Is it possible and necessary to privatize a garden plot?
All garden plots are divided into two types, depending on their intended purpose:
- under individual housing construction - were issued to an individual for the implementation of individual housing construction (country house);
- for private plots - intended for running personal subsidiary plots.
It is possible to obtain ownership of municipal lands in order to be able to subsequently sell and lease them out only through privatization. There is no point in delaying the re-registration, since according to the legislation “on dacha amnesty”, citizens of the Russian Federation have this opportunity free of charge until March 1, 2021. Subsequently, if the Government of the Russian Federation does not once again extend the deadline, privatization can only be carried out for a fee.
Free privatization of gardens and vegetable gardens is possible if all the following conditions are met:
- lands are transferred for individual housing construction/LPH;
- gardeners have a contract for perpetual use of land or a lease agreement;
- the plot was assigned to an individual until October 25, 2001 (during the period of validity of the old tax legislation);
- the site has not been withdrawn from circulation and is not part of the environmental protection zone.
Almost all existing garden plots fit these conditions, so if your plot has not yet been privatized, you can re-register it at any time.
The procedure for privatization of a land plot
Registration of land privatization usually follows a standard scenario, but sometimes certain nuances may arise in the process of its preparation and implementation.
The standard procedure for appropriating state land to an individual or legal organization includes paying a state fee and documenting the transaction.
When is free privatization of land possible? Every citizen of the Russian Federation has the right to free ownership of certain lands on an indefinite basis. In this case, when re-registering the plot, the owner must pay only the fees provided for by the legislation of the country. Simplified land privatization saves time. This provision applies to heirs of private houses and apartments, buildings and outbuildings. The same applies to those premises that were erected before the adoption of the provisions of the Land Code of the Russian Federation in 2001.
Before privatizing the land plot under the house, you need to decide what category this land belongs to. The problem is that it will definitely not be possible to privatize environmental or municipal territories. The same applies to land included in the sphere of state security. If the site that interests you does not fall into these categories, it is quite possible to talk about the privatization of private territories.
People who have lived in a house on a specific plot for a long time or have some property here can take land for personal use. They will be given preference in all matters relating to the privatization of private land plots. The same applies to the area under outbuildings and the area around the house. If you have a house on the land that is private property and you have all the documentation, you can definitely count on purchasing the plot and privatizing it.
- all tenants of land plots who took possession of real estate for the purpose of constructing residential buildings or for the opportunity to conduct subsidiary farming before 2001;
- citizens who inherited real estate where ownership has already been registered;
- owners of plots of gardening and garage cooperatives;
In all other cases, privatization of the land under the house is carried out for a fee.
The amounts of mandatory contributions are calculated individually each time, which often leads to inaccuracies and errors. If you are not satisfied with the price of the plot that the competent authorities have reached, then with us the challenge of the value of your land plot will take place on time. We will file an application with the court or a higher authority to defend the fair value of the land purchase. We have gone through the procedure of privatization of a land plot by court more than once on instructions from our Principals.
Legislation
The main law regulating land legal relations is the Land Code of the Russian Federation. The procedure for simplified land privatization, which has been in force in Russia since 2006, is regulated by Federal Law No. 93 “On the dacha amnesty.” After the adoption of this regulatory act, the process of registering ownership of gardens became much easier and faster. Currently, permission for privatization from the local administration is not required. The documents, along with the application, are immediately submitted to Rosreestr, and after 10-14 days, ownership passes to the applicants (provided that everything is in order with the cadastral papers).
Timing and cost
The timing of privatization of dacha plots varies. If the documents are reviewed by a local authority of the Federal Registration Service or MFC , it takes up to 14 weeks . If the procedure is approved, the “amnesty” lasts another 10-14 days . If a person is served according to general rules , then the process may take about 3-4 months , taking into account the consideration of the package of documents.
The cost depends on the type of object and the necessary procedures . According to the new rules, in any case, you will have to take a certificate from the Unified State Register of Real Estate (packages with a cadastral passport are more often rejected), and it costs 300 rubles . The state duty is also 300 rubles if the land includes a house . For other types of objects you will have to pay 2000 rubles .
You can pay the fee in cash at a bank, using a special terminal or through the Government Services portal. This does not include the services of lawyers and notaries , which cost differently.
What is it for?
Having become land owners, gardeners do not have to worry about the safety of their plots. The authorities do not have the right to gratuitously confiscate private property. Therefore, if the site is required for state or municipal needs, the citizen will be paid mandatory monetary compensation.
This is not the only advantage of privatization; after the re-registration is completed, you will be able to:
- sell;
- give;
- exchange;
- to rent;
- include in the will;
- lay down
Once the boundaries of the site are officially recorded in cadastral documentation, disputes over the distribution of land between neighbors will automatically disappear.
After privatization, you will be responsible for paying an annual property tax, the amount of which is 0.3 percent of the cadastral value of the land.
Example. The Garchev family, on the basis of a contract of perpetual use, for many years grew agricultural crops on the garden plot, without having any documents for the land. The users of the neighboring plot decided to privatize their plot, occupied under the same conditions. The question arose about land surveying. Unbeknownst to the Garchevs, a small but very fertile plot of land was alienated from them. The family found out about this when they saw the beautiful fence put up by the neighbors immediately after the land survey was completed. The Garchevs expressed dissatisfaction with the “violators,” but never recaptured the land. After all, from a legal point of view, everything was done correctly - the Garchev family did not have cadastral documents for the land in their hands, they could not confirm the right to the plot alienated in favor of their neighbors, which means that even through the court it would not have been possible to restore justice.
This example clearly shows the advantage of privatization. After all, if the Garvchevs had started the re-registration first, the truth would have been on their side and the court would have forced the violators to remove the illegally erected fence.
Is it necessary to privatize a summer cottage?
It’s impossible to answer the question with certainty, since people’s situations are different. definitely worth privatizing land if a person wants to sell it . Thus he receives ownership . If you own a plot according to a garden book, then everything can be transferred to another citizen. You will have to prove your rights through court, which is expensive and not always effective.
It's best to consider the pros and cons of this approach to land management. There are positive and negative aspects to the privatization of a summer cottage. Experts recommend studying them carefully immediately before registration. The main advantages include:
- The ability to dispose of property at the owner's discretion. This could be a sale , rental transfer .
- After the death of the owner, the property is transferred to his direct relatives and is included in the inheritance.
- It is possible to use the object for transfer to a bank or other financial organizations for the purpose of collateral .
However, experts recommend making sure that the existing advantages are more significant than the disadvantages. Among them:
Free legal consultation
+7 800 350-51-81
- Simplified privatization of summer cottages has been extended until 2026 . Those who do not have the right to count on it can carry out the procedure for a fee.
- There is no information about the conditions the procedure will be carried out after 2026 .
- After registering a summer cottage, the owner is forced property tax for the property every year , the amount of which depends on the cadastral value of the property.
Reference! Due to the existing shortcomings, it is recommended that even before starting the registration process, you carefully evaluate how feasible it is to privatize a dacha plot. To do this, you should contact a professional lawyer.
How to privatize a garden plot
Re-registration can be carried out in two ways - with the participation of the chairman of the SNT or by the gardener independently. It is easier and faster to privatize a plot of land on your own, but a number of legal features of the procedure must be taken into account.
Order, stages
When carrying out the privatization of garden plots, it is necessary to act according to the following algorithm:
- we prepare a package of documents and submit it to the territorial department of the Federal Property Management Agency or to the administration of the locality;
- We are waiting for a positive decision;
- we verify and, if necessary, update cadastral information;
- we sign a privatization agreement;
- we pay the state fee;
- We register land rights in Rosreestr.
If the site corresponds to lands falling under the “dacha amnesty”, we collect documents and submit them immediately to Rosreestr. In this case, the application for privatization can be submitted directly through the State Services portal or by personal visit to the MFC GBU “My Documents” closest to your home.
Procedure, process
If on garden plots transferred for individual housing construction, users have already managed to build a house, a bathhouse, a garage and any other capital buildings, these objects must be legitimized, and preferably before the start of registration of ownership of the plot itself.
We are starting to independently privatize a garden plot in 2021:
- Step 1. Determine the status of the land. Check whether the plot was previously withdrawn from circulation, what purpose is indicated in the extracts from the Unified State Register of Real Estate (from 2021, this document began to be issued instead of a cadastral passport).
- Step 2. We draw up an application, collect documents and submit the papers for consideration. It is important to correctly determine who initially owns your land; if the garden is located within the city, apply to the local administration; if the plot is located outside the border of the locality, the Federal Property Management Agency is responsible for it. You can get more accurate information about the owner in the same extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
- Step 3. We are waiting for the owner’s decision. Government officials are given 60 calendar days to consider citizens’ appeals. An official response from the authorized body is sent to the applicant with the signature of the head of the locality and seal.
- Step 4. We carry out cadastral registration. If any changes have previously occurred on the garden plot, for example, boundaries have been shifted or outbuildings have been erected, it is necessary to re-landmark and update the information in the cadastral documents. If no changes occurred during the use of the land, this item can be skipped.
- Step 5. We conclude a privatization agreement with local authorities. If several people are involved in privatization, then all of them must appear to sign the agreement.
- Step 6. Register property rights in Rosreestr. This stage is final; the procedure becomes possible only after payment of the state fee. Employees of the cadastral chamber check the documents submitted for consideration and draw up a new extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
Deadlines
A simplified option for re-registration of municipal land ownership takes no more than a month. In most cases, gardeners keep it within 14 days. If the procedure is carried out in a standard way, be prepared that the re-registration will take 3-4 months. To protect yourself from hours-long queues, submit applications on the State Services electronic portal or use the services of the MFC.
Price
If the privatization of a garden plot is carried out free of charge, then it is not required to buy it at the full cadastral price. Your main expenses will consist of the following items:
- state duty (regular registration procedure/dacha amnesty) – 2000/350 rubles;
- for an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate – 300 rubles for each individual participant, 950 for a legal entity;
- for issuing a notarized power of attorney (if a representative will act on your behalf) – from 1000 rubles;
- for carrying out cadastral registration of land: geodetic survey, land surveying, drawing up an extract from the Unified State Register (if the plot was not previously included in the register) - from 15,000 to 50,000 rubles (depending on the region).
Documents for privatization of a garden plot
In addition to the application for privatization, gardeners must provide both the owner and the registrar with the following documents:
- passports of all participants;
- extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate;
- document of title (agreement on the perpetual use of a garden plot or a lease agreement);
- notarized power of attorney (if the registration is handled by a representative).
In some cases, Rosreestr employees may require additional paperwork. Be sure to make copies of each document before submitting them.
Free privatization
The main requirement imposed by the state on land plots subject to free privatization is the issuance of the allotment for use by an individual until October 31, 2001. On the basis of what title document the land was given to the citizens, it does not matter; the plot could be transferred after concluding an agreement on perpetual use, on the basis of a lease agreement, or by transferring the right from the tenant to the heir.
If you received land on November 1, 2001 and later, you can forget about free privatization. You can register ownership only by purchasing the plot from the municipality at the full cadastral value.
Is privatization of a country house necessary?
Based on the passport, a certificate of ownership of property is issued. Lands are privatized according to the standards available in the current legislation of the Russian Federation. Thus, the dacha plot will become privatized, but someone may be concerned about the question: is it necessary to privatize the dacha house if the land is privatized? There is a lot of controversy about this issue. However, if this is done, the cost of the dacha will be higher.
We recommend reading: Is it possible to obtain shared ownership of an apartment with a mortgage?
Reasons for refusal
Sometimes authorities refuse to privatize citizens' garden plots. If this happens, be sure to request a written justification, this document will be the basis for appealing the actions of the authorities in court. But, before starting a lawsuit, it is necessary to analyze the reasons for the refusal and, if they are valid, try to eliminate the errors.
Common reasons for refusal are:
- the allotment is withdrawn from circulation;
- the summer resident does not have rights to privatization;
- a number of certificates are invalid or expired.
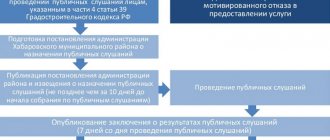
What to do in case of refusal?
The refusal can only be challenged in court. You must submit a statement of claim along with documents confirming your case to the office of the district court. Be as responsible as possible when drawing up your claim; before going to court, do not forget to attach a receipt for payment of the state fee to the package of documents.
Procedure
If you receive a refusal, carefully read the reasons; the plots withdrawn from circulation cannot be privatized even through the court, so there is no point in appealing. If you consider the negative decision to be unfounded, you can safely proceed to litigation, but be prepared to provide the court with irrefutable evidence that you are right, otherwise your demands will be left unsatisfied by the court.
Recommended course of action:
- after receiving a written official refusal from the municipality or the Federal Property Management Agency, we collect a package of documents and draw up a statement of claim;
- we pay the state fee;
- we submit the papers to the office of the district court;
- We actively participate in court hearings;
- If the claims are satisfied, we take a copy of the writ of execution and, on its basis, conclude a privatization agreement or register property rights in Rosreestr.
It is not easy to win legal disputes with the authorities, so if you decide to defend your case to the end, be sure to enlist the support of an experienced, qualified lawyer.
Procedure
The participants in all disputes regarding the refusal of privatization are two parties: the plaintiff (individual or legal entity) and the defendant (municipal body or branch of the Federal Property Management Agency). Hearings are carried out in several stages. The plaintiff has the right to express written requests to obtain missing information on the case, for example, extracts from archives that were not previously issued at the request of the summer resident.
If the court, having heard the positions of the parties, satisfied the plaintiff’s demands, the gardener has the opportunity to continue privatization on the basis of a copy of the writ of execution, which can be obtained 30 days after the verdict is issued in the court office.
Statement of claim
This application to recognize the refusal to privatize as illegal is drawn up in accordance with the requirements of Art. 131 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.
Expenses, cost
The mandatory cost column when appealing a government decision through the court is 300 rubles (state fee). Additional funds may be required to pay for the work of a qualified lawyer who will represent your interests in court. You should not skimp on this point, especially since if you win, all legal costs will be transferred to the defendant if you indicate this in advance in the claim (clause 1 of Article 98 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).