Every city in Russia has enough debtors for utility bills. When negotiations with them reach a dead end, resource supply and management organizations submit an application for the issuance of a court order for housing and communal services. After all, this is the easiest way to collect debt through the court.
There are obvious advantages. The parties are not invited to the meeting. The review of documents itself takes 5 days, which cannot be compared with traditional claims.
Another advantage is that this procedural document has the status of an executive document. After it comes into force, the claimant sends it to the bailiffs. Next, they will be forced to return the accumulated housing and communal services debt.
Court order for collection of debt for housing and communal services
Art. 153 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation establishes obligations for residents to pay for housing and other utility bills. In turn, Article 154 provides a breakdown of tariffs.
Art. 155 says that, as a general rule, money is deposited monthly before the 9th.
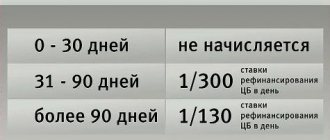
It is permissible to establish other terms in the agreement with the management company, based on the decision of the meeting of owners, HOA or housing cooperative. For late payment, a penalty is charged in the amount of 1/300 of the Central Bank refinancing rate.
According to Art. 122 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, all utility debts, including accrued penalties, are collected through writ proceedings. This category is attributed to the powers of justices of the peace.
There is a state fee for filing an application, which is equal to 50% of the tariff established for claims with the same requirements.
The concept of a court order
Russian legislation is constantly being improved, changing and adding provisions to regulations. Since the beginning of June of this year, changes have been made to the Civil Procedure Code regarding the collection of debts for housing and communal services. The requirements for which the order is issued are expanded in connection with the changes:
- on debt collection for housing and communal services;
- on requesting payments for the use of a landline telephone and international communications;
- on the collection of debt in favor of homeowners' associations, construction and other cooperatives.
A court order is a decision made independently by the magistrate's court.
The only limitation is that the cost of the claim cannot exceed half a million. The issued order form is the fundamental document for the enforcement service in the process of collecting money from an unscrupulous payer. It is possible that payment of penalties will also be collected on the basis of this document; there is no clarity on this issue yet. The articles posted on our website are informative in nature, and the author does not always keep up with the changes made to regulatory acts by legislators. The site’s lawyers, who are familiar with judicial practice first-hand, are ready to give free advice to guests of our portal 24/7. To receive a consultation, leave a request using the feedback form.
Questions on the topic
It would seem that utility companies have lawyers whose duties include debt collection. However, often after receiving the order, a long struggle with debtors only begins.
Technical errors, ignorance of procedural rights - all this occurs. As a result, there is an unreasonable delay in time.
Therefore, calls to specialists are not decreasing. Below are answers to some of them, and the situations are typical regardless of the region of the Russian Federation.
Penalty
The client has a basic debt to pay for hot water, as well as an accrued penalty. Tell me, what amount should I write in the application for a court order?
Of course, the base amount must be included unambiguously in the application. However, with penalties the situation is not so simple.
So, if the magistrate considers that there are problems in the calculations, he can return the application. After all, in this case there will be a dispute about the law.
Enforcement proceedings
When a court order comes into force, is it necessary to send it to the bailiffs yourself? Or are there some other options. Thank you in advance!
First, let us remind you when the court order comes into force. This occurs after 10 days following receipt of correspondence from the court. During this time, the second party (the debtor) must file an objection to the order.
Otherwise, it becomes a full-fledged executive document. In order not to waste time sending it to the bailiffs, you can ask the court to do this directly in the application.
State duty
We filed an application for a court order to forcefully collect debt from one of the residents for electricity. However, it was canceled and now there is a need to bring a claim. Tell me what to do with the previously paid duty?
In this case, there is simply an additional payment up to the required amount. That is, the original money does not disappear, but forms an offset.
It’s just that in addition to the new payment order, you should also attach a copy of the previous one. In the claim itself, it is necessary to make reference to the circumstances related to the cancellation of the order.
When to file an objection to an order
I received a court order from the court to collect the debt for heating. I don't agree with him. What to do in this case, because the amount is large for me. Thank you in advance!
We need to act quickly. Within 10 days, it is necessary to address the magistrate with an application to cancel the court order.
The period is calculated from the next day after receiving the mail. If its end falls on a weekend, the transfer occurs until the first working day.
Actions of the defaulter to repay the debt
It says that the debtor must put the received document into effect within five working days, that is, pay the debts. Do not ignore the order under any circumstances. Take care of your financial condition and avoid huge fines.
Sometimes it happens that the defaulter, for some objective reason, does not repay the debts. According to the law, he has the right to a deferment. But to do this, you must immediately, after receiving a copy of the order, contact the FSSP to write an application. The reason for the inability to pay the debt must be documented. A certificate of long-term treatment and checks confirming expenses for it, or a work book with a record of recent dismissal, are suitable for this.
This is also important to know:
Application for a court order to collect debt: sample
In this situation, by mutual agreement, a debt repayment schedule will be drawn up. If the defaulter has not done any of the above, bailiffs will take over the case.
Features of filing a claim
As previously mentioned, the court considers the received application within 5 days, after which it either satisfies the requirements and issues an order, or rejects the requirements.
After the order is issued, it is transferred to the bailiffs, who monitor the debtor’s accounts and, if they exist, seize them.
In addition to the bailiffs, the order is sent to the debtor for review. In case of disagreement with the order, he has the right to send objections, which substantiate the inconsistency of the requirements of the utility service. Objections are sent no later than 10 days from the date of receipt of the order.
After objections are received, the court schedules a hearing, which is held in the usual manner, with the utility service as the plaintiff and the debtor as the defendant.
If no objections are received, then, on the basis of the order, funds are withdrawn from the debtor’s accounts to repay the debt.
Withdrawal of funds is carried out on the basis of information transmitted to the bank by the bailiff on the basis of a court order.
Note! After receiving the order, the debtor has the right to repay the existing debt within 5 days. If this right is not used, the accounts from which funds are written off will be seized.
Another right of the debtor is to receive a deferment, but for this they must provide weighty arguments (serious illness, loss of job).
A negative consequence of debt is eviction. However, in this case, the administration undertakes to provide other living quarters.
When examining the materials presented by the utility service, the court will check the application of the pre-trial procedure for resolving this issue.
Please note! The utility has only three years to go to court. After the expiration of this period, debt collection is unacceptable.
Sample application
If it is necessary to collect debts on utility bills, you should draw up an application for the issuance of a court order. Housing and communal services services are mainly involved in drawing up such an application.
applications for a court order for utility bills free in word format
The application contains the following list of information:
- the name of the judicial authority that must issue the order,
- information about the applicant, in this case about the utility service,
- information about a person who does not pay utility bills,
- information about the circumstances that contributed to the formation of debt,
- documents confirming the right to claim debt obligations,
- list of information that is attached to the application.
Note! The author of the application must pay the state mandatory fee. Its amount depends on the size of the resulting debt.
Such applications for the issuance of a court order are considered by the magistrate court located at the defendant’s place of residence.
After reviewing the document, two copies of the order are issued.
ATTENTION! Look at the completed sample application for a court order for utility payments:
Algorithm of actions
The law does not provide for the need to explain the grounds for cancellation. It is enough that the citizen does not agree with the court order.
To revoke a writ of execution, it is necessary to send a written objection to the magistrate court that issued the order.
Procedure:
- Obtaining a court order.
- Appeal to court within 10 days.
- Direction of objection.
- Receiving a cancellation decision.
Important! If the management company managed to send the documents to the FSSP, then it is necessary to submit a decision on cancellation to the department. The duties of the bailiff include stopping the collection of funds upon receipt of information about the cancellation.
Where to look?
Expert opinion
Stanislav Evseev
Lawyer. Experience 12 years. Specialization: civil, family, inheritance law.
A court order is understood as a court order that is issued at the request of a management company to collect a debt for housing and communal services. It has the force of a writ of execution.
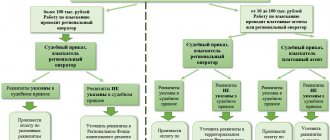
The law does not set a time limit for when the management company must go to court. A prerequisite for issuing a court order is that the maximum amount of debt is not more than 500,000 rubles.
As a rule, the organization initiates legal proceedings 6 months from the date of debt formation. However, this is not necessary. In practice, it happens that the debt accumulates even for 10 years.
Often, the management company applies to the magistrate's court to obtain a court order.
| No. | Main reasons |
| 1 | Debtors do not often appeal court orders |
| 2 | The process is carried out as quickly as possible (no more than 2 months) and without the presence of the parties |
| 3 | The state duty is 50% of the duty for claims proceedings |
| 4 | The law does not provide for the defendant’s ability to influence the decision |
That is why the defendant often finds out about the extradition after the document is issued. The management company, as a rule, does not notify the debtor about the issuance of a court order.
How can a debtor find out about the issuance of a writ of execution:
- upon delivery of the order;
- from the bailiff.
If you suspect that the management company will be able to initiate a lawsuit, you can independently monitor the information on the FSSP website. As soon as enforcement proceedings are initiated, the information will become publicly available.
All organizations involved in the management of apartment buildings are faced with the problem of collecting debt from owners, and therefore in this issue we decided that it is time to tell how to collect debt in the Hot Topic section of the issue. Before going to court, organizations involved in the management of apartment buildings can take measures aimed at repaying the debt, namely:
- Send a notice (claim) about the need for payment;
- A warning about the possibility of shutting off the supply of gas, water or electricity, indicating the period within which it is necessary to correct the situation;
- You can also suggest drawing up a payment schedule in installments in case of a large amount of debt.
If, after the measures you have taken, the debtor owners have not repaid the debt, then organizations involved in the management of apartment buildings can go to court to collect the debt.
In this article we will look at a simplified procedure for collecting debts for housing and communal services - this is a court order.
Court order
- this is a court decision made by a single judge on the basis of an application for the collection of sums of money or for the recovery of movable property from the debtor according to the requirements provided for in Article 122 of this Code, if the amount of money to be recovered or the value of the movable property subject to recovery does not exceed five hundred thousand rubles (clause 1 of article 121 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation). Thus, this is a decision that is made by the court unilaterally, in accordance with the application and information received from the plaintiff. It is the basis for the commencement of enforcement proceedings by bailiffs.
An application for a court order is submitted to the court according to the general rules of jurisdiction: at the place of residence of the debtor or the location of the property (if the place of residence is unknown). The court order is issued within 5 working days from the date of receipt of the application with supporting documents attached. The application is drawn up in any form. At the end of the application, documents are listed with which organizations involved in managing MKD confirm the validity of their claims for debt collection. In this case, there is no specific list of documents. We can roughly recommend attaching the following documents:
- A document that confirms the debtor's ownership of the premises (for example, an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate).
- Minutes or minutes of general meetings of apartment building owners, at which payment tariffs for housing and communal services were approved; if tariffs established by local government are used, then they should be attached.
- A copy of the agreement concluded between the organization managing the apartment building and the debtor. (if there is one)
- Receipts for payment of utility services that are unpaid by the debtor
- Notifying the debtor about the existing debt
- Calculation of the amount collected from the debtor
- Power of attorney for a representative of the organization
- Receipt for payment of state duty
- Other documents that can confirm the existence of debt.
The completed application for a court order is submitted to the magistrate's court at the address where the debtor is registered in triplicate. If you do not know the debtor's registered address, then you file at the location of the debtor's property.
The date of entry into force of the court order will not necessarily coincide with the date of its preparation. The time after which the order will come into force must be indicated in the document, otherwise the bailiffs, who are obliged to monitor its execution, will have no grounds for collecting the debt.
If you disagree with the collection of debt for housing and communal services by order, the debtor should send to the court an application to cancel the court order within 10 days from the date of receipt of the copy. In this case, the hearing of the case will take place in the usual (claim) manner. If the court order has not been canceled, it has the force of a writ of execution and, upon presentation to the bailiffs, the usual enforcement procedure begins.
If the magistrate refuses to accept an application for a court order to collect arrears of payment for housing and utilities on the grounds specified in Part 3 of Article 125 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, or the court order issued on these requirements was canceled (Article 129 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation), these claims can be considered in a claim procedure, including simplified proceedings.
Let's consider cases from whom it is possible to collect debt for housing and communal services, except for the owners of premises in apartment buildings:
If the owner of the residential premises (share) is a minor, then the responsibility for paying for the residential premises and utilities lies with his parents, regardless of the fact of living together with him (Articles 21, 26, 28 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and Articles 56, 60, 64 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation) . At the same time, minors aged 14 to 18 years have the right to independently pay for housing and utilities. If a minor has insufficient funds, the obligation to pay for housing and utilities is subsidiarily assigned to his parents (Article 26 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). , debt for children-owners is collected from both parents. At the same time, one application for issuing a court order to collect the debt from the parents jointly and severally is drawn up.
If the premises in an apartment building are in shared ownership, a separate application must be submitted for each owner of a share of the premises indicating the amount of debt (which must be calculated in proportion to the share in ownership).
If the premises are in joint ownership without indicating the share in the right. According to Part 1 of Article 253 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, participants in joint ownership, unless otherwise provided by an agreement between them, jointly own and use common property. In this case, as a general rule, the debt is collected jointly and severally from the owners in one application for the issuance of a court order.
If you know that there is nothing to take from the owner (tenant), collect the debt jointly from all members of the debtor’s family. Family members of the housing tenant bear joint and several obligations with the tenant to pay for housing and utilities (clause 25 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Council No. 22).
Under a social rental agreement for residential premises, the obligation to pay for residential premises and utilities arises from the date of conclusion of such an agreement (clause 1 of part 2 of Article 153 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation). It should also be remembered that arrears in payment of contributions for major repairs cannot be recovered from the tenant. if the tenant does not pay or has disappeared, you can try to collect the debt from the municipality.
Sample documents:
1.
2. Application for recovery by court order through bailiffs
Consequences of cancellation
The main consequences of canceling a court order:
- Debt collection stops.
- The management company receives the right to go to court through legal proceedings.
- The debtor receives the right to challenge the amount charged by the applicant.
Thus, it is advisable to initiate the cancellation of a court order for utility payments only if you have evidence of the unlawfulness of the debt accrual.
Example. Irina and Kirill are the owners of the apartment with ½ share. Irina regularly pays utility bills. And Kirill created a debt. The management company went to court and collected the debt from the two owners jointly and severally. Irina challenged the court order. When the management company applied for legal action, the woman presented receipts for payment. The court refused to satisfy the applicant's demands.