (“Causing grievous harm to health through negligence”). The article states that causing grievous bodily harm through negligence is punishable by a fine of up to 80 thousand rubles. or in the amount of wages or other income of the convicted person for a period of up to six months, or compulsory work for a period of up to 480 hours, or correctional labor for a period of up to two years, or restriction of freedom for a period of up to three years, or arrest for a period of up to six months. It is significant that according to the materials of the Consultant Plus service, as of March 17 of this year, one could find only 8 appeal decisions of courts of general jurisdiction at the level of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation (at the same time, decisions and sentences passed by magistrates and district courts were not examined), referring to Part 1 Art. 118 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
However, if serious harm to health is caused, large sums may be recovered. This is due to the need for rehabilitation of the victim. As an example, we can cite the circumstances of the tragic story, which was reflected in the cassation ruling of the Samara Regional Court5. In 2011, the court recovered half a million rubles from the owner of a dog that bit the face of a two-year-old girl. The owner of the pit bull was found guilty of committing a crime under Part 1 of Art. 118 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. He was sentenced to 180 hours of compulsory labor.
However, more often a dog bite results in mild or moderate harm to health. At the same time, the courts often support the victims in such cases. Thus, in 2021, the Moscow Regional Court recovered damages in the amount of 30 thousand rubles. against the owner of a Spitz because the dog bit the boy on the shin6.
What to do if you are bitten by someone else's dog?
- Contact a medical facility to prevent the risk of rabies and record damage.
- Then contact the police - submit a statement, register it using a KUSP coupon with the number and date of application, tell about the circumstances of the bite and provide copies of medical documents.
- Pass a medical examination as part of a medical examination appointed by the detective, district police officer or investigator as part of the pre-investigation check.
- Find and provide the authorized police officer with information about witnesses who can confirm what happened.
- Apply to an authorized police officer to seize video recordings if there are video cameras near the scene of the incident.
If serious harm is caused, a criminal case will be initiated.
In this case, the victim must follow all the doctor’s recommendations and the investigator’s instructions regarding the documentation of treatment measures, medications, vaccinations, etc., in order to avoid disputes about the severity of the harm. Remember: if the harm turns out to be mild or moderate, the criminal case will be dismissed. After the case is transferred from the preliminary investigation authorities to the court, a criminal trial will be held and a verdict will be rendered.
A claim for compensation for damage due to a bite can be brought after the initiation of a criminal case and before the end of the judicial investigation when considering the case in the court of first instance. When filing a claim, the civil plaintiff is exempt from paying state duty (Part 2 of Article 44 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation).
If minor harm is caused, then you should apply to the district court at the place of residence of the dog owner with a claim for compensation for damage. It will be necessary to provide evidence that the victim incurred expenses for medicines, doctors’ services and experienced moral suffering in order to recover compensation for moral damage. In addition, a resolution should be attached to refuse to initiate a criminal case, where the fact of the bite and the dog’s belonging to a specific owner are established, or a resolution to bring the owner to administrative liability.
Where to go if your neighbors dog is constantly barking
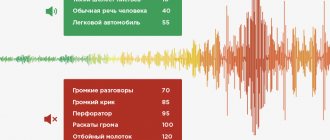
What to do if your neighbor’s dog won’t stop barking all day long? It is quite difficult to answer this question unambiguously. Animals often become anxious when left alone in a confined space for a long time. First, you should inform the owner that the dog’s barking and howling does not subside, and this causes discomfort to the neighbors.
If it is established that neighbors are cruel to the animal, beating them, shouting, then you should immediately contact the police. For such cases, a special article has been developed - 245 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation “Cruelty to Animals”. If there is evidence of this fact (photo or video), then these materials should be presented to the authorities.
If contacted, police officers are required to visit the owner of the animal and check the conditions of detention.
ATTENTION! Look at the completed sample application to the district police officer for violation of the rules for keeping a dog:
You can DOWNLOAD sample complaints from the links below:
- Application to the district police officer
- Application to Rospotrebnadzor
- Statement of claim to court