Basis for regulation of public easements State registration of public easements Definition of the concept of public easements in legislation Establishment of public easements. Order. Goals Public easement and public hearings Grounds (goals) for establishing a public easement Challenging the regulatory act on establishing an easement in court. Jurisdiction of the dispute Easement in relation to a site located in state or municipal ownership New: norms of the Land Code of the Russian Federation on public easement from September 1, 2021
Basis for regulation of public easements
The basis for regulating private easements is contained in civil legislation (Article 274 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), public easements - in land legislation (Article 23 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation).
Article 23 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation does not contain a definition of easement, but describes the types of easements established in relation to land plots and the specifics of their establishment.
The specificity of public easements is that their establishment is determined by the interests of society, and not the individual owner of the neighboring land plot.
The concept of public easement was introduced by Article 23 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, which came into force on October 30, 2001.
According to Article 23 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation (as amended in force until September 1, 2018), a public easement on a land plot is established by law or other regulatory legal act of a state authority or local government if this is necessary to ensure the interests of the state or local government , local population. In accordance with Article 23 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation (as amended in force from September 1, 2018), a public easement is established not by law (another regulatory act of the Russian Federation, a subject of the Russian Federation or a local government body), but by an administrative legal act - a decision of the relevant body.
Types of encumbrances
The distinction is made based on the purposes of their approval. In addition to the tasks described above, an encumbrance can be issued in relation to the following objects:
- Water fund (an easement defines the limited right of each citizen to use objects of a public water fund; a public water easement is issued for the abstraction of water resources without special technical devices, for organizing a watering place for agricultural animals, for the movement of small watercraft).
- Forest fund (an easement presupposes the emergence of the right of citizens to unhindered and free presence on the territory of forest fund objects, to collect and use food forest resources, and to participate in various non-prohibited activities).
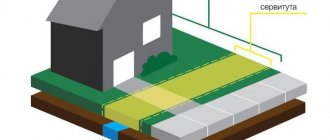
- Public easement for a road - areas of territory within the allotment zones of public roads of federal significance (public encumbrances are established for the installation, transfer and re-equipment of technical communications and their use).
Next we will talk about the procedure for establishing a public easement on a land plot.
Definition of the concept of public easement in legislation
Public easement is the right to limited use of someone else’s land plot (real estate) in the interests of an indefinite number of persons, established by law or other legal act of the Russian Federation, a legal act of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, a legal act of a local government body, taking into account the results of public hearings in cases where necessary to ensure the interests of the state, local government or local population, without seizure of land plots. The territory of the easement is determined at the stage of preparing documentation for the planning of the territory - the land surveying project (Decision of the Council of Deputies of the Shcherbinka Urban District of the Moscow Region dated March 23, 2012 N 404/91 “On approval of the Rules for land use and development of part of the territory of the Shcherbinka Urban District of the Moscow Region”)
Public easement is the right to limited use of someone else’s land plot, established by law or other regulatory legal act of the Russian Federation, a regulatory legal act of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, a regulatory legal act of a local government body, taking into account the results of public hearings to discuss documentation on the planning of the territory, in cases where this necessary to ensure the interests of the state, local government or local population, without seizure of land plots (Article 1 of the Land Use and Development Rules of the city of Kirov, approved by decision of the Kirov City Duma dated April 29, 2009 N 28/10)
Public easement is an easement established in relation to a land plot by law or other regulatory legal act of the Russian Federation, a regulatory legal act of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, a regulatory legal act of a local government body, to ensure the interests of the state, local government or local population. The regulatory legal acts specified in this paragraph of the Methodological Recommendations may establish the obligation of the body that established the easement to pay the person whose land plot is burdened with the easement a proportionate fee for the easement, and the amount of this fee may also be established (“Temporary Methodological Recommendations for assessment of proportionate payment for easement”, approved by Roszemkadastr on March 17, 2004 (later declared invalid by the decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated December 18, 2014 N AKPI14-1093)
Establishment of a public easement. Order. Goals
Unlike a private easement, which is established either by agreement of the parties or on the basis of a court decision, a public easement is established by authorities or local self-government.
To establish a public easement, the consent of the owner of the land plot is not required, nor is an agreement concluded with him.
The rights of persons using a land plot on the basis of a public easement are determined by law or other regulatory legal act that establishes such an easement (Clause 2 of Article 41 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation).
Public easement, according to paragraph 2 of Art. 23 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, can be established by a decision of the executive body of state power or local government in order to meet state or municipal needs, as well as the needs of the local population, without seizure of land plots.
Registration procedure
The encumbrance begins to operate from the moment of its state registration - entering information about it into the Unified State Register.
Peculiarities
A public encumbrance is registered if there is information in the Register about previously arisen rights to land. The following list of documents is required for registration:
- a statement from a state authority or local government authority that issued a resolution on the establishment of a public easement;
- receipt of payment of state duty;
- confirmation of the authority of the representative;
- Legal acts that have a public encumbrance;
- cadastral plan showing the boundaries of the encumbrance when it is established only on part of the site.
The registration authority has the right to request other documents.
Next, we will talk about the protocol of public hearings on the establishment of a public easement.
Protocol of public hearings
The results of public meetings are the following documents:
- list of participants;
- minutes of the public hearing;
- list of received questions and comments.
However, the defining document is the protocol, which must contain the following information:
- location of the meeting;
- debated issue;
- participants describing their opinion on establishing a public charge;
- the results of the public meeting indicating the number of persons who voted “for”, “against” and “abstained”;
- final decision.
The norms of land legislation prescribe that in order to make a decision on registering a public encumbrance, the results of the meeting are only taken into account.
However, constitutional norms, protecting the rights of citizens and the interests of the local population, make the results of the meeting mandatory for their implementation. Otherwise, you can go to court to protect public interests.
Resolution establishing an encumbrance
Based on the final decision of the public meeting, the government agency issues a resolution to establish a public charge. This document contains:
- decision to establish an encumbrance;
- information about the site indicating the cadastral number and location;
- the purpose of registration of the easement;
- an order for completing the state registration procedure for a specific organization;
- order for publication of the document in official media;
- indication of a specific person who is obliged to exercise control over the implementation of the resolution.
The following video will tell you even more about public easements, their establishment, challenging and similar nuances:
Public easement and public hearings
Note: 1). Mandatory public hearings before 09/01/2018
The establishment of a public easement on a land plot is carried out taking into account the results of public hearings (clause 2 of Article 23 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation in the previous version).
The procedure for holding public hearings may be established by regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and municipalities. For this purpose, the population is informed through the media about the planned establishment of an easement, indicating ways of expressing the opinions of interested parties.
If, for example, a public easement is established by a resolution of the city administration in relation to a land plot owned by an organization, and public hearings do not contain information about the need to establish the said public easement to ensure the interests of the local population or the interests of local governments, then in relation to this land plot, this regulatory act is declared invalid (for example, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga-Vyatka District dated June 18, 2009 in case No. A43-31249/2008-1-452).
At the same time, it should be borne in mind that public hearings, as a rule, are held formally, and the opinion of the “public” obtained as a result of their conduct may not be taken into account by local or federal authorities.
Note: 2). From 09/01/2018, public hearings are not held to establish a public easement
Federal Law dated August 3, 2018 N 341-FZ, Article 23 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation is set out in a new wording, effective from September 1, 2018. Unlike the previous version of the article, from the specified date, a public easement is established not by law (another regulatory act of the Russian Federation, a subject of the Russian Federation or a local government body), but by an administrative legal act - a decision of the relevant body. Public hearings are excluded from the procedure for establishing a public easement.
Registration procedure
So, how to establish a public easement on a plot of land? Its approval goes through several successive stages.
Making an application
The right to submit is vested in citizens and organizations, government agencies or local authorities. There is still a gap in the legislation in regulating the issue of which body to submit an application to. The practice boils down to the fact that in order to register a public encumbrance, it is necessary to contact either the legislative bodies or the executive authorities.
Therefore, in a situation where the interested party is a local government body, the application is submitted to the administration of the municipality. If the interested party is a subject of the federation, then it is necessary to contact the executive body competent to resolve land issues.
The application must contain the following information:
- information about the site on which it is planned to install the encumbrance.
- the purpose of its approval;
- period of encumbrance;
- landowner data;
- information about interested parties.
Consideration of the application
The federal regulatory legal act determines the appropriate body that is authorized to consider the application and take measures to formalize the public encumbrance. This document also contains an indication of the time frame for consideration of such an application along with the submitted documents.
Acts of federal significance do not contain such requirements.
Organization and holding of public meetings
This event is one of the types of public participation in resolving public issues. The result of such hearings shall be a protocol that sets forth the views of the persons participating in the meeting regarding the establishment of the public charge.
The following take part in this procedure:
- the interested population of a specific territorial unit;
- persons representing the interests of organizations located in a specific territory;
- the landowner on whose site it is planned to install an encumbrance;
- persons representing the interests of a state authority or local government.
Decision making and publication of legal acts
The decision to establish an encumbrance must be contained in the legal acts indicating the following information:
- land plot;
- its location;
- cadastral number, which is assigned during the process of surveying the boundaries of the site;
- the landowner whose plot is encumbered;
- the name of the encumbrance and its contents;
- period of validity of the encumbrance and other conditions.
Grounds (goals) for establishing a public easement
Article 23 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, as amended before September 1, 2018, contained an exhaustive list of grounds (goals) for establishing a public easement. Thus, this article contained rules on the possibility of establishing a public easement for the purposes of:
1) passage or passage through a land plot, including for the purpose of ensuring free access of citizens to a public water body and its shoreline; 2) use of the land plot for the purpose of repairing utility, engineering, electrical and other lines and networks, as well as transport infrastructure facilities; 3) placement on the land plot of boundary markers, geodetic points of state geodetic networks, gravimetric points, leveling points and entrances to them; 4) carrying out drainage work on the land plot; 5) intake (withdrawal) of water resources from water bodies and watering places; 6) driving farm animals through the land plot; 7) haymaking, grazing of farm animals in the prescribed manner on land plots at a time the duration of which corresponds to local conditions and customs; use of land for the purposes of hunting, fishing, aquaculture (fish farming); 9) temporary use of a land plot for the purpose of survey, research and other work
2) use of the land plot for the purpose of repairing utility, engineering, electrical and other lines and networks, as well as transport infrastructure facilities; 3) placement on the land plot of boundary markers, geodetic points of state geodetic networks, gravimetric points, leveling points and entrances to them; 4) carrying out drainage work on the land plot; 5) intake (withdrawal) of water resources from water bodies and watering places; 6) driving farm animals through the land plot; 7) haymaking, grazing of farm animals in the prescribed manner on land plots at a time the duration of which corresponds to local conditions and customs; use of land for the purposes of hunting, fishing, aquaculture (fish farming); 9) temporary use of a land plot for the purpose of survey, research and other work
As amended, effective from September 1, 2021, the goals of establishing a public easement in Article 23 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation have not changed significantly: clause 4 of the article contains a similar list of goals, with the exception of:
- pp. 2 “use of a land plot for the purpose of repairing utility, engineering, electrical and other lines and networks, as well as transport infrastructure facilities”
- pp. 9 (“temporary use of a land plot for the purpose of survey, research and other work.”
- pp added 8 (“use of the land plot for the purposes provided for in Article 39.37 of this Code”).
Challenging the normative act establishing an easement in court. Jurisdiction of the dispute
Persons whose rights and legitimate interests are affected by the establishment of a public easement can protect their rights in court, that is, demand in court that the said legal act be declared invalid (Clause 8 of Article 23 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation as amended, valid until September 1, 2021) .
From September 1, 2021, paragraph 14 of Article 23 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation contains the following rule of law:
“Persons whose rights and legitimate interests are affected by the establishment of a public easement may protect their rights in court.”
Paragraph 1 of Article 61 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation provides that ... a normative act that does not comply with the law or other normative legal acts and violates the rights and legally protected interests of a citizen or legal entity in the field of use and protection of land may be declared invalid by the court.
According to Part 1 of Article 27 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, the arbitration court has jurisdiction over cases on economic disputes and other cases related to the implementation of entrepreneurial and other economic activities.
According to paragraph 2.1 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2013 N 58 “On some issues arising in judicial practice when arbitration courts consider cases challenging normative legal acts,” an application for declaring a normative legal act invalid can be filed with the arbitration court if Federal law directly provides for an appeal of a normative legal act to an arbitration court, and also, if the federal law contains an indication for the consideration of disputes in a certain area of legal regulation in an arbitration court, since this means, among other things, the possibility of appealing to an arbitration court of normative legal acts in this domain.
Thus, the legislator, in addition to connecting the subject of the dispute with the implementation of entrepreneurial and other economic activities, determined the need for the court to establish a federal law that would bring the consideration of these cases within the competence of the arbitration court.
Based on the provisions of paragraph 8 of Article 23 and paragraph 1 of Article 61 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, which do not contain instructions that disputes regarding the invalidation of a normative legal act establishing a public easement are within the competence of arbitration courts, such disputes are not subject to consideration by an arbitration court.
Considering the above, for the protection of your rights, in this case, you should apply not to an arbitration court, but to a court of general jurisdiction in the manner set out in the Code of Administrative Proceedings of the Russian Federation with an administrative statement of claim to invalidate a normative legal act of the Russian Federation, a subject of the Russian Federation, or an authority local government.
Easement in relation to a site in state or municipal ownership
Chapter V.3 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation (“Establishment of an easement in relation to a land plot located in state or municipal ownership”) was introduced by Federal Law dated June 23, 2014 N 171-FZ.
Now the Land Code provides for the possibility of establishing an easement in relation to a land plot that is in state or municipal ownership). If such a plot of land is provided for permanent (indefinite) use, lifelong inheritable possession, or for rent or gratuitous use for a period of more than one year, in order to conclude an agreement on the establishment of an easement, it is necessary to contact the land user, landowner, tenant (clause 1 of Article 39.24 ZK RF).
New: norms of the Land Code of the Russian Federation on public easements from September 1, 2021
In addition to the fact that from September 1, Article 23 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation is set out in a new edition, other significant changes have been made.
The Land Code of the Russian Federation has been supplemented with a new chapter V.7 “Establishment of a public easement for certain purposes.” This chapter includes articles regulating the procedure, goals, conditions, terms for establishing a public easement, issues of payment for an established public easement and a number of other issues:
Chapter V.7 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation. “Establishment of a public easement for certain purposes”:
- The purposes of establishing a public easement (Article 39.37 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Bodies making decisions on establishing a public easement (Article 39.38 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Conditions for establishing a public easement (Article 39.39 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Persons who have the right to apply for the establishment of a public easement (Article 39.40 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Petition for the establishment of a public easement (Article 39.41 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Identification of rights holders of land plots in order to establish a public easement (Article 39.42 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Decision to establish a public easement (Article 39.43 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Refusal to establish a public easement (Article 39.44 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Duration of public easement (Article 39.45 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Payment for public easement (Article 39.46 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Agreement on the implementation of a public easement (Article 39.47 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Consequences of the impossibility or significant difficulty of using a land plot (part thereof) burdened with a public easement (Article 39.48 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Features of a public easement established for the purpose of reconstructing an engineering structure that is transferred in connection with the seizure of a land plot for state or municipal needs (Article 39.49 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Rights and obligations of the owner of a public easement (Article 39.50 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation).
Increasing the lease term of a land plot for the period of establishing an easement on it
Article 39.8 of the RF Land Code is supplemented by clause 12.1, according to which:
If, after concluding a lease agreement for a land plot located in state or municipal ownership, a public easement is established in accordance with Chapter V.7 of this Code, the tenant has the right to demand amendments to the lease agreement for a land plot in terms of increasing the term of this agreement by the period specified during which the use of the land plot in accordance with its permitted use is impossible or significantly hampered due to the implementation of a public easement...
Public easement for the construction of linear structures
Public easement for the construction of linear structures
On September 1, 2021, Federal Law No. 341 of August 3, 2021 “On amendments to the Land Code of the Russian Federation and certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation regarding simplification of the placement of linear objects” came into force. The adoption of this law is due to the fact that registration and approval of the construction of linear facilities takes too much time. To simplify this process, the Government of the Russian Federation proposed to introduce a public easement, that is, an administrative decision of a state authority or local government to restrict the right to use a land plot, made at the request of certain organizations. To locate a linear object, a public easement is of interest to its owner because it does not require the formation of a land plot. This means that there is no need to carry out a lot of cadastral work and registration actions, change the category of land and types of permitted use of land plots, seize or provide land plots for use.
The Land Code of the Russian Federation establishes the goals of public easement:
— placement of electrical grid facilities, heating networks, water supply networks, drainage networks, communication lines and structures, linear facilities of the gas supply system, oil pipelines and oil product pipelines, their integral technological parts;
— storage of construction and other materials, placement of temporary or auxiliary structures that are necessary to ensure the construction, reconstruction, repair of transport infrastructure facilities for the period of construction, reconstruction, repair;
— arrangement of intersections of motor roads or railway tracks with public railway tracks, intersections of motor roads or railway tracks with motor roads, or junctions of motor roads with other motor roads;
— placement of roads and railways in tunnels; — carrying out engineering surveys in order to prepare documentation on the planning of the territory, providing for the placement of linear objects, for carrying out engineering surveys for the construction and reconstruction of these objects.
Public easement in relation to land plots for their use for the purposes provided for in Article 39.37 of the Land Code is established by decisions of authorized federal executive authorities, executive state authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, executive authorities, local governments in cases of placement of engineering structures, respectively, federal, regional or municipal significance.
Within five working days from the date of the decision to establish a public easement, the body authorized to establish a public easement is obliged to:
¾ post the decision to establish a public easement on your official website;
¾ ensure publication of the decision at the location of the land plots in respect of which the said decision was made;
¾ send a copy of the decision to the rights holders of the land plots in respect of which the decision to establish a public easement was made, as well as to Rosreestr;
¾ send to the owner of the public easement a copy of the decision to establish a public easement, information about the rights holders of land plots, information about persons who submitted applications for registration of their rights (encumbrances of rights) to land plots, methods of communication with them, copies of documents confirming the rights of these persons to land plots plots.
A public easement will be considered established from the day information about it is entered into the Unified State Register of Real Estate. The decision to establish a public easement may be challenged by the owner of the land plot in court before the expiration of thirty days from the date the owner of the land plot receives the agreement on the implementation of the public easement. Provision of a land plot encumbered with a public easement, transfer of rights to it, formation from it or from lands in respect of which a public easement has been established, a land plot, transfer of rights to an engineering structure located under the terms of a public easement, and identification of rights holders of land plots after the expiration of the term , specified in paragraph 8 of Article 39.42 of the Land Code, do not affect the validity of the decision to establish a public easement and are not grounds for its revision.
When establishing a public easement, a certain fee is provided. Thus, the fee for a public easement in relation to a land plot that is in state or municipal ownership and not encumbered by the rights of third parties is set at 0.01% of the cadastral value of such a land plot for each year of its use. If a public easement is going to be established in relation to private lands, then the fee is determined in accordance with the Federal Law of July 29, 1998 No. 135-FZ “On Valuation Activities in the Russian Federation.” In addition to the fee for a public easement, compensation is subject to losses caused by the inability of the owner of the land plot to fulfill obligations to third parties, as well as other losses caused to the owner of the land plot as a result of activities carried out by the owner of the public easement on the land plot, including losses caused by damage to property.