Home » Inheritance » How to write a will without a notary
33
A will is nothing more than a written statement of the posthumous dispositions of the testator. It becomes a legally significant document only after a certain procedure has been completed. And responsibility for its correctness and legality rests with notaries. Authorized specialists ensure compliance with all established rules, certify the document and enter information about it into a specialized register.
But in real life, citizens do not always have free access to a notary. Due to a remote location, serious illness, or being in extreme, life-threatening conditions, the testator objectively cannot resort to the services of a notary, but this should not become a basis for a violation of his legal rights. That is why the law provides exceptions.
What should a will be in theory?
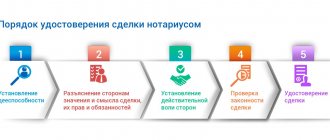
The standard procedure for probating property is as follows:
- The testator contacts a notary office or calls a specialist to your home.
- Then he draws up the will itself. The declaration of will can be written in the presence of a notary or in advance. In the first case, the statement of the citizen’s last will is not necessarily carried out by him personally - a notary can do this instead of him. But this requires certain reasons, for example, poor eyesight of the testator, illiteracy or general physical weakness.
- The notary explains the key legal provisions to those present.
- The document is signed by the testator in the presence of a notary. However, if the testator is objectively unable to sign with his own hand, a specially invited person (a hand-appler) can do this instead.
- An authorized person (notary) makes the certification - puts a personal signature and seal, and indicates the necessary notes.
- The testator receives his own copy of the will, with which he is free to do as he pleases.
In addition, when registering a declaration of will with a notary, it is important to consider the following points:
- The will is drawn up in two copies.
- A citizen may not present title documents for bequeathed property, since he has the right to dispose of his future property.
- There should be no unspecified corrections, cross-outs or blots in the text of the will. If the notary or the testator made a technical error, its correction must be certified separately.
- If you want to make significant amendments to the document (cancel or change some orders, or even completely cancel the expression of will), corrections in the already written text are not made. To do this, the testator draws up a new act with instructions that are relevant to him or simply a statement to cancel the will.
- Any discrepancy between the will and the established form entails its nullity (any notary has the right to recognize such an act as invalid without the participation of a judge).
- For certification of the act of last will by a notary, a citizen must pay a state fee and for notarial services of a legal and technical nature.
Some of these instructions are significant not only in cases of notarial execution of a will. Read more about this below.
Why do you need a will?
To dispose of personal property after death at your own discretion, you need to prepare a will in advance. According to the law, property is usually transferred to close relatives, but if you draw up a written statement of will, you are allowed to transfer assets to third parties (friends, colleagues, lovers).
In this case, you need to know whether you need to contact a notary’s office or you can draw up an order at home. To answer this question, you need to understand the purpose of the expression of will and the legal requirements for the document.
Purposes of writing the paper:
- determination of the circle of persons who are entitled to issue an inheritance;
- compiling a list of property that is due to successors;
- inclusion of a friend, colleague, acquaintance or stranger among the heirs (the third party does not need to prove the existence of family ties with the deceased, it is enough to provide a copy of the last will of the deceased);
- determining the share of each claimant to the inheritance.
To dispose of one’s property, a minimum number of requirements are put forward to a citizen. The main thing is that the person is of age and capable. An individual aged 16 years who is officially employed or married can also draw up a document.
To draw up the paper, you only need a passport. In rare cases, you will need a certificate confirming the citizen’s legal capacity. You should also provide information about the heirs, but their passports are not required, the data is dictated by the testator.
A will without a notary is drawn up at your own request. If it can be confirmed that the testator was forced to write the document, then the document is considered invalid. The main requirements for the testator are a clear mind and full awareness of what is happening. A notary will not accept the will of a drunk or drugged person.
The order must be drawn up by one person on his own behalf. But at the same time, this person has the right to write several statements of will at once. So, in one document it is written down who the house is assigned to, in the second - a car, in the third - a testamentary refusal (the successor is assigned responsibilities associated with a third party).
The composition of the order is kept secret, information is not disclosed to people who did not participate in the execution of the paper. After the death of the testator, the act of the deceased’s last free will is read out. You can challenge a will in court by proving the incapacity of the deceased, the absence of special circumstances, the presence of pressure on the citizen, etc.
The order does not deprive relatives of their obligatory share. This portion is due to people who are temporarily or permanently unable to engage in labor activity: young children, dependents, disabled partners, etc. Also, a widow or widower cannot be deprived of a marital share (50% of property acquired jointly during marriage).
Is it possible to write a will without a notary?
It is definitely possible to write a will without a notary. The testator has the right to even involve a lawyer in this matter in order to avoid mistakes and use the powers granted to him to the fullest. The main thing is to sign the document in the presence of an authorized person. But even at this stage, the services of a notary are not at all necessary.
Strictly speaking, it is not always permissible to fully execute a will without a notary. To do this, certain circumstances must exist, namely:
- absence of a notary at the place of residence of the testator;
- the presence of a serious threat to the life of a citizen who wishes to leave posthumous orders;
- limited physical capabilities of the testator;
- bank deposit will.
Depending on the conditions that prevent the receipt of notarial services (permitting their absence), the following may certify a will instead of a notary:
- Heads or other officials of administrations of remote settlements or inter-settlement areas where there are no notaries.
- Consuls of the Russian Federation's missions abroad.
- Directors, chief or duty doctors of homes for the disabled or elderly.
- Chief or duty doctors of medical institutions.
- Captains of ships sailing under the flags of the Russian Federation.
- Heads of intelligence, scientific, research bases, expeditions or stations.
- Heads of prisons.
- Commanders of military units.
- Authorized bank employees.
However, according to Art. 1127 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, if a citizen still wants to certify his posthumous orders with a notary, the persons specified in paragraphs 3–8 are obliged to take the necessary measures for this (if there is an objective possibility).
Who can certify a will instead of a notary?
Previously, heads of local administrations could certify a will. However, according to the new rules, certification is carried out only by a notary. Therefore, residents of small settlements will have to go to the city to contact a notary office.
The following persons can certify an order instead of a notary:
- the head physician of the hospital where the testator is being treated;
- commander of a military unit;
- director of a correctional facility;
- captain of a ship sailing in the Russian Federation;
- head of the expedition.
Is a will valid, not certified by a notary, written by hand?
The absence of a notarization does not always invalidate a will. A declaration of will that was drawn up under the circumstances described above is equivalent to a notarized declaration. But for this it is important to comply with the following conditions:
- presence of the signature of an authorized person (acting notary specified in the previous block);
- the presence of witnesses (their number depends on the specifics of the act);
- subsequent transfer of the document to a notary at the place of residence of the testator or to the notary chamber.
Wills, which by law must be executed exclusively in notarial form, may be declared invalid without a notary’s certification. This applies to all property orders of the testator that do not relate to bank deposits and those that he can independently and at the right time formalize with a notary. For example, a closed will (transferred by the testator in a sealed envelope) without the notarial actions necessary in this case is void.
As for acts of last will written out by hand, doubts about the validity of the document are absolutely unfounded. The “Methodological Recommendations for Certifying Wills”, approved by the Board of the Federal Chamber of Notaries, repeatedly mentions the freedom of the testator in choosing the method of writing the act. Orders written by hand or by means of technical writing media (PC) will be equally valid.
Moreover, when making some types of wills, the text written by the testator’s hand is a criterion for the validity of the will. This applies to documents drawn up in closed form or drawn up in emergency circumstances.
How to make a will
The main nuances of drawing up orders are specified in Article 1118 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. There are two options for writing a document:
- the applicant makes the will personally;
- The text is written by the notary from the words of the testator.
The order must be created in writing and requires notarization. Handwriting or typing on a computer is acceptable. The text of the document should be simple, understandable, avoiding inaccuracies and ambiguities.
The following types of orders do not require notarization:
- Written in emergency circumstances in the presence of two witnesses.
- Certified by bank employees. The effect of such testamentary dispositions applies only to bank accounts opened in a specific financial institution.
The text of the order must contain the following information:
- Date and place of compilation.
- Title of the document;
- Information about the testator: full name, passport details, address.
- Information about alienated property.
- List of heirs indicating their shares. If the testator does not indicate the size of the share of each of the recipients, then the property will be distributed equally between them.
- Signature of the testator or his authorized representative. In the latter case, the reason is indicated why the compiler cannot independently sign the document.
- Details of witnesses present when drawing up the order.
- A reference to the fact that the testator is aware of the need to allocate a share to obligatory heirs.
- A note confirming payment of the notary fee and state fee.
What documents will be required
To draw up a testamentary disposition, a citizen will need an identity card. In addition to the passport, the testator can present the following documents to the notary:
- military ID;
- international passport;
- birth certificate;
- personal electronic card;
- seafarer's identity card;
- service ID (for employees of the prosecutor's office).
The main requirement for drawing up a will is legal capacity. Therefore, minors cannot draw up such orders unless they provide one of the following documents:
- Marriage certificate;
- court decision on emancipation.
Drawing up a will for close relatives
The nuances of writing orders do not depend on the degree of relationship between the testator and the recipient of the property. If a citizen wants to transfer his assets to his closest relatives, then he just needs to indicate the recipients in the text of the document. But in some cases, drawing up a will for family members is inappropriate. For example, a man assigns his property to his daughter and son, who are his only heirs and will therefore receive the assets by law.
Drawing up a will makes sense when the testator wants to change the order of distribution of the inheritance. You can do this as follows:
- Transfer property to third parties, depriving it of legal heirs.
- Determine the objects that will go to each recipient. For example, a citizen signs off an apartment to his wife, and a car to his son.
- Leave all property to one successor if there are other legitimate claimants.
- Eliminate one or more heirs, recognizing them as unworthy. For example, a daughter did not care for her elderly father. The man indicated in his will that she would not receive anything by distributing the property between his son and wife.
How to make a will without a notary (sample)
As mentioned above, a citizen has the right to write his posthumous orders in advance, before his visit to the acting head. O. notary. In most cases, he can use a computer and then print out the typed text. And only when making a closed will is the last will of the testator expressed by hand.
However, the above does not deprive the testator of the right to choose a different method of drawing up the document - directly during execution. An authorized person can even help with this and transfer the essence of the will onto paper instead. In this case, the contents of the act are written down by him under dictation, after which a mark is placed next to it stating that the will was written according to the words of the testator, as well as the reason for such execution.
In the case of a will being presented from the words of a citizen, it is important that the testator re-read what was written, but he can also entrust this task to an authorized specialist, who records this circumstance with the phrase “read out loud to the testator for a reason (name of a physical disability or other feature of the will-maker).
After the preparatory stages, the certification procedure begins. It consists of signing the document by the testator and an authorized person, affixing a seal indicating special powers, etc. O. notary, and registration of the deed.
Serious illness, infirmity or illiteracy of the testator frees him from the need to personally sign the will. In such situations, a person who is capable of action and, no less important, is not interested in the inheritance is needed. He signs instead of the testator, and next to it indicates his full name and permanent address.
Attention! If the property dispositions of the testator are certified not by officials of local administrations and consuls, but by other authorized persons, the signature of the testator must be made by him personally and always in the presence of a witness. The witness also puts his signature on the paper.
Design rules, form, content
Writing a declaration of will begins with the words “Will”. If the text is typed on a computer, this inscription can be written in capital letters (Caps Lock).
The next line indicates the date of the act in words, for example, “December tenth two thousand and seventeen.”
Next, the testator needs to introduce himself - write his full name (in full), date of birth, place of registration and passport details. After this, you can move directly to the essence of the expression of will. Here you can specify:
- desired heirs and persons who can inherit in their place (in case of refusal, non-acceptance or death of the former);
- objects of inheritance separately or all property belonging to the day of death (this will include even that which was not the property of the testator at the time of drawing up the will);
- the size of the shares due to the specified successors (if this is not done, the property will pass to them in equal parts), or the full name plus a brief description of the individual objects that the citizen intends to bequeath;
- orders regarding the disinheritance of specific heirs by law;
- the obligation to fulfill a testamentary refusal (a material service that the heir will have to provide to the appointed person at the expense of the property received);
- testamentary assignment (actions aimed at achieving a generally beneficial goal of a property or non-property nature, which the successors will have to fulfill);
- executor of his last will, a list of tasks assigned to him and recommendations for their implementation.
At the end of the will, it is necessary to note the features of writing the will - whether it was done personally, or from the words of the testator by the certifying person, who read it, and, of course, the signature of the testator (in the cases provided for this, also the signature of witnesses and the executor).
A will executed without a notary may look something like this:
Will made in emergency circumstances
In exceptional cases, posthumous orders of a citizen may be recognized as valid even without the identification of authorized persons. This applies to acts of expression of will committed under emergency circumstances.
The very concept of emergency situations is not directly disclosed by the legislation of the Russian Federation. As legal practice shows, this means that the testator is in conditions that clearly threaten his life and prevent him from contacting a notary or other authorized persons. In this case, it does not matter whose fault the extreme situation arose, the only important thing is that the testator found himself in the very epicenter of it and acted of his own free will.
Will made under emergency circumstances:
- It is stated in simple written form, necessarily in the hand of the testator.
- Signed personally by the testator in the presence of two witnesses.
- Contains direct and unambiguous instructions regarding the future fate of the testator’s property.
But that is not all. To become a legally significant document, the will of the testator must be recognized as valid. And this can be done in two different ways (the procedure depends on whether the testator remained alive or died within a month after the will was made).
If a citizen who has expressed his own will in extreme conditions manages to survive, he must secure the legal force of the act within a month with a notary or another person replacing him. Otherwise, such a will will be revoked.
The death of the testator before the specified period entails other consequences. The text he wrote will be recognized as a legal expression of will by his heirs or other interested parties in court. They will have to prove the existence of extraordinary circumstances, the impossibility of the now deceased turning to a notary and his freedom of will when presenting posthumous orders. And only after receiving the appropriate court decision do they receive the right to inherit under a will.
Testamentary disposition
Another type of will that can be written without a notary is a testamentary disposition for a bank deposit. The testator has the right to make it directly at the branch of the credit institution where the deposit was opened.
The powers of the person certifying the act are vested in the bank specialist, and otherwise the procedure for drawing up the document is identical to the execution of the act of last will by a notary (another authorized person). In general, the testator’s algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Visit to the branch of the bank that opened the deposit.
- Notice of intention to leave a testamentary disposition.
- Writing an order by hand or using office equipment. You can also involve a bank employee in the process (ask him to type the text of the declaration of will on the computer).
- Certification of what is written with a personal signature and transfer to an authorized specialist for certification.
The text of the testamentary disposition must contain the following information:
- location and name (number) of the bank branch;
- date of certificate;
- testator's registration address;
- Full name of the individual or name of the legal entity to whom the contribution is bequeathed, as well as their place of residence or legal address;
- number of the bequeathed account(s);
- an indication of the shares due to the heirs (you may not indicate them, but in this case the funds will go to them equally);
- conditions for issuing money (if desired, you can determine the age at which the rights to the deposit will be transferred to the successor).
At the end of the registration procedure, the authorized specialist registers the document in the book of testamentary dispositions, gives one copy of the testamentary disposition to the testator, and places the second in a fireproof cabinet.
Drawing up a will without a notary
When drawing up a will without notarization, no form is required. It is enough to adhere to the requirements:
- the document is drawn up manually or on a computer;
- the testator writes the text independently or his instructions are recorded by an authorized official;
- if the document is drawn up according to the words of the testator, then the latter must read it before signing;
- if the will-maker does not have the opportunity to personally read the text, then the official reads the document out loud.
The testator has the right to amend or cancel the act of expression of his will, drawn up without a notary.
Documents to be drawn up
To correctly draw up a testamentary disposition, the following is required:
- testator's identity card;
- list of subjects - intended successors of the inheritance estate.
The execution of wills without the participation and certification of notaries can be carried out in the absence of title documents for the property. It is enough to provide the wording in the text: “I bequeath all movable and immovable property that will belong to me on the day of death.”
When registering a document, you do not need to pay a state fee. Typically, material costs consist of the cost of notary services for its registration (from 1,000 rubles/page) and certification (from 100 rubles). Any attempt by authorized persons to collect fees is illegal.
Form
All such documents, in order for them to acquire legal force, must be in writing. This especially applies to the inheritance of real estate, apartments, securities, and cars. Personal belongings, household items, and small amounts of money can be transferred by verbal agreement.
Using a sample to write a will without the participation of a notary will help eliminate errors in the execution.
Compilation rules
In order to avoid conflict situations between successors, the type of will in question is drawn up according to the following mandatory rules:
- The document provides the necessary details.
- The text must be clearly formulated and reflect in detail the last will of the person.
- Errors and typos are not allowed.
The likelihood that a correctly executed document will not be recognized is low.
Content
Wills without notarization include:
- name of the document being drawn up;
- information about the place and date of registration (in words);
- in full - last name, first name, patronymic of the testator;
- accurate information about the composition of the inheritance mass;
- reliable information about the intended successors;
- number of issued copies;
- a record that the document was drawn up personally by the testator without coercion;
- signatures of the testator, witness and two witnesses.
The execution of wills for apartments without notary services does not differ in form and the presence of mandatory details from will documents regarding other valuable property. There must be information about the exact address of the property, its area and the number of rooms to be inherited. Indicate what part of the property goes to each of the receivers.
Who can become a testator
All capable citizens have the right to bequeath their property. By law these are:
- adults (over 18 years old);
- emancipated (children over 16 who were granted full legal capacity due to marriage or in accordance with a decision of the guardianship and trusteeship authority or the court).
However, these categories of persons may be deprived of the opportunity to independently dispose of their property and bear responsibility for their actions (at least within the boundaries of the legal space). This occurs when a citizen is diagnosed with a severe mental disorder - a disease that makes a person unable to think logically and clearly, be aware of his actions and soberly assess the environment.
There are also milder degrees of deviations, when a person is partially deprived of these abilities, due to a less serious deviation or unhealthy psychological dependence. In this case, he will be recognized as having limited legal capacity. But this does not in any way affect the ability to dispose of one’s property—a citizen with limited legal capacity also does not have the right to draw up a will.
A court can deprive or limit a person of legal capacity based on an application from relatives or other interested parties. The full scope of civil rights is restored in a similar manner (when the patient’s mental health has returned to normal).
The capacity of the testator at a personal reception must be verified by the person certifying the expression of will instead of a notary. This is done not on the basis of the presence or absence of an official document on deprivation of legal capacity, but on the external signs of the applicant. Since a testator may be incompetent or partially capable, regardless of whether he is recognized as such by the court. And, if something in the behavior of the testator arouses the suspicions of the authorized person, he has the right to demand from him a certificate from a psychoneurological dispensary or refuse the certificate.
Witnesses
Certification of the property dispositions of the testator without the participation of a notary in most cases requires the presence of witnesses. They are needed:
- When making a will in emergency circumstances.
- In cases where the certifiers are ship captains, commanders of military units, doctors, directors and heads of places and expeditions, while staying in which the testator was deprived of access to receive notarial services.
In the first case, two witnesses are required, in the second, one is sufficient. And in each of them, the persons present must meet the following requirements:
- literacy;
- full legal capacity;
- knowledge of the language in which the expression of will was made;
- obvious disinterest (the heir or legatee under the will, their parents, children and spouses, as well as the person certifying the deed cannot be chosen as a witness);
- adequacy and sobriety.
All requirements presented to witnesses are equally relevant for the person who committed the assault (if his participation is provided for by law).
When making posthumous property dispositions, the availability of documents for the testator is important, regardless of whether a notary is involved in the procedure or not. The only exception is a will in emergency circumstances, which, for already known reasons, is made in a special manner.
In all other cases, the testator is required to provide identification. This document does not necessarily have to be a passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation. Instead, it is allowed to present:
- passports of a sailor or military personnel;
- passport of a citizen of another country;
- resident card;
- temporary residence permit on the territory of the Russian Federation;
- another document that allows you to reliably establish the identity of the applicant.
And about. A notary in a locality or outside the Russian Federation may require a certificate from a psychoneurological dispensary from the testator, but the testator is not obliged to provide it. At the same time, when refusing to provide a medical report, the testator (especially those over 70 years of age) must keep in mind that this may be followed by a refusal of the certificate and even a subsequent challenge to the act due to “incomplete legal capacity of the testator.”
Witnesses or the person presenting the hand must also carry identification and, upon request, provide documentary evidence of their own legal capacity.
It is important for all will-holders to pay attention to the following point: they are not required to provide any title documents for the bequeathed property, since they have the right to order the posthumous transfer of all their property or individual objects that they intend to acquire in the future. More than one year may pass from the moment the will is certified until his death, and during this time the personal material assets of the testator may be significantly replenished or, conversely, reduced. Therefore, sales contracts, donations and certificates of inheritance do not have much significance at this stage.
Expenses under a will made without a notary
Some believe that the absence of notary services completely frees testators from material costs. However, this opinion is only partly true.
Persons making a posthumous expression of will in emergency circumstances and persons performing the powers of a notary on a temporary and irregular basis (doctors, commanders, captains, etc.) are exempt from paying state fees and notarial services of a legal and technical nature. In other cases, the testator will have to pay a state fee and the State Property Certificate for certifying the will.
According to Art. 333.24. Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the state duty for this service is only 100 rubles. In addition, additional payment may be required, which is charged for the provision of legal and technical services. The exact amount is established annually by the notary chamber of each subject of the Russian Federation, but its value is 10–20 times higher than the amount of the state duty.
What else does the testator need to know?
In addition to all of the above, general rules apply to all types of wills, the essence of which is as follows:
- Free will of the testator. This means the absence of any external pressure - a citizen has the right to freely express personal property orders without regard to the opinions of others. Violation of this clause may become grounds for challenging the will.
- Clarity of consciousness of the testator and other participants in the procedure (certifier, witnesses, handicapper). Intoxication with alcohol, drugs and chemicals is a sufficient reason to invalidate a document in court.
- Individuality of will. A will made on behalf of two or more persons is void.
- The secret of the will. Regardless of how the last will of the testator was stated, persons who did not participate in the certification process should not learn about its contents before the death of the testator. Disclosure of a secret may result in administrative liability and the collection of a fine from the violator. The ban does not apply to the testator - he has the right to share such information at his own discretion.
- Possibility of cancellation and modification. The testator has the right to cancel the expression of will at any time after its completion by drawing up a document with instructions that are similar in essence, but different in content (example: in the previous act one recipient of the apartment was indicated, and in the new one - another) or by filing an application for cancellation. Individual orders can also be annulled, while the legal force of the will as a whole will be preserved.
- The right to make multiple wills. A citizen is in no way limited in the number of statements of will drawn up. And, if they contain completely different instructions, each of them will be valid (example: the content of one document is the transfer of a land plot, another - an apartment, the third - the appointment of a testamentary refusal, etc.).
- Invalidity of acts of last will. A will, as well as an application for its cancellation, can be declared invalid - void (declared by a notary when opening an inheritance case) or voidable (by a court decision). The reasons for this: the inconsistency of the form and order of the act, as well as some of the rules described here.
- Mandatory share. When bequeathing his property, a citizen must remember the legal holders of the obligatory share of the inheritance - his disabled parents, children, spouse and dependents, who, even if the testator is unwilling, will receive their part of the inheritance, albeit half as much as they could have received by law.
- Marital share. In addition to the personal property of the testator, the estate may include the property of his legal spouse. The marital share takes up exactly half of the material assets and funds acquired by the husband and wife during marriage (even if only one of them was the acquirer, in the truest sense of the word). The only exception is inherited and donated property. It belongs only to the heir or donee and cannot be removed from the estate by the surviving spouse. The rest is separated from the inheritance or, conversely, included if part of the joint property of the deceased was registered in the name of a widow or widower.
- Executor of the will. The testator has the right to order the appointment of an executor - a person who will implement or monitor the execution of his last will. It should be taken into account that the executor, in the course of performing the tasks assigned to him, may incur certain expenses, which will be reimbursed from the inherited property.
The absence of a notary does not negate compliance with the rules and regulations necessary when making an expression of will. Moreover, the importance of knowing the current legislation and its application in such cases increases markedly. Not all persons replacing notaries have sufficient competence to explain to the testator the legal consequences of his actions. As a result, the risk of the will being declared invalid increases, and the testator is not fully aware of the rights and opportunities granted to him.
Even if you do not have access to a notary, you can contact the lawyers of the website ros-nasledstvo.ru through an online form and receive competent advice on drawing up a will and other issues that interest you.
FREE CONSULTATIONS are available for you! If you want to solve exactly your problem, then
:
- describe your situation to a lawyer in an online chat;
- write a question in the form below;
- call Moscow and Moscow region
- call St. Petersburg and region
Save or share the link on social networks
(
1 ratings, average: 1.00 out of 5)
- FREE for a lawyer!
Write your question, our lawyer will prepare an answer for FREE and call you back in 5 minutes.
By submitting data you agree to the Consent to PD processing, PD Processing Policy and User Agreement
Useful information on the topic
46
Entry into inheritance after death under a will
The procedure and rules for entering into inheritance under a will are established by the chapter...
23
Lawsuit to restore the deadline for accepting an inheritance in 2021
The judicial hearing of the case on restoration of the period for accepting an inheritance begins with...
28
How to draw up a will for an apartment
The legislation of the Russian Federation establishes the right of every capable citizen to perform posthumous...
10
How to find out if there is an inheritance
The sudden death of the testator or lack of contact with other applicants may...
17
Mandatory share in the inheritance by will and by law (without a will)
The legislative act regulating civil law in the field of inheritance (section V...
15
Are loan debts inherited?
The short answer is YES, debts are inherited if the heir accepts the inheritance...