The legislative framework
The procedure for operating apartment buildings is regulated by the rules for managing apartment buildings, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 416 of May 15, 2013. The second legal document regulating methods of house management is the Housing Code. According to the article, part 3 of Art. 161 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, a residential building can be managed by only one organizational structure. Owners of apartment building premises cannot refuse to exercise the functions of managing joint property. Legislatively, all possible ways of managing apartment buildings are enshrined in Part 2 of Art. 161 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation. The operating procedure of the chosen method is described in detail in Art. 162–164, sections V, VI of the RF Housing Code.
How to register a management company?
To register you will need to complete the following steps:
- register a legal entity;
- obtain a license to engage in such activities;
- carry out the necessary measures to identify all deficiencies, as well as an inventory of fixed assets and other equipment and buildings;
- equip office space;
- calculate the number of required service personnel;
- carry out legal procedures to take the house on the balance sheet of the house management;
- sign agreements with enterprises that provide necessary services for the functioning of the home.
At the very first stage, before creating the most effective management company for apartment buildings, it is not necessary to register a new legal entity, if one already exists. If necessary, you can make changes to the charter of an LLC or organization of another form of ownership.
ATTENTION : the procedure for registering a company has nuances, mistakes lead to monetary losses - watch the video with advice from a lawyer and subscribe to the YouTube channel to get a free consultation in the comments to the video online.
Types of organization of management of apartment buildings
Housing legislation provides for three ways to manage an apartment building. The general meeting of owners, based on its decision, chooses the method of operation and can revise it at any time. Owners of apartments in a new building are also required to make a joint decision on a scheme for maintaining and monitoring the condition of the building. Residents are given 6 months to make an appropriate decision. If the form of property management is not determined within the allotted period, local authorities will organize the selection of a management company using the method of open competitive collection of applications (Part 4 of Article 161 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation).
Direct control
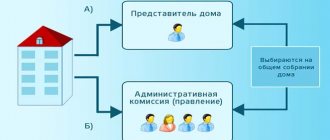
Refusal to involve third parties in the operation of the facility is expressed in the need for the owners to perform these functions independently. There is a restriction for organizing independent maintenance - there should not be more than 30 apartments in the building. With the above method of operation, contracts for the maintenance and repair of the house are signed based on the decision of the general meeting of owners. In this case, all or most of the apartment owners act as one party to the signed agreements. Contractual relations for the provision of utility services are drawn up by each owner on his own behalf.
At a general meeting of residents, one of the owners or another person can be given the right to dispose of common property on behalf of the entire house. To do this, a non-notarized power of attorney is issued to the authorized person in writing, signed by the majority of the owners. When such a document exists, contracts can be concluded by a trustee on behalf of the entire house.
Direct management is a complex type of operation in organizational practice, but a fairly simple type of operation in structure. Local governments are not loyal to this form of administration, because all residents bear equal criminal and administrative liability in the event of any violations. In practice, this means that it is almost impossible to impose a fine on the Civil Property Inspectorate and appoint someone responsible for the violation.
In large houses, this method of operation is impossible; a legal entity will have to be involved in management.
Management through HOA
The general meeting may choose to create a HOA (Housing Owners Association). Such an organization is a legal entity that has the legal form of a real estate owners' partnership (TSN).
The partnership represents the interests of a specific house or group of houses connected by common communications (for example, a common transit water supply). The HOA has the status of a legal entity and is created specifically for the management of the building and cannot engage in third-party issues or any business activities. All contracts with utility companies are concluded on behalf of the HOA and are signed by the chairman. The created structure is responsible to homeowners to the fullest extent of the law. The Partnership is authorized to independently organize, control and carry out work, either with full-time employees or with contractors.
It is assumed that the HOA will only be assigned the functions of organizer and controller. In this case, the management of the partnership enters into operating contracts with contractors and does not have its own staff. At the same time, the HOA is also responsible to the residents for the quality of work.
Operation by management company
The method of managing houses with the involvement of a professional management company is the most common. This method is also supported by local governments as the most manageable structure. The management company, like the HOA, organizes the process of maintaining the housing stock at the proper level by attracting contractors or using its own staff. The company fully ensures the progress of the process, being responsible for the result to the owners of the premises.
Managing an apartment building: methods, practices, problems and prospects
sob is low-cost. However, this only applies to the costs of managing the house; the owners must bear the remaining costs associated with the provision of housing and communal services.
It is not difficult to assume that the real effectiveness of independent management will manifest itself better in conditions of a small number of premises owners. This is due to the fact that effective planning, organization and control of all processes aimed at managing a house are possible if there is a sufficiently small number of owners who have common interests and sufficient moral incentives. The advantages of this management method are especially evident in rural areas, when there is no multi-apartment development.
The decision to choose a method of managing an apartment building directly by the owners is made at a general meeting of owners, who vote by a majority vote of those present. If a direct management method is chosen, the owners of an apartment building, like the owners of individual housing, directly enter into contracts with resource supply organizations.
Housing maintenance in the case of choosing a direct method of managing an apartment building is carried out either by the owners themselves or by contractors brought to the site. One management company can also act as the latter. But at the same time, it is also only a contracting company performing the work; its responsibilities do not include either protecting the rights of owners or resolving other organizational issues.
1.3 Homeowners Association Management
When managing an apartment building by a homeowners' association or a housing cooperative or other specialized consumer cooperative, the said partnership or cooperative is responsible for the maintenance of common property in a given building in accordance with the requirements of technical regulations and the rules established by the Government of the Russian Federation for the maintenance of common property in an apartment building, for the provision of utilities depending on the level of improvement of a given house, the quality of which must meet the requirements of the rules established by the Government of the Russian Federation for the provision, suspension and limitation of the provision of public services to owners and users of premises in apartment buildings and residential buildings. The said partnership or cooperative may provide services and (or) carry out work on the maintenance and repair of common property in an apartment building on its own or attract, on the basis of contracts, persons carrying out the relevant types of activities.
When concluding an agreement for the management of an apartment building with a management organization, the specified partnership or cooperative exercises control over the management organization’s fulfillment of obligations under such an agreement, including the provision of all services and (or) performance of work ensuring the proper maintenance of the common property in this building, the provision of utilities services depending on the level of improvement of a given house, the quality of which must meet the requirements of the rules established by the Government of the Russian Federation for the provision, suspension and limitation of the provision of utility services to owners and users of premises in apartment buildings and residential buildings.
A homeowners' association is a membership-based non-profit organization, a voluntary association of owners of premises in an apartment building for joint management, maintenance, ownership, use and, within the limits established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, of a complex of real estate (common property).
The HOA has special legal capacity. It has the right to engage only in those types of activities that are specified in its charter and correspond to the purposes for which it was created.
The owners of premises in an apartment building can choose only one management method; therefore, only one HOA can be created to manage an apartment building. The basis for the management of an apartment building by an HOA is the decision of the general meeting on the choice of the appropriate management method, which is adopted by a majority vote of the number of votes of the owners who took part in the general meeting or in absentee voting. Therefore, at the general meeting to create the partnership, it is also necessary to make a decision on choosing the appropriate method of management.
The object of management of a homeowners' association can be not only an apartment building, but also several houses that are united by a single land plot, adjacent land plots or other common property (engineering communications). Moreover, this common property should be intended to serve only these few houses.
Experts consider the management of an apartment building by a homeowners' association to be the most progressive method, since the association, being a legal entity, is able to most effectively conduct business activities and lobby for the interests of residents. Unlike individual homeownership, in an apartment building where hundreds or thousands of people live, the direct method of management is ineffective. At the same time, the HOA consists of the home owners themselves - in contrast to a third-party management organization, the purpose of which is to make a profit from someone else's property.
When managing an apartment building by a management organization, it is responsible to the owners of the premises in the apartment building for the provision of all services and (or) performance of work that ensure the proper maintenance of the common property in this building and the quality of which must meet the requirements of technical regulations and rules for the maintenance of common property established by the Government of the Russian Federation property in an apartment building, for the provision of utilities depending on the level of improvement of the building, the quality of which must meet the requirements of the rules established by the Government of the Russian Federation for the provision, suspension and limitation of the provision of utilities to owners and users of premises in apartment buildings and residential buildings.
1.4 Management of the management organization
A management organization is a commercial organization to which, by decision of the general meeting of premises owners, the powers to manage the common property of an apartment building, create favorable and safe living conditions for citizens and provide housing and communal services can be transferred. Management organizations carry out their activities in accordance with the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and federal laws “On limited liability companies”, “On joint stock companies”, “On state and municipal unitary enterprises”, “On production cooperatives”, “On state registration of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs”, as well as on the basis of management agreements for an apartment building.
Owners of apartment building premises can choose a management organization:
* on a competition basis;
* according to the list prepared by the initiative group, i.e. without competitive selection.
The owners of the premises must develop and approve the Regulations on the competitive selection, which sets out the criteria for selecting the organization. All organizations that submitted applications to participate in the competition are selected taking into account the criteria specified in the Regulations.
If the owners do not conduct a competitive selection, then the selection of the organization's managers is carried out arbitrarily at the discretion of the majority of the owners of the premises. First, a list of management organizations is compiled, then at the general meeting the advantages and disadvantages of each of them and the conditions for concluding a management agreement are announced. By decision of the general meeting, a management organization is selected, and then contractual work with it begins, which ends with the signing of a management agreement between the selected management organization and the owners of the premises.
The management agreement for an apartment building is concluded in writing by drawing up one document and signed by the owners of all premises of this residential apartment building, on the one hand, and the head of the management organization, on the other. The required number of copies of the contract is determined by the number of premises in the house.
The method of managing an apartment building is chosen at a general meeting of owners of premises in the apartment building and can be chosen and changed at any time based on its decision. The decision of the general meeting on the choice of management method is mandatory for all owners of premises in an apartment building.
The local government body, in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation, holds an open competition for the selection of a management organization if, within a year before the date of the said competition, the owners of premises in an apartment building have not chosen a method of managing this building or if no decision has been made on choosing a method of managing this building implemented.
CHAPTER 2. PRACTICE, PROBLEMS AND PROSPECTS FOR MANAGING MULTIPLE APARTMENT BUILDINGS
2.1 Management practice of apartment buildings
As practice has shown, the choice of method for managing an apartment building is influenced by a number of subjective factors: technical features and condition of the object, the mentality of the owners, the level of development of market relations in the local housing sector. In different cities and regions, preferences are given to different forms of management of apartment buildings, which is also largely influenced by the number of floors and building density.
Currently, on the territory of the municipal formation “City of Vologda” there are about 3 thousand apartment buildings with a total area of 6,957 thousand sq.m.
More than 64% of them have served longer than 25 years and require major repairs.
As part of the major repair work carried out, the largest share is occupied by work on the repair of elevator equipment.
Another problem of the housing stock is dilapidated housing. The demolition of dilapidated housing in the city of Vologda is carried out by the department for organizing the maintenance and major repairs of municipal housing stock of the Department of Urban Planning and Infrastructure of the Vologda City Administration as part of the implementation of the Federal Law of July 21, 2007 No. 185-FZ “On the Fund for Assistance to the Reform of Housing and Communal Services” according to the approved List.
The list of the “city of Vologda” includes data on 84 Managing organizations, 182 HOAs and 27 housing cooperatives, serving 2,506 houses with a total area of 6,919,661 sq.m., in which 180,849 people live.
In most regions, the largest number of apartment buildings have chosen the direct method of management. But if you measure indicators not in the number of buildings, but in areas, management companies often come in first place.
2.2 Problems of managing apartment buildings
As is known, the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, introduced in 2005 by Federal Law 189-FZ “On the Enactment of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation,” significantly changed the management system of the housing stock in general and apartment buildings in particular. He proposed new approaches to regulating social relations that arise between the owners of premises in an apartment building regarding their common property.
The main thing is that an exhaustive list of types of residential premises - objects of housing rights - was determined. The legal regime of the common property of premises owners in an apartment building, the procedure for owning, using and disposing of it are regulated in detail. The methods and bodies for managing an apartment building and the procedure for coordinating the will of the owners of the premises have been determined. Both external contractual and internal representative relations were reflected in the implementation of management activities.
In fairness, it must be admitted that the LC is replete with innovations that fill previously existing legal voids, and contains obvious achievements. However, not everything is so smooth, since you don’t need to be a major specialist to see the obvious: most of the progressive norms adopted at first glance have not worked fully.
Owners of premises in apartment buildings, despite the obligations assigned to them by the Housing Code, have today taken a very restrained position regarding their participation in the management of the building. Their lack of enthusiasm for self-organization is motivated by distrust and serious concerns; they believe that the authorities are still disingenuous when they present the process of transferring to the owners of premises the right to manage the entire complex of real estate (formed on the basis of their apartment building) as a great blessing. The only thing that guided them was the desire to quickly get rid of the extremely dilapidated housing stock that was weighing heavily on the state. This suspicion, unfortunately, is partly confirmed by the current norms of housing legislation.
The Housing Code no longer contains the concept of “housing stock management” and the state’s responsibilities associated with such management. Apparently, the legislator considered it possible to replace it with the management of an apartment building, the implementation of which is entrusted to the owners of the premises. Meanwhile, it would be naive to believe that by transferring the management of individual apartment buildings to the owners of the premises, in one fell swoop one can solve all the existing problems and relieve oneself of responsibility for the state of affairs in this area. The state, as before, in addition to regulation and control, must provide assistance in the creation, maintenance, operation and development of the housing stock.
The creation in 2007, on the basis of Federal Law N 185-FZ dated July 21, 2007, of the state non-profit corporation “Fund for Assistance to the Reform of Housing and Communal Services” with a capital of 240 billion rubles, intended for the “reanimation” of dilapidated housing stock, was a serious step in the right direction. However, in order to provide financial assistance, the Law on the Fund (Article 14) provides for a long list of difficult conditions, designed, in the opinion of the legislator, to simultaneously solve, along with restoration measures, organizational problems in the housing and communal services sector, namely, to encourage owners to create HOAs en masse.
In addition, by ordering the owners of premises to manage their apartment building, housing legislation establishes that such management must ensure favorable and safe living conditions for citizens (Part 1 of Article 161 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation). It seems that such requirements for the owner and the management carried out by him are not entirely acceptable, since in accordance with Article 1 of the Federal Law “On the Sanitary and Epidemiological Welfare of the Population”, the concept of “favorable conditions” means the state of the environment in which there is no harmful impact of its factors per person, and “security” is the state of protecting the vital interests of the individual and society from all threats. Obviously, neither one nor the other can be fully provided by the owners of premises in an apartment building. Moreover, assigning such responsibilities to them is a direct substitute for the competence of numerous government bodies directly charged with ensuring favorable and safe living conditions for citizens, as provided for in Articles 5 and 6 of the Federal Law “On the Sanitary and Epidemiological Welfare of the Population.”
Most apartment owners, even today, know little about the scope of their rights, much less about the possibilities and necessity of participating in the management of an apartment building. It also failed to create a competitive market for services offered by management organizations, which is extremely necessary for the success of housing and communal reforms.
Alas, almost every apartment building (with the exception of elite buildings) is represented by owners with disproportionate levels of wealth. Some, who make up the majority, received as a result of privatization the ownership of premises occupied by them under a social tenancy agreement, and have difficulty paying for utilities, others purchased an apartment in the same building, and can afford additional costs for the development and improvement of the local area. The existence of such social and property inequality also negatively affects the process of self-organization and development of agreed decisions by the owners of premises in one apartment building.
Many provisions of housing standards, regulating various issues of managing an apartment building, do not take into account, and often neglect, the interests of the owners. Thus, the legal status of the general meeting of owners of premises in an apartment building, the procedure for making decisions by the general meeting, as well as the mechanism for appealing them, leaves a very ambiguous impression.
2.3 Prospects for managing apartment buildings
apartment building partnership management
Today, housing and communal services are a technically complex economy that requires new developments and new technologies so that service structures “not only load residents with volumes of services, but also reduce the cost of these services.”
In the conditions of improvement of the national economy (reform of housing and communal services), the most important criterion for assessing the work of housing and communal services is customer focus. What customer focus is is, first of all, a characteristic of the business itself. It reflects the place of the client’s interests in the system of priorities of management and owners.
If we want to work professionally and efficiently, then the management of an apartment building must be “smart”. It is necessary to break the stereotype of the “Soviet Department” in management. That is, in our management there are now 2 types of managers of apartment buildings:
- leaders who left the
Some of the work is hidden to preserve uniqueness. Register and receive fragments + free estimate of the cost of unique work by email.
Vetish governing structures;
- managers whose main goal is to quickly make a profit.
Accordingly, no type of management is suitable for client-oriented, high-quality management of an apartment building. We need leaders of the “new generation” who will have a sufficient level of knowledge, education and the desire to put them into practice in the field of management. And this does not mean at all that it is necessary to change a leader of type 1 or 2 to a leader of the “new generation” - this means that improving the management of an apartment building should be in the “minds” of managers, which will lead to further professional transformation of management in the industry.
It is no secret that customer service is one of the weakest points in the activities of housing and communal services enterprises. Many have experienced the increase in housing and communal services tariffs and the reason for our indignation is not that they have actually increased, but that with the increase in tariffs we do not see an improvement in the quality of service. After all, if you compensate for the increase in tariffs by at least improving service and focusing on the consumer, then consumer loyalty will increase. In turn, the formation of public opinion will include an understanding: increased tariffs - improved quality of service. The quality of services can be improved through transparency of accounting and prompt response to consumer requests, and for this it is necessary to introduce modern software in the industry, keep up with the times, through automation of business processes, and the creation of a unified information system.
As you know, the current housing legislation provides for three ways to manage apartment buildings: management by a management organization, management of an HOA and direct management. The recently adopted federal law of July 21, 2014 N255-FZ on licensing activities for managing apartment buildings affects all three of these methods.
The overwhelming majority of the provisions of federal law 255-FZ came into force on September 1, 2014, but many specialists in the housing and communal services sector have been concerned about the upcoming licensing of activities for managing apartment buildings since the drafting of the bill. I would like to note the following point: according to the adopted law, only management organizations are subject to licensing. It turns out that of the three methods of managing apartment buildings provided for by law (management of the management organization, management of the HOA, direct management), only one will be affected in the licensing process.
And it seems that HOAs and owners who manage houses directly can “exhale a sigh of relief,” but it turns out that 255-FZ makes changes to the Housing Code of the Russian Federation not only in terms of licensing. Thus, Article 4 of the new law establishes that an HOA created in two or more houses, if these houses have a total of more than 30 apartments, must be reorganized before July 1, 2021.
Paragraph 5 of Article 7 establishes that the owners of apartment building premises, the number of apartments in which is more than 16, in the case of direct management of such a house, are obliged to hold a general meeting of premises owners before April 1, 2015 and choose a different method of management.
Thus, direct management can only be maintained in small buildings, the number of apartments in which is no more than 16. Large HOAs that manage two or more buildings will be reorganized.
It seems that management companies do not care about these processes, if not for one significant point. If direct management is not possible in an apartment building, and the HOA has been reorganized, such a house can only be managed by a management organization, which will either be elected by a general meeting of premises owners, or selected by local government bodies based on the results of an open competition.
It turns out that Law 255-FZ provides for the transition of the overwhelming majority of apartment buildings in Russia to the management of management organizations, which will be required to be licensed. Accordingly, the presence in the market of HOA management and owners who manage their homes directly can be minimized.
CONCLUSION
The research carried out within the framework of this work allowed us to formulate a number of main conclusions.
Previously, in all regions there was a situation in which the majority of the market for services for managing the municipal housing stock was occupied by municipal unitary enterprises. Small businesses produced only 6% of the volume of services in housing and communal services.
The process of reforming the management of the housing stock is currently being completed. The state gives homeowners the right to choose the method of management and thereby take part in reforming the housing and communal services. And the sooner homeowners realize this, the more benefit they will be able to take advantage of the rights granted to them. After all, in the end, self-government in the housing sector is one of the most effective ways to protect the rights of homeowners, control on the part of the population over the volume and quality of housing and communal services, influence the cost and quality of services provided, and allows creating conditions for attracting additional sources of financing for housing maintenance and repair.
Owners of premises in an apartment building are required to choose one of the management methods: direct management by the owners of premises in an apartment building; homeowners association management; management of the management organization. In the first case, the owners do not have the status of a legal entity, and therefore are limited in economic activities, without which the management of an apartment building is difficult, and in the latter, they are deprived of the ability to control the activities of the management organization and influence it. The most rational form of management is the creation of a homeowners' association.
With the introduction of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, emphasis is placed on the homeowners' association as one of the effective forms of managing an apartment building. He is given a wide range of powers: managing an apartment building, concluding agreements on the maintenance and repair of common property in an apartment building, and on the provision of utilities.
The reform of housing legislation should not be stopped. It needs further improvement, which will cover a wider range of issues, and contribute to the introduction of self-management of housing.
Supplement the Housing Code with a number of rules to ensure the exercise of the rights of HOA members to participate in general meetings and prevent possible abuses in this area. In particular, it is necessary to establish the exclusive nature of the competence of the general meeting; the timing of the annual general meeting and the issues that must be resolved at it; the procedure for convening and holding general meetings, including the rules for the participation of members of the partnership in the formation of the agenda, the procedure for the participation of members of the partnership in general meetings, the rules for documenting the convocation, conduct and results of the general meeting; the procedure and conditions for holding extraordinary general meetings and meetings in the form of absentee voting; the period for appealing decisions of the general meeting in court. It is also necessary to establish requirements for the content of the HOA charter and the procedure for members of the partnership to receive information about its activities.
Supplement the Housing Code of the Russian Federation with rules governing relations between a cooperative managing an apartment building and owners who are not its members.
In my opinion, the choice of method for managing an apartment building is influenced by a number of subjective factors: technical features and condition of the object, the mentality of the owners, the level of development of market relations in the local housing sector. In different cities and regions, preferences are given to different forms of management of apartment buildings, which is also largely influenced by the number of floors and building density.
LIST OF SOURCES USED
1. The Constitution of the Russian Federation (adopted by popular vote on December 12, 1993) (taking into account the amendments introduced by the Laws of the Russian Federation on amendments to the Constitution of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2008 N 6-FKZ, dated December 30, 2008 N 7-FKZ, dated February 5, 2014 N 2 -FKZ, dated July 21, 2014 N 11-FKZ) // SPS ConsultantPlus, 2014.
2. Housing Code of the Russian Federation dated December 29, 2004 No. 188-FZ (adopted by the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation on December 22, 2004) (current edition dated July 21, 2014) // SPS ConsultantPlus, 2014.
3. Federal Law 189-FZ of December 29, 2004 “On the implementation of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation” (as amended and supplemented, entered into force on September 1, 2014) // SPS ConsultantPlus, 2014.
4. Federal Law of July 21, 2007 N 185-FZ (as amended on July 21, 2014) “On the Fund for Assistance to the Reform of Housing and Communal Services” // SPS ConsultantPlus, 2014.
5. Federal Law of March 30, 1999 N 52-FZ (as amended on June 23, 2014) “On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population” // SPS ConsultantPlus, 2014.
6. Federal Law of July 21, 2014 N 255-FZ (as amended on November 24, 2014) “On amendments to the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation and the recognition as invalid of certain provisions of legislative acts of the Russian Federation” // SPS ConsultantPlus , 2014.
7. Alexy, P. V. Housing Law: a textbook for university students studying in the specialty “Jurisprudence” / P. V. Alexy et al.; edited by I. A. Eremicheva, P. V. Alexia. – 7th ed., revised. and additional – M.: UNITY-DANA: Law and Law, 2012. – 480 pp.
Which option is preferable?
The management method is selected based on the owners’ ability to organize the process. If among the residents there are proactive citizens who are capable of creating a partnership with their own hands and managing all issues related to housing and communal services, then this option of individual management cannot be excluded as the optimal choice.
Pros of HOA:
- better service than any other management method
- low operating and repair costs
- high involvement of residents in the process of property operation
- with the proper persistence and efficiency of the chairman, the house can be carried out according to city improvement and repair programs.
- transparency of the financial balance of the house and reporting to residents
Disadvantage of HOA:
- low competence of staff specialists or their absence
- lack of own material resources
- high management costs
- low financial stability in case of errors in tariff setting
Transferring affairs to the management of a management company is the best option for managing a large city house. Residents will not need to be distracted from their own concerns and regularly participate in solving specific issues. This is the competence of the management company. This option is considered convenient and not burdensome for most apartment owners.
Pros of the management company:
- high competence of staff specialists
- financial stability
- own material base
- high integration with resource supply organizations
Disadvantages of the management company
- high tariffs
- low quality of service
- slow reaction to changes occurring in the house
- higher level of house receivables
- non-transparency of the financial balance of the house and incomplete reporting to residents
Self-government of MKDs is rarely organized. This is due to the low efficiency of this type of property management, the high responsibility resting on the owners of the premises themselves, and the owners’ lack of free time. All this does not encourage such a choice.
Pros:
- no administrative expenses
- maintenance and cleaning of the house can be carried out by residents
- low estimates for all work
- everyone is responsible only for their debts on utility resources
Minuses:
- very low controllability
- low competence of residents in housing and communal services surveys
- it is impossible to use subsidies from the Housing and Communal Services Reform Fund for major repairs
- there is no single person responsible for any of the issues
The procedure for selecting the control form of MKD
It is mandatory for all premises owners to decide on the algorithm for operating MKD. After putting a new house into operation, the developer, within a period of no more than 5 calendar days, engages an operating organization for operation for a maximum period of 20 days. During this time, new residents must choose one of the control methods.
In practice, the following are considered facts confirming the absence of the selected management option:
- the owners did not sign a contract for the maintenance and repair of common property
- there is no certificate of registration of the HOA
- there is no agreement with the management company
If the choice of option for servicing the house by the residents is not made, local authorities (district or city administration), after 20 days from the date of delivery of the house, organize a competition, within the framework of which a company is determined with which a management agreement is concluded on behalf of the residents of the house. The competition lasts no more than 40 calendar days. Based on the selection results, residents are informed about the results of the event. After the completion of the competition, 2 months are allotted to draw up an agreement with the winning company or legally formalize another decision of the residents.
Citizens can also reconsider the way the building is used at any time. The right to determine the method is vested in the general meeting of residents. To make a change, the initiative group organizes a vote, the result of which is the choice of one of three management methods. The choice is considered legal if at least 50% of the owners vote positively. Documentary evidence is considered to be a properly drawn up protocol on the choice of method for managing the microdistrict.
How do you choose a home control method?
To begin with, a group of activists is created that is preparing for a general meeting of residents. It is necessary to ensure the attendance of more than 50% of owners.
If, based on the results of the meeting, direct management or cooperation with the management organization was chosen, then it will be necessary to conclude agreements with suppliers of the necessary resources or with the company. If an HOA is created, you will need to go through the procedure of registering a legal entity with the Federal Tax Service.
The meeting may be held in person or in absentia. In the first case, the personal presence of the owners of residential premises is implied. This is rational if there are few apartments in the house. In absentia form, the owners convey their decision on paper (using a questionnaire or ballot). Subsequently, the results are entered into the protocol.
If you have any questions, please seek legal advice. You can get legal assistance on our website.
Now you know how to choose a method for managing an apartment building. Particular attention should be paid to the characteristics of each option and the procedure for holding a general meeting of residents.
Procedure for completing the protocol
The decision of the general meeting of owners, especially on an agenda requiring confirmation of legal force, must be properly documented in minutes. It is carried out in full-time and correspondence form. It is important to know what is included in the list of required protocol parameters. The following items are required:
- number, date, number of people gathered, exact address of the object
- agenda with a list of issues
- decision on each item on the agenda with the indicated number of votes “for” and “against”
- signatures of authorized persons (chairman, secretary)
- Additionally, the approved decision is written down
Sample minutes of the general meeting
It is important for homeowners of any apartment building to have an understanding of management functions and the procedure for their implementation. Everyone has a choice to make. It is necessary to approach the decision-making process carefully and seriously, since there is nothing more important than the conditions in which we live.