Congratulations, most likely you needed a topographical survey, perhaps to lay a gas pipeline or connect your house to water supply networks, etc. You absolutely don’t know where to start. How to make the right choice and is it possible to make it yourself? We will try to answer these questions in our article. Learn more about topographic surveys, in particular conducting and creating a topographic plan of a site or area. Let's look at all the nuances of performing and ordering this type of service.
What is topographic survey of a site
Topographic survey is the result of a complex of geodetic work, which is based on measuring the area and drawing up a plan. For this purpose, surveying instruments and specialized software are used. The final result is a topoplan or, as it is also called, a geological basis of a certain scale using approved symbols.
Purpose of topographic survey Generally, topographic survey is divided into two types: before the start of construction to create and approve design documentation and after completion of construction to calculate and identify deviations from the given project.
Main purposes:
- For construction
- Laying of utility networks
- Landscape design
- Registration of land ownership
- Obtaining a building permit
- Territory planning
- Creating a dendraplane
- Cadastral works
- Conducting engineering and geodetic surveys
Executive topographic survey is carried out after carrying out a certain type of construction, laying communication routes, and planning the territory.
The data is used to determine how accurately the construction was carried out and what actual deviations from the design documentation were. Methods of topographic surveys Carrying out topographic surveys depends on many parameters, the purpose of the future geo-base, the area of the object and its location, accessibility. We can name the main methods that surveyors use to obtain field data (measurements).
Tacheometric - at the moment it is one of the main methods of carrying out geodetic work; when performing it, an electronic tacheometer is used, which measures angles, lengths and elevations between certain points on the ground. It refers to the most accurate type of measurement, the error that occurs during tacheometry is up to 2 mm in plan.
Satellite - GPS surveying, this type is gaining more and more popularity; to perform this type of measurement, high-precision geodetic GPS receivers are used, which are capable of calculating the location of points on the ground with an accuracy of 1-2 cm. One person is enough to perform measurements using a GPS receiver. For high-quality and accurate GPS data, you need many related things, calibration of the coordinate system, installation of base stations, and so on.
Filming using unmanned aerial vehicles or quadcopters - this method is not so widespread at the moment.
The main reason that does not allow the use of UAVs is the accuracy of the issued topoplan, about 10 cm. The advantages of aerial photography is its speed in the field; aerial photography is used mainly for large objects with an area of more than 30 hectares. The resulting scales are 1:1000 1:2000 and beyond; for the design and construction of utility networks, aerial photography is currently not fully suitable due to the many variables that can affect the quality of the produced material.
3D scanning - when using 3D scanning, a huge number of points are obtained; it is called a point cloud. The disadvantages of using it are the cost of the equipment and the complexity of its processing. 3D scanning is most often used for measurements inside buildings - premises for developing planning projects and so on. The use of a 3D scanner in the production of topographic surveys is unjustified; the high cost of the equipment and the difficulty in processing the results obtained complicate the drawing process.
Stages of work
It is divided into stages; there are several main ones, which we will discuss below:
the first stage preparatory - at this stage, information is collected about the areas of future topographic measurements, configuration range, relief shape, presence of vegetation and other infrastructure elements.
The optimal shooting method is selected to obtain a more accurate result that will correspond to the technical specifications. In this section we can include the signing of contracts, approval of technical specifications, and so on. The second is direct measurements on the ground (as they say in the field), depending on the method of implementation. A team of surveyors or a surveyor must go to the land plot to take measurements. By measurements we mean determining the coordinates of the main elements (Points): buildings, structures, roads, fences, relief elevations, collecting field data for subsequent processing on the basis of which a topographic plan will be formed. Third - After taking measurements, the data that was received in the fields needs to be processed. Field measurement data is processed using various technical and information programs that make it possible to competently and correctly draw a topographic plan of the area. This type is called deskless, it takes place remotely in the offices of geodetic companies. The end result is a topoplan in electronic form in the AutoCAD program in a certain coordinate system and scale, which is ready for printing and further development of design documentation. To the fourth and final stage we can include such types of work as the coordination of utility networks, this means the passage of services that operate communications that fall into the area of topographic survey to confirm the correctness of their application.
How is topographic survey carried out?
It all starts with the approval of the technical specifications, the purpose of this type of document is clarified, for what purposes it will serve, after the surveyors have received all the necessary information, they go to the land plot, make all the necessary measurements on the ground, then process this data and hand over the received documents to the customer.
- Measurements are made in a specific coordinate system , which is approved by the customer or other legal document. Most often, the coordinate system of the corresponding region is selected, for example MSK50, MSK36. SC implies metric coordinates of the X Y format. The Baltic system of heights is used for the elevation mark; it was adopted back in the USSR. System of heights - the zero count of which is carried out from the zero of the Kronstadt footing rod; from this mark, all the heights of the benchmarks forming the leveling network of Russia are calculated.
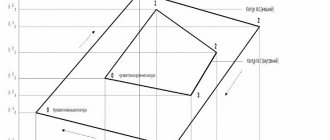
- The plan consists of linear point and area objects. Each of the objects is assigned its own individual symbol. Based on this, surveyors take measurements and calculate the coordinates of objects that should be indicated on the topoplan. The measurement includes determining the elevations of the relief and its configuration.
- Processing of field data - Using specialized software, coordinates are calculated to obtain characteristic points of the future topoplan.
- The diagram is drawn by substituting its own symbol for each point and connecting linear objects. All conventional signs have their own characteristic parameters. The use of signs makes the plan easy to read.
- The final stage is transferring the diagram to the AutoCAD where 1 drawing unit will correspond to one meter on the ground.
What tools are used
To carry out geodetic measurements, specialized geodetic equipment is used, which must be certified - verified for compliance with state accuracy standards. Verifications are carried out on equipment once a year, which confirms the suitability of the equipment; if the equipment has not passed verification, it cannot be used.
Basic geodetic equipment:
- Electronic total station
- GPS receiver
- Quadcopter or other aircraft
- Tool for scanning underground utilities (router)
Main scales
The scale varies from the purpose of a specific topographic survey; according to statistics, for design and survey work on an area of up to 100 hectares, a scale of 1:500 is used; it can be increased if the object is linear and its length is more than 10 km. The scale for the topoplan is selected individually based on its application; you can read about the scale and accuracy in our article.
Legislation
- GKINP (ONTA)-02-262-02 Instructions for the development of survey justification and terrain survey using global navigation satellite systems GLONASS and GPS
- GKINP-02-033-82 Instructions for topographic survey on scales 5000, 2000, 1000,500 (approved by the USSR State Administration on October 5, 1979)
- SNiP 11-02-96 Engineering surveys for construction. Basic provisions
- SP 11-104-97 Engineering and geodetic surveys for construction
- SP 11-104-97 part 2, Surveying underground utilities
- Conventional signs for topographic plans of scales 1_5000, 1_2000, 1_1000, 1_500
Generalized execution scheme
Specific instructions for topographic surveying are drawn up taking into account its type and method, instruments used, map scale and other factors. Meanwhile, without going into the details of one or another method, you can draw up a general scheme for performing the survey. It can include the following steps:
- Drawing up a technical project.
- Collection of data on previously carried out topographical and geodetic work on the ground.
- Selecting a shooting method.
- Creation of a support network (if it is not available on the ground).
- Shooting.
- Materials processing.
- Creating a model.
- Printout of the map.
A survey network is necessary to condense local and state networks to a certain density. Its standards depend on the type of shooting and are regulated by instructions and other industry regulations.
Why do you need a topographic survey of the site?
And now, probably the most important question: why do you need a topographic survey of the site? The answer is very simple - before the start of any construction. Topographical surveying is done to determine the characteristics of a given land plot, real estate object, and based on the measurement results, projects, territory plans, security zones and much more are drawn up. Without a high-quality and accurate diagram, it will be difficult to design and place any technical structure, be it a house or ending with highways and electrical substations.
Stages of topography
The topographic survey process includes three main stages.
- Preparatory stage, during which the goals of the work are determined and an analysis of the previous survey is performed. The results of the shooting will depend on the quality of this stage.
- Field. At this stage, the land plot is inspected, geodetic reference points are selected, all measurements are taken - distances, height differences, structures, utilities, etc.
- The desk stage involves the analysis and processing of the received data, on the basis of which a topographic plan of the site is drawn up.
The result of this work is reliable information about the land plot - shape, size, elevation changes, landscape, buildings, etc. Upon completion of the work, you can begin to improve the site or begin construction. You can think about landscape design. You can even install landscape lighting posts.
Do-it-yourself topographic survey
Engineering and geodetic work of any type and direction must be carried out by an engineer-geodesist who has a specialized education in the field of geodesy. A surveyor must be a member of an organization that has permission to perform a certain type of work - SRO permission for engineering and geodetic surveys.
- Additional information about conducting topographic surveys can be obtained from public documents. But to perform these measurements you need high-precision geodetic equipment.
Mode
Topographic survey of a land plot can be carried out in digital or analogue mode. The choice depends on the method of storing and providing information to the customer.
The analogue mode involves the issuance of materials (topographic plans or maps) on paper.
Digital mode is currently considered more preferable. In this case, all information obtained during topographic survey of the land plot is stored on magnetic media, disks, flash drives, etc.
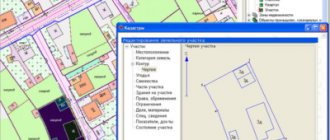
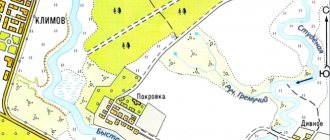
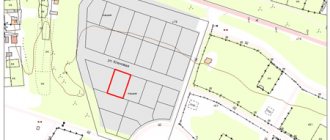
Samples of topographic surveys
Sample topographic survey
Sample topographic survey
Sample geobase
Why saving on work is not always good
Nowadays, there are a large number of organizations that carry out topographic surveys (Engineering surveys), and not always of high quality and affordability. Let's look at a couple of examples where saving money can hurt. Probably the worst thing that can happen is that the implementation option itself, by saving, you can get a scheme that does not comply with state regulations, SNIPs, STANDARDS, which are aimed at regulating cadastral and engineering geodetic activities. An ordinary person who does not know all the intricacies of design, symbols, and so on will not be able to distinguish high-quality work from its similarity. The worst thing will be that when you get a poor-quality result of engineering and geodetic work, you will not be able to use it for its intended purpose and the work will have to be redone.
Who to order the service from
When performing topographic surveys that fall into the category of engineering surveys, the organization or individual entrepreneur must be a member of the SRO and have an extract no later than three months before the work is performed. If the organization - legal entity does not have this extract, the work is illegal and cannot be used in design bodies. Therefore, ordering from an organization that is a member of a self-regulatory organization in construction can guarantee the quality of its implementation. The organization must have geodetic equipment that undergoes regular maintenance and has a certificate of conformity of measuring instruments that are approved in the Russian Federation; without this certificate, work on the equipment is impossible.
Cost of work
The cost of work is calculated according to the reference book of basic prices for engineering and geodetic surveys. Works are divided into categories of complexity. Category is the presence of elements that fall within the measurement area.
Main list:
- The first category is an open field.
- The second category is rural buildings, fields overgrown with bushes and the like.
- The third category is urban development.
- The fourth category is operating enterprises, the most expensive type of engineering survey.
The cost of the work is affected by additional services: drawing cadastral boundaries of land plots, surveying utility lines, installing gas distribution points and fixing boundary signs.
Deadlines
Completion time is from 3 working days, depending on the complexity, area of the object, and so on. If it is necessary to coordinate the survey, in particular, of utility networks with their balance holder, then the time for completing the work increases several times, depending on the number of authorities with which approval is needed.
Need to know
For high-quality performance of geodetic services, as well as drawing up a topographic plan that is suitable for solving the task at hand, it is necessary to accurately formulate the terms of reference for the survey.
Before execution, you should know the purpose of the topoplan for what purposes it will be used in the design solution, to obtain a construction permit or laying utility networks, connecting a gas pipeline. The cadastral number of the land plot is also required to determine the location of the plot. You can be advised by phone about all the nuances and subtleties of the work.
Fundamentals of legislation
The basis of the legislation in accordance with which topographic surveys are carried out is. They approved:
- basic principles of topographic survey and creation of topoplans;
- the order of use of the main metric values;
- content of topoplans;
- the procedure for their registration and updating;
- the procedure for carrying out certain types of shooting;
- methods and purposes of collecting topographic information.
To detail the technical requirements set out in the Basic Provisions, a detailed Instruction for topographic survey was developed and approved. It describes on 98 pages:
- Engineering and topographical plan of the land plot.
- The procedure for designing and collecting topographic information.
- Features of reconnaissance, triangulation, leveling.
- Types of topographic signs.
- The procedure for drawing up technical requirements and so on.
The remaining regulatory legal acts relate to topographic surveys only indirectly.