When legal entities can enter into a free transaction (agreement)
Two legal entities can enter into a gratuitous agreement if the following conditions are simultaneously met:
- such an agreement may be free of charge by virtue of law. For example, it is impossible to conclude a gratuitous rental agreement, since paying a fee for the use of the facility is a distinctive feature of this agreement. If you agree on the gratuitous provision of a thing for temporary use, your agreement will be a loan agreement and other rules will apply to it (Article 606, paragraph 1 of Article 614, paragraph 1 of Article 689 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- The law does not directly prohibit the conclusion of this agreement between legal entities. For example, an agreement on the alienation of an exclusive right may be gratuitous, but as a general rule, commercial organizations are prohibited from concluding such an agreement among themselves (clause 3, 1 of Article 1234 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). If you enter into an agreement in violation of a prohibition expressly expressed in the law, it will be void (clause 2 of Article 168 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, see Position of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation);
- the transaction does not meet the criteria of a gift . This condition applies to contracts between commercial organizations. If at least one of the parties is a non-profit legal entity, it is not necessary to comply with it (Clause 1 of Article 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
A distinctive feature of a gift is the obvious intention of one of the parties to transfer the ownership of a thing to the other (or transfer a property right, release from a property obligation) in order to benefit the donee. That is, the gratuitousness of the transaction is not related to any economic interest of the donor (see the Position of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation). For example, an agreement to forgive debt under a loan agreement is a gift, but an agreement to forgive accrued interest with the condition that the principal amount will be repaid as soon as possible is not.
If two commercial organizations enter into an agreement by virtue of which a gift occurs, it will be void as a violation of the prohibition expressly established by law. However, there may be exceptions. For example, the ban on gifts between commercial organizations does not apply if the parties to the transaction are a subsidiary and a main company (see the Position of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation). In addition, commercial organizations can give each other ordinary gifts worth up to 3,000 rubles. For example, flowers, sweets, business souvenirs (Clause 1, Article 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
It is important to know! Article 381 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Consequences of termination and failure to fulfill an obligation secured by a deposit
Transactions are divided into paid and gratuitous
A compensated transaction is a transaction in which the obligation of one party to perform certain actions corresponds to the counter obligation of the other party to provide material or other benefits.
Only bilateral transactions can be compensated
In a gratuitous transaction, there is no obligation to provide consideration to the other party.
Unilateral transactions are always free of charge. For example, transactions involving the transfer of property into ownership or use are compensated; a gift transaction is gratuitous. Compensation in a transaction can be expressed in the transfer of money, things, provision of counter services, performance of work, etc. Gratuitous transactions are relatively rare in relations between legal entities; they are more common in relations between citizens and organizations.
According to the moment at which the transaction occurs, transactions are real (from the Latin word res - thing) and consensual (from the Latin - consensus - agreement).
All transactions are recognized as consensual, for the completion of which it is sufficient to reach an agreement on the transaction.
For example, a contract of sale is considered completed when an agreement is reached between the seller and the buyer.
Transactions that are made only upon the condition of the transfer of a thing are called real (donation, loan, storage).
It is characteristic of a real transaction that rights and obligations cannot arise before the transfer of the thing.
Conditional transactions. A conditional transaction is a transaction, the legal consequences of which are made dependent on some circumstance (event or action of a third party) that may or may not occur in the future.
The transaction can be concluded under a suspensive or disqualifying condition.
A transaction is considered completed under a suspensive condition if the parties have established the occurrence
rights and obligations depending on a circumstance for which it is unknown whether it will occur or not.
The transaction is considered completed under a severable condition if the parties have terminated
rights and obligations depending on circumstances regarding which it is unknown whether it will occur or not.
If the occurrence of a condition was prevented in bad faith by a party for whom the occurrence of the condition is unfavorable, then the condition is considered to have occurred. If the occurrence of a condition was facilitated in bad faith by a party to whom the occurrence of the condition is beneficial, then the condition is considered not to have occurred. If there is no bad faith in the actions of the party, then the event is considered to have occurred without any restrictions.
17.Form of transactions and consequences of non-compliance
The form of a transaction is the way of expressing the will of the person who made the transaction. Transactions are made orally or in writing (simple and notarial).
Oral form of a transaction - verbal expression of a person’s will to complete a transaction
.
Any transactions can be made orally if: 1) legislative acts do not establish a written form for them ( simple or notarial );
2) if they are executed upon their very completion, with the exception of transactions for which a notarial form has been established and transactions, failure to comply with the simple written form of which entails their invalidity; 3) the transaction is made in pursuance of a written contract and there is an agreement between the parties on the oral form of execution. Silence is recognized as an expression of the will to complete a transaction in cases provided for by law or agreement of the parties. So, according to Art. 592 of the Civil Code, if the tenant continues to use the property after the expiration of the lease agreement in the absence of objections from the lessor (with his silence), the agreement is considered renewed on the same terms for an indefinite period.
The written form of a transaction is an expression of the will of the parties to the transaction by drawing up a document that reflects its content.
The document must be signed by one person when making a unilateral transaction or by two or more persons when making a bilateral or multilateral transaction.
Instead of the parties, the document can be signed by their authorized persons. Legislation and agreement of the parties may establish additional requirements for a simple written form of a transaction - making a transaction on a certain form, sealing it, certifying the transaction not only with the signature of the manager, but also with the chief accountant, etc.
In cases and in the manner provided for by law or by agreement of the parties, when making transactions, facsimile reproduction of the signatures of the parties using mechanical or other copying means, an electronic digital signature or another analogue of a handwritten signature is allowed.
If a citizen, due to a physical disability, illness or illiteracy, cannot sign with his own hand, then, at his request, another citizen can sign the transaction.
The signature of the latter must be certified by a notary or other official who has the right to perform such a notarial act, indicating the reasons why the person making the transaction could not sign it with his own hand. At the same time, a citizen who signs a document at the request of another person (the signer) himself should not be a party to the transaction.
Transactions must be made in simple written form (with the exception of transactions requiring notarization):
1) legal entities between themselves and citizens;
2) citizens among themselves in an amount exceeding at least 10 times the minimum wage established by law, unless otherwise provided by law.
Failure to comply with the simple written form of a transaction deprives the parties of the right in the event of a dispute to refer to witness testimony in support of the transaction and its terms, but does not deprive them of the right to provide written and other evidence that is not testimony.
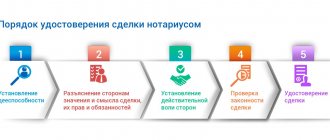
The notarial form of a transaction is a way of state legitimation of the will of the persons making the transaction. When formalizing a transaction, the notary ensures the legality of its conditions, purpose, and establishes the true will of the subjects. Notarization of transactions is carried out by making a certification inscription on the document by a notary or other official who has the right to perform such a notarial act. agreement of the parties on notarization of a transaction that is not required by law. A notarial form is usually required for transactions the subject of which is real estate or property of great value. A notarial form is required for a will.
In cases established by law, its certification is equivalent to notarized transactions. The notarial form of the transaction must be observed both in cases provided for by law and in the presence of a certain official (commander of a military unit, chief physician of a hospital, captain of a sea vessel, head of places of detention freedom, etc.)
For the validity of a transaction, in some cases, in addition to the notarial form, the law establishes its mandatory registration. These are transactions with land and other real estate - buildings, structures, etc. Legislation may establish registration of transactions with movable property.
Failure to comply with the notarial form of the transaction or the requirement for state registration of the transaction entails its invalidity. If one of the parties has fully or partially completed a transaction requiring notarization, and the other party evades such certification, the court has the right, at the request of the party that performed the transaction, to recognize the transaction as valid. In this case, subsequent notarization of the transaction is not required.
A party that unreasonably evades notarization or state registration of a transaction must compensate the other party for losses caused by the delay in completing or registering transactions.
18. Conditions for the validity of transactions. Types of invalid transactions and consequences of their invalidity .
The validity of a transaction means recognition of the qualities of a legal fact that gives rise to the legal result that the parties to the transaction sought. The transaction is valid subject to compliance with the conditions :
1) the legality of its contents.;
2) the ability of legal entities and individuals committing it to participate in the transaction.;
3) correspondence of will and expression of will.
4) compliance with the form of the transaction..
The invalidity of a transaction means that an action performed in the form of a transaction does not give rise to the consequences that the subjects desired. Taking into account the significant differences in the degree of violation of the law when making invalid transactions, it is customary to divide them into absolutely invalid (void) transactions and relatively invalid (voidable) transactions.
The absolute invalidity (nullity) of transactions means that the transaction is invalid by virtue of the law and does not require a court decision to declare it invalid . Absolutely invalid transactions include: transactions aimed at limiting the legal capacity or capacity of citizens; transactions made for a purpose that is obviously contrary to the interests of the state; transactions of a legal entity that contradict its statutory goals; transactions made by incapacitated persons; imaginary and feigned transactions; transactions made in violation of the form, if the law specifically provides for such a consequence.
Relative invalidity of a transaction (disputability) means that actions performed in the form of a transaction are recognized by the court as invalid if there are grounds provided by law for a claim by interested parties . Relatively invalid transactions include: transactions concluded partially or with limited legal capacity; committed by a citizen unable to understand the meaning of his actions; transactions with vices of will - made under the influence of delusion, deception, violence, threats, made on extremely unfavorable conditions under a combination of difficult circumstances.
The general rule on the consequences of invalid transactions is contained in Art. 168 Civil Code. If the transaction is invalid, each party is obliged to return to the other everything received under the transaction, and if it is impossible to return what was received in kind, to compensate its value in money (bilateral restitution), unless other consequences of the invalidity of the transaction are provided for by the code or other legislative acts. Restitution (“restoration”) Other consequences of the invalidity of the transaction are the prevention of restitution in general and the recovery of what was received under the transaction into the income of the Republic of Belarus; unilateral restitution, as well as compensation for actual damages. Unilateral restitution - the other party returns to the victim everything received under the transaction, and the property received under the transaction by the victim from the other party is turned into state income (for example, transactions made under the influence of deception, threats, violence, malicious agreement of a representative of one party with the other, as well as due to a combination of difficult circumstances). Prevention of restitution – in case of entering into a transaction prohibited by law. If there is intent on the part of both parties, everything received by them under the transaction is recovered from the state; if there is intent from one party, everything received by it from the transaction must be returned to the other party, and what the latter received from the guilty party in compensation for what was done is recovered from the income of the Republic of Belarus.
What contracts can be free of charge?
These may be contracts that are called gratuitous in the law or in respect of which the parties have agreed to be gratuitous.
According to the law, gratuitous contracts are those whose nature provides for the receipt of something by only one party. These are, in particular, agreements of donation and gratuitous use (clause 1 of article 572, clause 1 of article 689 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). They cannot be made compensatory at the will of the parties. If a party to such an agreement receives payment or other consideration, the agreement may be considered sham, and in this case the rules that govern the transaction actually completed by the parties will apply. For example, if the donor received money from the donee for the transferred item, the rules on purchase and sale will be applied to the relations of the parties (clause 2 of Article 170, clause 1 of Article 572, clause 1 of Article 454 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
By agreement of the parties , any contracts may be gratuitous, except for those for which, due to their nature and (or) the law, the presence of consideration is mandatory. Such exceptions include, for example, purchase and sale, rent, agency (Clause 1 of Article 454, Article 606, 1006 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Please note that by default the contract is usually paid. To make it gratuitous, you must indicate in it that no fee (other consideration) is charged under the agreement (clause 3 of Article 423 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Such a condition, as a general rule, can be agreed upon, for example, for storage, assignment, license agreement (clauses 1, 5 of Article 896, clause 1 of Article 972, clause 5 of Article 1235 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Please be aware that the law may prohibit certain individuals and/or conditions from entering into a gratuitous contract. For example, a commercial organization does not have the right, as a lender, to enter into an agreement for free use with its founder (clause 2 of Article 690 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, we recommend that you first check your agreement by type, subject and status of the parties for the possibility of agreeing on a gratuitous clause in it.
It is important to know! Article 414 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Termination of an obligation by novation
How to conclude a free contract?
Let's now find out how to conclude any free contract in 2021:
- Agree with your partner . At the initial stage, discuss the upcoming transaction with your business partner. If necessary, sign a preliminary framework agreement with him to secure the upcoming transaction (in the framework agreement, be sure to reflect the following issues - type of agreement, parties to the transaction, main points of the upcoming agreement, and so on).
- Draw up and sign a free agreement . The text of the contract must include the following points: parties to the transaction, date, type of contract, force majeure, termination conditions, responsibilities of the parties, and so on. Be sure to indicate in the text that this agreement is free of charge. Also, do not forget to write down the terms of the transaction in detail: for example, you are transferring a car to a legal entity - in this case, be sure to indicate basic information about the car, determine the timing and procedure for returning the vehicle, and also describe the current condition of the car (since depreciation costs are subject to a free use agreement is assumed by the borrower). Another example: you want to give a person an interest-free loan - in this case, indicate the size and procedure for repaying the loan.
- Register the agreement with a notary . After signing the contract, it is recommended to contact a notary to register the transaction - this will increase the overall reliability of your contract.
So, a gratuitous contract has been concluded - after that you must begin fulfilling your part of the contract.
If the other party to the transaction violates the terms of the contract in any way (misses deadlines for completing work, does not transfer money or property in full, and so on), then in this case you can go to court.
If as a result of the transaction you have tax obligations, then do not forget to pay all necessary taxes in accordance with your fiscal regime.
In what cases can a contract for the provision of services be concluded free of charge?
The possibility of concluding a contract for the provision of services free of charge depends on who the parties to the contract are.
Commercial organizations and individual entrepreneurs cannot provide services to each other free of charge.
Most often, gratuitous agreements are found in relation to non-profit organizations within the framework of charitable activities.
To ensure that the contract you conclude is free of charge, clearly indicate in it that the services are not subject to payment.
Rent agreement, paid or gratuitous
Based on the analysis of the norms of this chapter, it is not difficult to identify the following advantages and disadvantages of using deeds of gift. Positive aspects of giving:
- Availability of its execution (availability of oral and simple written form in accordance with Art.
Donation and rent Additional mandatory conditions indicating the amount and terms of payment of payments, the risk of accidental death or damage No The presence of a transfer act of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for this document as mandatory (however, if the provisions of the sale and purchase apply when transferring property for rent, then the acceptance act -transfer becomes mandatory - Art.
Compensation and gratuitousness of the annuity agreement and the procedure for its execution
- The lessor acts as the new owner of the apartment.
Free transaction. compensation deal
- To become a full-fledged owner of the property, the rent payer will have to wait for an indefinite period.
- Taxation in some cases applies to both parties to the transaction.
- For the rent payer, not only the payment of rent payments is established, but he may also be assigned additional responsibilities, as well as payment of utilities (if we are talking about residential premises).
- The transferred property may be alienated by the annuity recipient to the payer on a paid basis.
- With a lifelong annuity, it is impossible to redeem it at the will of the payer.
- Disposal of the transferred property by the payer is possible only with the written consent of the annuity recipient.
- Rent is an encumbrance upon alienation of real estate (Art.
Rent paid or gratuitous transaction
Rent agreement
- Concept, meaning, place of the annuity agreement in the GP system. Types of annuity agreement
Article 583 of the Civil Code - under a rent agreement, one party (rent recipient) transfers ownership of property to the other party (rent payer), and the rent payer undertakes, in exchange for the received property, to periodically pay rent to the recipient in the form of a certain amount of money or in the form of providing funds for its maintenance in a different form.
In the pre-revolutionary period, practice knew our legislation, but it was not enshrined in legislation.
The absence of remuneration provisions in the contract is allowed if this does not contradict the essence of the contract as a whole, therefore it is impossible to unequivocally answer the question of whether the lack of remuneration gives rise to adverse consequences for the parties. Is the gratuitous nature of the contract an essential condition?
Attention Based on Article 432 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the conditions on the subject of the contract are essential, the conditions that are named in the law or other legal acts as essential or necessary for contracts of this type, as well as all those regarding which, at the request of one of the parties, an agreement must be reached . The subject of the agreement must undoubtedly be present in any case. The subject of the contract reflects its essence as a whole, the rights and obligations of participants in civil legal relations and must contain individual characteristics in order to be able to distinguish it from other contracts.
How to draw up a free housing rental agreement
Some agreements, by force of law, can be either gratuitous or compensated, for example: – loan agreement; – contract of agency; – storage agreement.
Let us examine in more detail, for example, a loan agreement is essentially meant to be gratuitous, in which one party (the lender) must transfer into the ownership of the other party (borrower) money or other things defined by generic characteristics, and the borrower is obliged to return the same amount of money (loan amount) to the lender ) or an equal number of other things received by him of the same kind and quality.
It would seem that compensation, in this case, has no place to be, however, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes that the lender has the right to receive interest from the borrower on the loan amount in the amount and in the manner specified in the agreement, and the loan agreement itself is considered concluded from the moment of transfer money or other things. Or take a contract of agency.
Paid and/or gratuitous contract?
Important What is meant by remuneration/gratuitousness of a contract? The Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes that an agreement under which a party must receive payment or other consideration for the performance of its duties is compensated.
A gratuitous agreement is an agreement under which one party undertakes to provide something to the other party without receiving payment or other consideration from it. An agreement is assumed to be for compensation unless otherwise follows from the law, other legal acts, content or essence of the agreement.
Preparing a contract without knowledge of the law is a dangerous matter; you should contact a specialist. Let's take a more specific look and try to analyze the distinctive features of the concepts of remuneration and gratuitousness.
Rent agreement
If real estate is transferred for payment of rent, the recipient of the rent acquires the right of pledge over this property to secure claims related to rent payments. Types of rent:
Under it, rental payments are paid indefinitely
- Lifetime annuity agreement
Under it, annuity payments are paid during the life of the recipient. A lifelong maintenance agreement with dependents is a type of lifelong annuity agreement.
The rights of the annuity recipient can be transferred either by assignment or by succession (universal), i.e. by inheritance, during the reorganization of legal entities, etc. Features of this agreement: The recipients of the rent are citizens and non-profit organizations. Rent payments are paid in cash in the amount established by the agreement.
16 annuity agreement
The assignment of a claim by a creditor to another person is permitted if it does not contradict the law, other legal acts or an agreement. Since the assignment agreement must be compensated, legal disputes on this matter are very diverse.
Some courts believe that if the contract does not directly indicate the remuneration, its amount and payment procedure, the contract should be considered invalid, since it will be interpreted as a gift, but other courts take a different point of view.
If we do not indicate the price in the assignment agreement, but all the necessary conditions for this type of transaction are provided, the agreement will be concluded and have legal grounds for the parties.
The court will consider the agreement on its merits. Thus, consideration does not always affect the recognition of contracts as void or unconcluded.
An agreement is assumed to be for compensation unless otherwise follows from the law, other legal acts, content or essence of the agreement. Preparing an agreement without knowledge of the law is a dangerous matter; it is worth contacting a specialist. Let's take a more specific look and try to analyze the distinctive features of the concepts of remuneration and gratuitousness.
Paid and gratuitous transactions Legal illiteracy of elderly homeowners can play a cruel joke on them: the established minimum rent is 1 minimum wage. But this figure does not even reach the regional subsistence level. Therefore, it is necessary to clearly indicate the monthly amount and the need for its indexation to inflation.
- The legal capacity of the annuitant.
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation does not specify the signs of a counter-representation (size, definition, type, etc.), this is also observed in relation to the term “payment”, although it gives us a link to them in many articles, therefore transactions containing a requirement for payment determine this a requirement in the form of a monetary equivalent expressed in currency (rubles, euros, dollars, etc.).
Thus, the term “payment” is identified by us as monetary maintenance. Undoubtedly, the counter-representation can be either material or, conversely, intangible (provision of certain services). Both forms of counter-representation can be used in contracts for consideration.
The use of a variety of counter representation directly depends on the rule to which contractual obligations are subject.
The redemption is made according to the rules established for permanent annuity. Redemption of rent at the initiative of the payer is not allowed.
The obligation to pay annuity is absolute.
- Lifetime maintenance agreement with dependents
This is a type of life annuity. It is believed that this is the most common type of annuity in practice, therefore a separate paragraph is devoted to this agreement.
Agreement of lifelong maintenance with a dependent - the recipient of the annuity (citizen) transfers a residential building or apartment, land plot or other real estate belonging to him into the ownership of the rent payer, who undertakes to provide lifelong maintenance with the dependent of the citizen or a third party specified by him (Article 601 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Rent paid or gratuitous
Only after all the specified procedures have been completed, the agreement is considered concluded and acquires legal force. In addition, the amount of the annuity must be indicated and the procedure for its payment to the recipient is determined.
Donation and rent Assignment of a claim by a creditor to another person is permitted if it does not contradict the law, other legal acts or agreement. Since the assignment agreement must be compensated, legal disputes on this matter are very diverse.
Some courts believe that if the contract does not directly indicate the remuneration, its amount and payment procedure, the contract should be considered invalid, since it will be interpreted as a gift, but other courts take a different point of view.
If we do not indicate the price in the assignment agreement, but all the necessary conditions for this type of transaction are provided, the agreement will be concluded and have legal grounds for the parties.
Source: https://02zakon.ru/dogovor-renty-vozmezdnyj-ili-bezvozmezdnyj/
In what cases is a service agreement free of charge?
A contract is gratuitous when there is no need to pay for services rendered or give any other consideration (transfer goods, provide counter services, etc.) (Clause 2 of Article 423 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
We believe that it is possible to conclude a free government contract for the provision of services, since Law No. 44-FZ does not prohibit this.
Please note that the mere fact that there is no price or obligation to pay for services in the contract does not make it gratuitous. As a general rule, the contract will be considered compensated (clause 3 of Article 423 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the recipient of the services will have to pay for them at the price that, under comparable circumstances, is usually charged for similar services (clause 3 of Article 424 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
However, if the payment condition for a specific contract is essential, in its absence the contract may not be concluded (Clause 1 of Article 432 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Therefore, if you want to enter into a gratuitous contract, indicate directly in it that no payment or other consideration will be made for the provision of services (Clause 2 of Article 423 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Main types of gratuitous agreement
There are a large number of types of gratuitous agreements . Most often in practice, the following gratuitous transactions are concluded - use of facilities, provision of services and loans.
Below we will look at these agreements in more detail.
Free use
If a contract for gratuitous use is concluded, one of the parties undertakes to transfer to the other any movable or immovable property (car, apartment, land, etc.).
However, please note that under a gratuitous contract you cannot transfer ownership rights to another person or organization. From a legal point of view, a gratuitous use agreement is equivalent to a loan agreement, and is subject to similar rules and restrictions.
Key Features:
- The text of the agreement must necessarily specify the terms and conditions for the use of the property, and if necessary, it can be stated that the agreement is for an indefinite period. At the end of the contract, the other party is obliged to return the property in the same condition in which it received it, and, if necessary, the borrower is obliged to cover depreciation and related expenses.
- The borrower undertakes to reflect information about the property in accounting. If the borrower exploits the property and makes any profit, then in this case he is also obliged to pay the corresponding income tax. Please note that other taxes (transport tax, land tax, inheritance tax, etc.) must be paid by the actual owner of the property (that is, the lender).
- The loan agreement is not subject to state registration, however, by mutual agreement of the parties, it can be registered with a notary.
Free provision of services
When concluding a gratuitous contract for the provision of services, one of the parties undertakes to perform certain services in favor of the other party.
Services can be different - it can be delivery of goods, agricultural work, repairs, and so on.
Key features of the deal:
- Gratuitousness implies the absence of payment for the provision of services, but this does not relieve the contractor from fulfilling his obligations. If the contractor deliberately evades his obligations or he has performed his work poorly, then in this case the customer can demand through the court that the contractor fulfill his obligations in the proper form. Please note that the contractor is exempt from paying a fine (since the agreement is free).
- The customer must reflect the free service in accounting. In this case, both parties are exempt from paying all taxes (VAT and others), since there is no tax base in this case.
- The agreement is not registered with government authorities, but if necessary, it can be registered with a notary.
Free rental
A gratuitous lease agreement cannot be concluded on the territory of Russia, since the lease implies the payment of any payment for the transfer of property for temporary use, which contradicts the gratuitous condition.
If one party wants to transfer any property to the other party for free use, then in this case it is necessary to conclude a contract for free use (we discussed this contract above).
If two parties arbitrarily entered into a free rental agreement in circumvention of the current legislation, then in this case this contract will be declared void by the court, which will lead to its cancellation (also note that such an agreement cannot be registered with a notary).
Free transfer of goods
An agreement for the gratuitous transfer of goods in Russia is also not concluded, since this requires changing the owner of the goods, which is impossible in the case of concluding a gratuitous agreement.
However, it is still possible to transfer goods free of charge for a long period of time without the right to sell - to do this, you need to conclude a contract for free use, and the text of the contract should indicate that the agreement is unlimited.
Free loan
If one party wants to transfer money to the other party free of charge, then in this case it is necessary to conclude a gratuitous loan agreement.
Basic moments:
- The text of the agreement must include a clause that will clearly indicate that the loan is carried out on an interest-free basis.
- If necessary, the borrower can forgive the debtor an interest-free loan - to do this, he must draw up and give the debtor a special receipt (it is recommended to have it certified by a notary). Please note that the laws of the Russian Federation prohibit indicating in advance in the contract that the loan is irrevocable.
- The lender does not need to pay income tax, since in this case there is no tax base in the form of interest. If the creditor lent money and then forgave the debt, then the recipient of the money must pay tax on the profit received.
- A gratuitous loan agreement is not subject to mandatory registration with government agencies, however, to increase reliability, it is recommended to register the transaction with a notary.