General information
Taxation of individuals as property owners is now carried out according to new rules. In this case, we are talking about new calculation standards that have been used since 2015. All owners of residential and non-residential premises, as well as some other types of property, are required to pay tax taking into account the cadastral value of the property.
Previously, the tax was calculated on the basis of inventory value, which, as is known, is much lower than the market value. But the cadastral value is just close to the market price of real estate, so the tax amount increases. In order to prevent a serious increase in property taxes, a special reduced coefficient was introduced. Its size in 2021 is 0.2, but will increase annually.
Despite the fact that the use of cadastral value for taxation is established by regulations (including the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), each subject of the Russian Federation has the right to independently set the date for the introduction of new calculation rules. Therefore, in some regions of the country, property tax can still be paid on the basis of inventory value.
As for determining the cadastral value of property, this procedure, by law, cannot be carried out more often than once every 3 years, and no less than once every 5 years. In large cities, assessments can be carried out more often, but not more than once every 2 years. The owner of real estate can contact Rosreestr to obtain information regarding its cadastral value.
Which premises have higher taxes - residential or non-residential?
When calculating real estate taxation, tax rates are applied in appropriate proportions. Taking into account the type of real estate and the scale of prices, which are close to market prices, there are three types of rates:
- The rate is 0.1%. This includes garages, parking spaces, real estate complexes that have at least one living space, houses, outbuildings on summer cottages with an area of no more than 50 square meters. m, apartments, housing under construction.
- Rate 2%. This group includes non-residential premises of a commercial or administrative type (cafe, hairdresser, office, shopping center, canteen, etc.), as well as property whose price is more than 300 million rubles;
- The rate is 0.5%. This includes the remaining buildings.
Note! From November 2021, non-residential premises are equal to residential premises and are subject to tax. The tax is calculated based on the cadastral value. Consequently, you will have to pay more for living space.
Is it possible to challenge
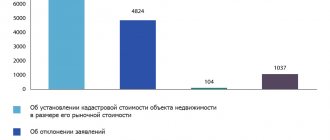
Innovations in tax legislation often cause disputes and conflicts. For example, not all owners may agree with the results of the cadastral valuation of property. If the amount is greatly inflated, this will seriously affect the amount of tax. Therefore, the law allows owners to challenge the assessment results.
You can do this in two ways:
- contact the nearest Rosreestr office,
- file a lawsuit.
In order to protect their interests, the owner will need the following documents:
- papers confirming the real cadastral value of the property (you must conduct an examination yourself),
- title documents,
- passport,
- statement (claim).
When contacting the registration authority, a decision on this dispute is made by a special commission. If the commission makes a negative decision, it can also be appealed in court. If a claim is filed immediately, a trial will be scheduled.
Video: Property tax for individuals
Innovations in 2021
The main novelty of 2021 for all property tax payers will be an increase in its rate; in Moscow it will be 1.5% of the cadastral or book value of the property, and in the country as a whole should increase to 2%.
Now, both individuals and legal entities, in order to protect their rights and challenge the cadastral value of real estate, can resort to considering this issue in court or the Cadastral Chamber. To do this, it is enough to write a special application and pay for the examination.
In addition, the authorities of most constituent entities of the Russian Federation have already prepared changes to the list of objects in respect of which the tax will be calculated based on their cadastral value. Thus, the corresponding list of papers for the capital was adopted under number No. 911-PP dated November 28, 2017. It is worth noting that the number of cadastral objects is growing from year to year. According to experts, the expansion of the list indicates the need to replenish local budgets from outside.
Tax benefits for office and other real estate are a universal category that every entrepreneur should know. After all, taking into account legislative features will help you avoid sending it to the state and save a tidy sum in 2021.
The video story will tell about the changes that have occurred in commercial real estate
Privileges
All citizens of the Russian Federation who are owners are required to pay property tax for individuals. But at the legislative level it is stipulated that certain categories of individuals have the right to receive benefits. Such relaxations are established both at the federal and regional levels. Taxpayers who may be exempt include:
- pensioners,
- veterans of the Second World War and other military operations,
- Knights of the Order of Glory, etc.,
- disabled people,
- Chernobyl victims, etc.
You should know that such a citizen can apply for a benefit only in relation to one type of real estate.
How to avoid or reduce taxes?
Certain categories of citizens have the right to benefits when paying taxes. These include disabled people of all groups, pensioners and large families. Those who are not included in preferential categories will not be able to avoid paying. However, you can reduce the amount of the accrual. To do this, you need to challenge the cadastral value. This option is possible if the data in the cost calculation is incorrect and the real market value is overestimated. You can challenge the cadastral value by contacting the Rosreestr commission.
All owners of non-residential premises are required to pay property tax. Only preferential categories of citizens are exempt from such charges. However, it is possible to reduce the amount of charges.
From this video you will learn how to reduce tax when selling an apartment:
Calculation
The tax on non-residential premises is calculated annually. The following algorithm is used for this:
- The cadastral value of the property and the amount of tax are determined.
- The inventory value of the object and the amount of tax are determined.
- The difference between these two indicators is calculated.
- The amount is multiplied by a special coefficient.
- The amount of payment, which was determined on the basis of the inventory value, is added to the result obtained.
How to pay
In order for a taxpayer to pay a property tax, the law determines
special terms. According to the established rules, payment must be made no later than December 1. Since the amount is calculated by the tax authorities, citizens do not need to carry out the procedure themselves.
The Federal Tax Service sends relevant notifications to all taxpayers, on the basis of which funds are transferred. The deadline for receiving such documents is October 20. If physical a person for some reason did not receive a notification, this does not mean that tax does not need to be paid. The payer needs to contact the Federal Tax Service independently.
Payment is made both at the bank and using special online services. A citizen can choose any suitable method, the main thing is that he keeps the receipt. And in order not to wait for notification, the payer can register on the official website of the tax service and gain access to his personal account.
To do this you need:
- Contact your local tax office and obtain a special registration card. It is issued on the basis of an application, TIN and other personal documents. This procedure can also be carried out by a representative on the basis of a notarized power of attorney.
- Next you need to get an electronic signature. They are issued at the relevant communication centers.
- Then the payer should register on the site using the received registration data (login and password).
After this, physical a person can not only monitor the amount of debts for certain taxes, but also pay them online.
Legislative framework: what are the rates for organizations, individual entrepreneurs and individuals?
Owners of non-residential real estate are required to pay property tax annually . This category includes not only offices, warehouses and premises intended for trade, but also the much more common garages and outbuildings.
Also in some cases it becomes necessary to pay additional fees. This happens if the room was:
- leased;
- Sales;
- given as a gift;
- provided for free use.
To understand the rates, you will have to seek help from the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This regulatory legal act includes detailed information on the calculation of mandatory annual and one-time payments. Some aspects of taxation are regulated by various subjects of the federation and depend on the decisions of the council of deputies.
Important! Personal property tax rates are partially regulated by provisions approved by local authorities (clause 3 of Article 406 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Property taxes are established by the following rules:
- For organizations - Chapter 30 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation “Property tax of organizations”; Clause 1 of Article 380 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - rates are established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and cannot be more than 2.2%, unless this is provided for in this article.
- For individuals and individual entrepreneurs - Chapter 32 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation “Property tax for individuals”. Also, rates in such cases are regulated by the laws of the constituent entities of the federation, but this applies only to Moscow, St. Petersburg and Sevastopol.
However, the size of tax rates, the subtleties of calculating the tax base, various benefits and rules for making advance payments can be established outside the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. All documents regulating such cases are publicly available on the official website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
Fines
All taxable property owners who fail to make payments on time will be held accountable. For example, for the fact that a citizen did not report the existence of a property (that is, withheld information from the tax authorities), a fine of 20% of the tax amount for this property is provided.
A penalty will be charged for late payments. Many people think that this is a type of fine, but this is not entirely true. The penalty is a certain percentage of the amount that is accrued daily. Even if the delay is only 1 day, a penalty will be added to the amount.
Help: Phys. a person can independently calculate this debt, since the penalty rate is standard and depends on the Central Bank rate.
If the owner does not pay for a long time, the Federal Tax Service sends an additional notification. This document contains:
- amount of debt,
- the amount of the penalty,
- the time frame given to the recipient to repay the debt,
- sanctions that will be applied to the violator in case of refusal to pay.
If a citizen ignores the notifications and does not pay the tax, the Federal Tax Service goes to court. To do this, the tax authorities must have certain grounds, that is, the amount of debt must reach a certain amount (3 thousand rubles). In practice, the case comes to court 6 months after the delay has occurred. If the court decides to forcefully collect the debt, the defendant will have to pay.
Moreover, the executive service will be in charge of collection, which means that various legal methods of obtaining funds can be applied to the violator. Most often, employees of the enforcement service seize the bank accounts of the offender and calculate the required amount. If the payer does not have a bank account, then appropriate measures are applied to his property.
In addition to the accrual of penalties for non-payment of tax, for individuals. the person will be fined. If the deadline is missed unintentionally, and the delay itself is insignificant, then the amount of the fine will be 20% of the tax amount. If the owner deliberately avoids payment and delays repayment for a long time, then the tax authorities may impose a fine of at least 40% of the amount.
Sale of non-residential premises
The owner of such property is required not only to pay real estate taxes, but also to pay additional fees for carrying out certain legal actions with such objects. First of all, this concerns the sale of property, since all individuals. individuals are required to pay income tax.
The personal income tax rate is fixed and amounts to 13% of the profit received. For non-residents of the Russian Federation, that is, foreign citizens, the tax rate is 30%. The calculation procedure has also changed somewhat, since now all taxes are paid based on the cadastral value.
Therefore, when calculating personal income tax, both the value of the property and the cadastral price are taken into account. If the actual price specified in the purchase and sale agreement is lower than the cadastral value, then the tax is calculated based on the cadastral price. In this case, a special reduction factor is also used, which is equal to 0.7.
For example, the cost of non-residential premises under the contract is 15 million rubles, and the cadastral value is 18 million rubles. The following formula is used for the calculation: 18 million * 0.7 * 13% = 1 million 638 thousand rubles. This will be the personal income tax amount calculated based on the cadastral value.
If the actual price paid by the buyer for the property is equal to the cadastral value or exceeds it, then the calculation is carried out differently. For example, the price of property is the same 15 million rubles. 15,000,000 * 13% = 1,950 rubles. This amount will have to be paid to the owner of the non-residential premises when carrying out a purchase and sale transaction.
But not all owners pay personal income tax when selling property. This rule applies only to those persons who have registered their ownership recently. Previously this period was 3 years. Now this rule also applies to property acquired before 2021, as well as to the method of acquisition. This refers to inheritance, donation, etc.
For all other owners, this period of ownership of the property has been extended to 5 years. Individuals who have been officially declared bankrupt are also exempt from paying personal income tax. In this case, all their income is used to pay off debts and is therefore not subject to taxation. To pay tax, individuals. the person must fill out and submit the declaration independently. The deadlines for applying to the Federal Tax Service remain unchanged, but personal income tax must be paid for the past tax period.
The tax on any non-residential premises for all individuals from 2019 must be paid no later than the specified period. Otherwise, a penalty and fines will be added to the existing amount. And then the enforcement service will find a way to collect the debt from the payer. If the owner does not agree with the results of the calculation, he can challenge them. But judicial practice on this issue is quite diverse, so it is difficult to say whose side the court will be on.
Benefits when purchasing office real estate
When purchasing office or any other commercial real estate, a person is required to pay tax to the state. However, since 2016, there has been a rule that if an object has been owned for less than 5 years, the owner can carry out a transaction with its alienation without paying tax.
There is no retroactive effect for this law, and therefore those objects that were purchased before 2021 can be sold without paying tax only if they were owned for up to 3 years.
However, there are exceptions to the rules; to obtain tax benefits, it is enough to own property for 3 years in the following cases:
- if it was received as a gift from a close relative;
- if it is inherited;
- if ownership arose after privatization.
In addition, a person has the right to take advantage of a tax deduction, the maximum amount of which is 250,000 rubles.
Useful video: taxation of commercial real estate transactions
The article was prepared by lawyer on family and civil issues Anton Nikolaevich Shcherbak
If the article was useful, please like it and add it to bookmarks.
If you do not find the information you need, you can get FREE legal advice on our website. Leave your question in the comments or contact a site consultant.