You can obtain land for farming for free in your own possession and for rent for a certain period or indefinitely. This can be done by persons who have the status of Russian citizen or who do not. But at the same time, they must carry out their entrepreneurial activities within the framework of peasant farming.
- Law
- Who can get the land
- What land can be provided
- Required documents
- The procedure for obtaining land for peasant farms
- When they can refuse
- Is it possible to build on farm land?
Legislative regulation
The activities of peasant farms are regulated by the provisions of civil legislation and Federal Law-74 of June 11, 2003.
They determine the possibility of creating a farming enterprise for individual entrepreneurs and organizations, and accordingly the plot is transferred to organizations and entrepreneurs.
The main areas of activity of farmers are established:
- Production and processing of agricultural products and livestock products;
- Their transportation, preservation, sale.
On lands owned by peasant farms, the following can be carried out:
- Crop farming (growing grain, fodder and other crops, tobacco, etc.);
- Animal husbandry (breeding various animals - horses, goats, sheep, pigs, rabbits, raising poultry, deer, camels, silkworms, beekeeping);
- Vegetable growing (picking nuts, mushrooms, berries, growing fruits and grapes).
IMPORTANT! The farm's land can be used by all the people included in its composition to produce products for their own consumption. In this case, registration of a company or individual entrepreneur is not required.
Farm property means:
- Earth;
- Structures and buildings;
- Outbuildings (warehouses, sheds, etc.);
- Reclamation structures and irrigators;
- Agricultural equipment and special equipment;
- Draft animals and poultry;
- Machines and equipment.
The procedure for providing plots for peasant farms, the requirements for them and their purpose are determined in the Land Code of the Russian Federation and the Federal Law “On the turnover of agricultural land”.
The procedure for the formation of peasant farms
Peasant farms first appeared in the Soviet Union towards the end of the 80s and are still developing dynamically in the Republic of Belarus. In Russia, the legal framework for their activities was formulated only at the beginning of this millennium. The Law on Peasant Farming (PF) of 2005 regulates the procedure for its organization and subsequent activities. It is characterized by some features:
- no more than three related families can participate in the society;
- there may be outsiders among the members of the enterprise, but no more than 5 people;
- You can join the association from the age of 16; the organization of a peasant farm takes place without the formation of a legal entity;
- legislation does not exclude the possibility of creating an enterprise by one person;
- when forming a legal entity, citizens pool their contributions;
- the property of the enterprise is its property;
- members of society personally participate in economic activities;
- registration of a peasant farm is allowed to citizens of the Russian Federation and other countries;
- Persons without citizenship can also form an enterprise;
- corporate relations are regulated by agreement between the participants of the enterprise; a charter is not needed;
- The peasant farm is registered by the tax office located at the place of residence of the head of the corporation;
- the participant is given the right to leave the company with appropriate compensation.
Who can get the land
Individuals and companies have the opportunity to obtain land.
When applying for land, it is not necessary to register as an entrepreneur or organization. But if you are planning a business activity in the form of selling agricultural products, you will have to register it in the prescribed manner. Both citizens of the country and other people with citizenship of another state have the right to engage in farming. They can rent land from a private person or from the state, or buy it for their own ownership.
Grounds for termination of activity
Grounds for termination of peasant farming:
- voluntary decision of its participants;
- withdrawal of all members from the enterprise;
- bankruptcy of the company;
- formation on its basis of an LLC or production cooperative;
- making a judicial decision.
If an enterprise cannot make mandatory payments on time and repay obligations, then the peasant farm goes bankrupt. The procedure begins:
- if there is an outstanding debt within three months;
- formation of debt exceeding 500 thousand rubles.
Bankruptcy is usually associated with the seasonal nature of agricultural enterprises.
What land can be provided
Land areas issued to peasant farms have agricultural purposes. They should be located outside the rural settlement and include various objects on which there are forests, fields, reservoirs, buildings and structures, roads, and various communications.
Particularly valuable agricultural areas are under state protection. These include territories whose cadastre value is 10% higher than the municipal average, and artificially irrigated or drained plots.
The presented plot is considered indivisible, therefore its owners have shares in it without dividing them into parts. It will be possible to divide it only if the farm ceases to operate.
The presented lands may be used for the purposes for which they are presented. Their possible uses include the following varieties:
- Planting flowers;
- Breeding poultry and fish;
- Gardening and vegetable growing;
- Viticulture;
- Beekeeping;
- Hunting grounds;
- To organize fisheries;
- Haymaking and grazing of livestock;
- Creation of protective forest plantings.
The applicant can determine the required size of the transferred plot.
Documents for the construction of facilities on agricultural lands
To understand whether it is possible to build a house on agricultural land, it is necessary to transfer this plot to another category. This is an organizationally difficult event.
You will need to collect an impressive package of documents, undergo approvals from numerous authorities, and obtain permission from the local municipality.
The outcome of the decision is not always in the interests of the applicants: the decision is always made on an individual basis, and both refusal and consent can be obtained equally.
Therefore, citizens have a question about how to build a house without all this paperwork. It turns out that it is possible, but you must adhere to a number of requirements.
These lands, as a rule, are included in the territorial formations of cooperatives and gardening partnerships. According to current Russian legislation, these lands are allocated for dacha construction.
And here the legislator again does not give us precise legal formulation. What exactly is meant by summer cottage construction?
But it is possible to build technical structures. These include sheds, rooms for birds and livestock, sheds, and greenhouses. You don't even need to obtain permission to build them.
The construction of a residential building, which by definition is a capital construction project, is prohibited. According to the law, this will be considered an inappropriate use of the allocated land.
The law also prohibits engaging in commercial activities on agricultural plots. To build a house on such plots, you need to change the category of land. This is difficult to do, but possible.
Other regulations apply to these land plots.
Let's first figure out what is allowed to be done here. Farms are intended for:
- breeding livestock, birds, developing pastures;
- breeding wild animals and organizing hunting grounds;
- cultivation of fertile and arable lands, cultivation of agricultural plants;
- construction of structures and storage facilities to ensure the functionality of the farm.
The last point directly assumes that in order to maintain the farm, the farmer needs to live somewhere. Therefore, building a house on agricultural land intended for farming is permitted. This is stated in Article No. 263 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and in provisions 40 and 43 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation.
But it's not that simple. There are also a number of restrictions. Construction of a private house up to 3 floors is allowed. But it can be officially registered and transferred to the category of personal property. He is assigned an address and is allowed to register.
This category includes lands allocated for cultivation and production of plant materials. But is it possible to obtain permission to build on agricultural land?
And to build non-permanent structures, permission is not required. For capital objects, there are different regulations that require compliance with certain requirements and standards.
The owner of the land plot that was allocated to him for farming must collect documents. Their list is determined by the type and purpose of the land.
The owner of a summer cottage needs the following documents:
- certificate of ownership;
- cadastral plan;
- contract of sale.
We suggest you read: Is it possible to complain to the labor inspectorate anonymously?
Before finding out what facilities can be built, the owner of farm land will need to complete much more paperwork:
- construction permit from local authorities indicating the completion date of the work process and the type of structure;
- title documents for property;
- certificate with cadastral number;
- cadastral passport indicating boundaries;
- decision of the relevant authorities to recognize the house as a residential premises;
- BTI documents with floor plans.
Entrepreneurs often wonder whether it is possible to build a store on agricultural land. After all, developed infrastructure and the presence of numerous farms imply the presence of a trading facility.
According to Article 40 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, residential, household, and industrial facilities can be built on agricultural lands within the framework of the intended purpose of the land, but with mandatory compliance with all construction and environmental standards.
The transfer of a plot from one category of land to another is carried out in accordance with the regulations of Federal Law No. 172 of December 21, 2004.
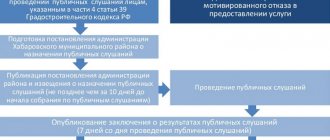
The procedure for obtaining land for peasant farms
This can be done in several ways:
- Organization of an auction initiated by municipal authorities when the plot falls within their sphere of disposal.
- Conducting a competition at the initiative of persons with the possible purchase of the object for personal ownership.
- Obtaining territory for rent without bidding for certain categories of persons.
- Lease obligations in relation to land that is not registered in the cadastral register, without tendering.
The provision of land for farming involves the following actions:
- Selecting the appropriate option . The selection can be made:
- By contacting your local municipality. They accumulate data on the presence of empty objects;
- By taking part in a public auction, information about which is published on electronic resources or in print media;
- Find information on the Rosreestr portal.
- Submission of an application for the allocation of land area . It is submitted to the administrative authorities authorized to accept it. The request must provide data about the object:
- Purpose of use:
- Authority of the applicant;
- Conditions for the transfer of land into ownership (free of charge or for a fee):
- The need to represent the territory of the required size (number of participants and employees, turnover volumes);
- Signed agreement on the establishment of a peasant farm;
- Temporary period, if the lease is intended for a short period.
applications for the provision of land for farming
The application is reviewed within 14 days, the draft boundary definition is approved in about one month.
- Organization of trades . Having received the application, the administration staff publishes a notice of intention to lease the land and invites applicants to participate in the competition. If no one has expressed a desire to participate in the event, the site is provided to the initiator without holding a tender. If there are still those interested, the rental price may increase significantly based on the results of the auction.
- Carrying out cadastral registration . In a situation where the administrative body has previously approved the application, the applicant must survey the property and register it at his own expense. Sometimes these costs are borne by the local municipality. The cadastral engineer of the land management organization establishes the boundaries of the territory, carries out topographic surveys and draws up the necessary documentation. Having received the papers, you need to submit them to Rosreestr to enter information into the unified cadastre and receive a passport.
ATTENTION! If the issuance of land is refused, the funds spent on the formation of the area will not be returned.
- If a positive decision is made in favor of the owner of the peasant farm, the administrative body signs an agreement with the applicant on the sale or lease of land property. It must indicate all the essential terms of the transaction, in particular:
- Amount of rental payments;
- Rights and obligations of the parties;
- Possibility of further purchase of the plot of land.
When its validity period expires, it can be:
- Extend;
- Terminate;
- Buy a plot of property
- Transfer of land into ownership . Land legislation determines the possibility of allocating agricultural territory for free lease with its subsequent transfer to private ownership if the site has been used for its intended purpose for five years. It can be purchased from the state after the end of the lease for a minimal amount.
IMPORTANT! The agreement must go through the registration procedure with Rosreestr, only after this the rights to own the plot will come into force.
Drawing up an application
It is very important to correctly draw up an application for a request for the provision of land plots for peasant farms. Please remember that this application must be drawn up on A4 sheet, and in printed font.
In the application, you provide information about yourself as a legal entity that intends to become the owner of a farm in a separate territory.
In addition, your direct contacts must be indicated. Another important information that should be located in this document is the possible presence of other owners of the farm, which should be indicated.
Next, you must outline how you intend to use the particular site taken, and also describe on what basis you are claiming it.
After you have stated in your application all your requirements regarding the provision of a plot of land for rent, you can indicate additional reasons that can work in your favor or vice versa. After this, you can attach any documents to the application, and then put a date and signature.
We do not recommend completing the documents yourself. Save time - contact our lawyers by phone:
8 (800) 350-29-87
When they can refuse
An applicant may be denied agricultural land. Reasons for this may include:
- The required area is greater than the limits established by the administration of the village council;
- This is not a complete list of documents;
- The papers contain inconsistencies and inaccuracies;
- The object is burdened with the rights of interested parties.
The applicant is informed of the decision, indicating the reasons for the refusal. The unfoundedness of the arguments may serve to challenge them in court.
Is it possible to build on farm land?
The construction of various non-agricultural buildings is allowed on the land territory of the peasant farm. These can be residential, industrial and recreational buildings. The area of such buildings cannot occupy more than 30% of the entire plot. The development is regulated by the emerging practice of the municipality and the approved project.
To officially register a residential building and register in it, it is necessary that its height does not exceed three floors. To build it, you need to provide evidence of the need for permanent human presence on the farm. This may be due to constant care of animals and other reasons.
The development of agricultural territories is regulated by the provisions of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, which establishes the importance of compliance with urban planning, fire safety, construction, and sanitary standards during its implementation.
In addition to housing, the owner of a peasant farm can erect other buildings at will. The construction of permanent buildings must be accompanied by obtaining a construction permit. Temporary buildings can be erected without coordination with the relevant services. These can be sheds, warehouses, sheds and more. Their registration with Rosreestr is not required.
It should be noted that for the development of farming in Russia, agricultural land is provided for rent or for own ownership. Various products can be grown on them or livestock, fish and other animals can be raised. The maximum size of the territory provided will depend on the number of participants in the farm and the standards established in the region.
Receiving a grant
- the number of employees should be no more than 100 people in small enterprises and 15 for microenterprises;
- the shares of members of a peasant farm - legal entities not related to small businesses, in the aggregate should not exceed 25%;
- the period of activity of the enterprise should not exceed three years;
- the cost of products sold per year is not less than 30 thousand rubles.
Various forms of peasant farms can act as participants in the program. This includes personal subsidiary plots and agricultural cooperatives. Agricultural enterprises that have been operating for more than 3 years can also count on government support. They are entitled to:
- reimbursement of a certain share of loan costs;
- guarantee fund guarantee;
- assistance in registering land ownership.